-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2012; 2(3): 25-28
doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20120203.02
Molal Solubility, Dissociation, Association and Solvation Parameters for Saturated Phenylalanine Solutions in Various Solvents at 298.15 K
Esam A. Gomaa
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt
Correspondence to: Esam A. Gomaa , Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Mansoura University, Mansoura, 35516, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The molal solubilities for saturated solutions of phenylalanine at 298.15 K in various solvents were determined. The solvents used are, water (W), ethanol (Et), dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), acetonitrile (AN), methanol (Me), acetone (Ac), 1-4, dioxane (Di) and N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF).From the experimental data for solubilities, pH and densities, the different volumes, molar: electrostriction and Van der Waals and apparent molar volumes were estimated. The free energies of dissociation (ΔGd), free energies of association (ΔGA), difference free energies (ΔΔG) and free energies of solvation (ΔGs) for phenylalanine saturated solutions in various solvents were also calculated. The solvation numbers were also estimated. It was concluded that the solute-solvent interaction increased by increasing the solvation free energies due mainly to the greater of the association parameters in the organic solvents.
Keywords: Solubility, Association Constants, Dissociation Constants, Densities, Different Volumes, Free Energies, Solvation Number, Phenylalanine
1. Introduction
- Knowledge of the existence of amino acids dates back over a century in many cases, as doe’s knowledge of their extended in proteins. When amino acids were discovered, their identity was established by isolating and purring the individual compounds and obtaining elemental analysis. After the advent of paper chromatography, this technique was used with a variety of different solvents to identify elution characteristic and demonstrate the purity of isolated compounds. Amino acids were located by the use of a reagent that produced colour with the compound. The most common reagent used for locating amino acids is ninhydrin. Which produces a purple colour with imines, a pink or yellow color with amino acids, and various intermediate colors, with compounds containing an amino group and a sulfonid group and so on. It also reacts with small peptides such as glutathione. The techniques of paper chromatography were applied to the separation of mixtures of amino acids, such as the components of the protein after hydrolysis, and then to the separation of free amino acids in physiologic fluids and tissues.It was extended by the use of two dimensional chromatography, in which a different solvent was used in each direction[1]. Later electrophoresis was employed as one of the separating techniques. After locating the amino acids by reaction with ninhydrin, the spots could be cut out, eluted with alcohol or acetone and measured spectrophotometrically[2]. In order to measure the free amino acids in biological tissues and fluids, all proteins must be removed. Various methods have been employed to accomplish this, such as ultra filtration, equilibrium dialysis, and proton precipitation. A Variety of protein precipitation has been employed for this purpose, the most common being picric acid. For extracting tissues the most common methods employ 10% trichloroacetic acid, usually by blending or homogenizing with 510 vol of acid followed by a high speed centrifugation[2]. Plasma, cerebrospinal fluid and urine are most commonly deproteinized using 5 vol 3% sulphosalicylic acid as protein precipitated, again followed by centrifugation. The precipitated proteins can be purified by washing with hot trichloroacetic acid to remove nucleic acids and with a Varity of organic solvents to remove lipids. The proteins can then be hydrolysed, usually with 6N HCl under vacuum at 120℃ for 24 h or more, and their amino acid composition determined[3].Many publications have done on the behaviour of weak acids in anhydrous solvents. Interesting work has been done by Kolthoff et al.[4,5]. Aleksandrov et al.[6,7] studied the dissociation of salicylic acid in butane-2-one. Kreshkov et al.[8] studied the dissociation of amino acids (as weak) acids) in mixtures of formic and ethylmethylketone and in mixtures of acetic acid-ethylmethylketone.Gomaa et al.[9] studied association, dissociation and hydrogen bonding of salicylic acid in water-N, N- dimethylformamide mixtures from solubility measurements.The aim of this work is to evaluate the solubility of phenylalanine in different solvents and discuss in details the solvation parameters for the solubility process. Study the effect of different solvents of the solubility and the physical behaviour accompanied is very important for the biochemical analysers. Also apply a theoretical model for evaluating different microscopic interactions of phenylalanine is necessary.The aim of this work is to evaluate the solubilities of phenylalanine in different solvents and discuss in details the solvation parameters for the solubility processes for phenylalanine which is one of the most essential amino acids.
2. Experimental
- The phenylalanine and solvents used, ethanol (Et), dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), acetonitrile (AN), methanol (Me), acetone (Ac), 1-4 dioxane (Di) and dimethylformamide (DMF) were supplied from Merck. The saturated solutions of phenylalanine were prepared by dissolving it in the solvents used. The solutions were saturated with N2 gas in closed test tubes. The tubes were placed in a shaking water bath of the type assistant for a period of four days, followed by another two days without shaking to reach the necessary equilibrium. The solubility of phenylalanine in each solution was determined gravimetrically by taking 1 ml of the saturated solution and subjecting it to complete evaporation using small aluminium disks heated by an infrared lamp. The pH readings of the saturated solutions were measured using a pH-meter of the type Tacussel /Minis 5000. The densities were measured by using weighing bottle 1 ml and analytical balance (4 digits) of the type Mettler Toledo DA.
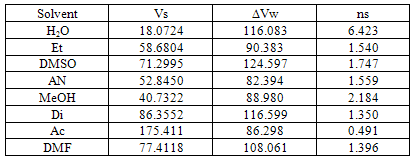
3. Results and Discussion
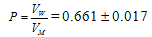 | (1) |
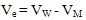 | (2) |
|
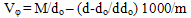 | (3) |
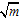 [17,18].Kass values were calculated[14] from the ratios of association constant to dissociation constant (i.e., K1/K2) for the dimmers of phenylalanine which form a complex ion ((
[17,18].Kass values were calculated[14] from the ratios of association constant to dissociation constant (i.e., K1/K2) for the dimmers of phenylalanine which form a complex ion ((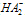 ) and hydrogen ion (H+), and the values of K` (where K` is the dissociation constant of the associated acid complex, H2A2) are given by the following equations
) and hydrogen ion (H+), and the values of K` (where K` is the dissociation constant of the associated acid complex, H2A2) are given by the following equations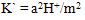 | (4) |
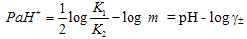 | (5) |
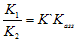 | (6) |
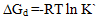 | (7) |
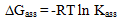 | (8) |
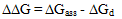 | (9) |
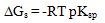 | (10) |
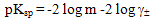 | (11) |
|
|
|
References
| [1] | Volker, F.Wedish,”Amino acid biosysthesis- pathways, regulation and metabolic enegineering”, Springer – Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg (2007). |
| [2] | Alan A.Bculton, Glen B. Baker and James d. Wood, “Neuromethods 3, amino acid.” The Humana Press Ins, Clifton, NJ O7015 (1985). |
| [3] | Gamerith, G., J.Chromatogr. 256, 326 (1983). |
| [4] | Kolthoff, I.M. and Chantooni, M.K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 87, 4428 (1965). |
| [5] | Kolthoff, I.M., Chantooni, M.K. and Bhownik, S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 90, 123 (1968). |
| [6] | Aleksandrov, V.V., Zudochkina, A.I., and Sandovinchaya, L.P., Zh. Fiz. Khim., 52, 1295 (1978). |
| [7] | Alekandrov, V.V., and Burakhovich, Fizicheskaya Khimiya Rastrorov (Physical Chemistry in Solutions), Nauka, Moscow, 1972, p. 154. |
| [8] | Kreshkov, A.P., Tanganor, B.B., Yarovenko, A.N. and Batoreva, T. Kh., Zh. Fiz. Khim., 54, 105 (1980). |
| [9] | Gomaa, E.A., Mousa, M.A. and El-Khouly, A.A., Thermochimica Acta, 89, 133-139 (1985). |
| [10] | Kim, J.T., Cecal, A., Born, H.J. and Gomaa, E.A., Z. Physikalische Chemic, Neue Folge, 110, 209-227 (1978). |
| [11] | El-Khouly, A.A., Gomaa, E.A. and Abou-El-Leef, S., Bull. of Electrochemistry, 19, 153-164 (2003). |
| [12] | El-Khouly, A.A., Gomaa, E.A., Abou El-Leef, S., Bull. Of electrochemistry, 19, 193-202 (2003). |
| [13] | Oswal, S.L., Desai, J.S., Ijardar, S.P. and Jain, D.M., journal of Mol. Liquids, 144, 108-114 (2009). |
| [14] | Dorota Bobicz, Waclaw Grzybkowski and Andrzej Lwandowski, J. of Mol. Liquids, 105, 93-104 (2003). |
| [15] | Marcus, Y. “The properties of solvents”, Wiley, London, 1998. |
| [16] | Moelwyn - Hughes, E.A., “ Physikalische Chemie ”, George Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, 1970, p. 489. |
| [17] | Gomaa, E.A., Mousa, M.A. and El-Khouly, Thermochim. Acta, 89, 133-139 (1985). |
| [18] | Gomaa, Esam, A., Thermochim. Acta, 120, 183-190 (1987). |
| [19] | Bondi, A., J. Phys. Chem., 68 (1964) 441. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML