-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Biochemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-3010 e-ISSN: 2163-3029
2011; 1(1): 4-8
doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20110101.02
The Cytotoxic and Haematological Effect of Coal Dust to Underground Miners
Meltem Maras Atabay
Department of Secondary Science and Mathematics Education, Biology Education Section, Ereğli Education Faculty,
Correspondence to: Meltem Maras Atabay , Department of Secondary Science and Mathematics Education, Biology Education Section, Ereğli Education Faculty,.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study is aimed to assess the hazardous effect of coal dust and to examine whether there still may be an increased risk of respiratory symptoms among underground miners such as working miners and retired miners in Zonguldak, Turkey. Current miners had to have worked for at least 5 years. Retired miners had worked 10-20 years. Both groups are historically associated with exposure to higher levels of coal dust. Some haematological markers of blood samples taken from coal miners were measured in this study. The variations on haematological markers such as hemoglobin, prolactin, lactat dehydrogenase of these miners were observed. There were higher mean values of hemoglobin levels in both current miners and retired miners. Ca+2 levels as releated with increase of lactat dehydrogenase increase almost 5 times. The differences in prolactin levels were releated with levels of haemoglobin, ferritin and anemia. There may be high risk of respiratory symptoms even in retired coal miners. Measurements of this parameters make an attractive approach for monitoring the effect of coal dust in coal workers. Coal dust together with aging factor effect accelerates to catch respiratory symptoms in the retired coal miners and working miners.
Keywords: Coal miners, Hemoglobin, Lactat Dehydrogenase, Prolactin, Cytotoxicity
Cite this paper: Meltem Maras Atabay , "The Cytotoxic and Haematological Effect of Coal Dust to Underground Miners", American Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 1 No. 1, 2011, pp. 4-8. doi: 10.5923/j.ajb.20110101.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Coal consists of carbon, hydrogen, oxigen, nitrogen, inorganic minerals, quartz and trace metals[1,2]. The inorganic portion of coal can range from a few percent to > 50% (by weight). Trace metals can include boron, cadmium, copper, arsenic, nickel, iron, antimony, cadmium, cobalt, copper, lead, and zinc, and represent only a very small fraction of the mineral matter. In general, aluminum and iron are the main metals in the coals[3]. Some of these trace elements can be cytotoxic and carcinogenic in experimental models. Common mineral and elemental contaminants are kaolin, mica, pyrite, titanium, calcite, sulfur, sodium, magnesium, and silica. The rank of coal increases from peat to lignite, sub-bituminous to bituminous, and anthracite. As rank increases, the ratio of carbon to other chemicals and mineral contaminants increases[4]. Coal is the most widely used energy source in Turkey. Coal mine beds in Zonguldak province is the biggest coal beds of Turkey[5,6]. Underground coal miners are under high risk due to their jobs. Coal miners have traditionally been exposed to high quantities of dust. Accordingly, dust-related health effects have been verified, such as detrimental influences on lung function and the development of chronic bronchitis. Compared to environmental concent- rations, dust exposure at the workplace can be many times higher, and occupational threshold values are reviewed scientifically on a permanent basis[7]. Inhalation of coal mine dust can lead to the development of several diseases including coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP), bronchitis, emphysema, Caplan syndrome, and silicosis[8,9]. Exposure to coal mine dust leads to a significant induction of cytogenetic damage in peripheral lymphocyts of workers engaged in underground coal mining. Cytotoxic quartz dusts induce the secretion of a potent phagocyte activator. The inhalation of coal dust particles is thought to participate in the induction of lung diseases like fibrosis emphysema and cancer[10,11]. The hazardous effect inhalated particles are mediated by the release of inflammatory mediators from activated alveolar macrophages[12]. Inhalated coal dust can deposit in lungs. Silicosis occurs frequently in certain occupations such as mining, sandblasting, surface drilling, stone cutting, construction, pottery making, silica flour mill operations, and other occupations in which silica dust exposures occur. Some studies showed an increased risc of stomach and lung cancer among coal miners. Coal workers’ pneum- oconiosis (CWP) is the paranchymal lung disease that results from the inhalation and deposition of coal mine dust[13,14]. Trace elements (nickel, lead, cadmium, zinc) in coal dust are cytotoxic[15,16]. Quartz could be a prominent risk factor for lung cancer in coal miners. Mutagenes formed from coal dust induce frame shift mutations. Oxidative DNA-damage was observed to be significantly higher in lymphocyts of coal miners in controls[10].This study is aimed to asses The prevalence of respiratory symptoms and disease among working miners and retired miners in Zonguldak and to examine whether there still may be an increased risk of respiratory symptoms among under- ground miners after decades of decreased exposure to coal dust.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Sampling
- Study comprised 75 current miners and 75 retired miners. Retired miners are normally granted a pension at 60 years of age (Table 1). Current miners had to have worked for at least 5 years. Retired miners had worked 10-20 years. Mean working time in the mining areas was 16,75 ± 0,58. They were all smokers. Both group worked as roofbolters and as driller at surface coal mine. Both jobs are historically associated with exposure to higher levels of coal dust. Groups were haematologically investigated. The subjects were asked if coal workers’ pneumoconiosis (CWP) or chronic bronchitis had been diagnosed by physician. Blood samples were taken from cubital venous blood in metal-free vacutainer EDTA tubes.
| |||||||||||||||
2.2. Analysis of Haematological Markers
- The following haematological markers were measured: Haemoglobin (HGB), Prolactin, Lactat Dehydrogenase (LDH) as well as other biomarkers. All blood tests were analysed in a central laboratory according to standard haematological methods. Control references values consid- ered for HBG, for prolactin and for LDH levels were 10,7-15,7 µg/dL, 6-30 ng/mL, 240-480 U/L respectively. Descripted statistics (mean ± SD) were analysed by using SPSS software (version 13.0) for hemoglobin, MCHC, LDH, prolactin levels and ages of these miners.
3. Results
- In the present study, several coal dusts were investigated to alter haematological parameters of current coal miners and previous miners. LDH, HGB, Prolactin levels were obtained from subjects’ cubital wein. Positive correlation was not found blood HGB levels and age (Figure 1). Differences were considered significant at p<0,05. As shown in Table 2, HGB mean values of HGB levels in current miners were 15,8±0,7 while in retired miners were 13,5±1,1 (P = 0,0013). There were differences between mean values of HGB in current miners compared to retired miners (2,2 ± 1,6).
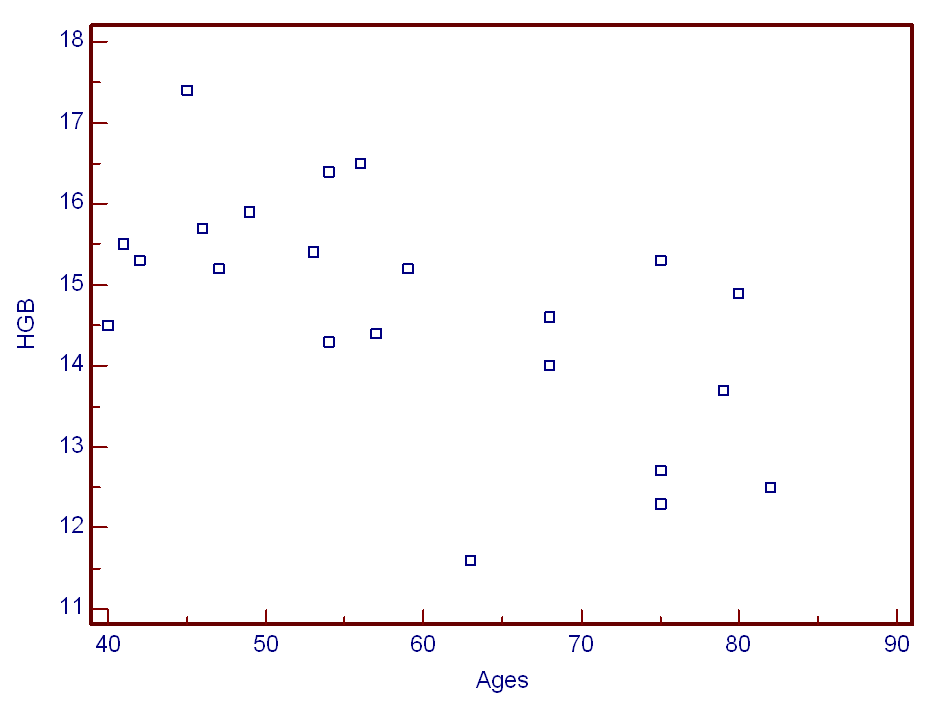 | Figure 1. Haemoglobin (HGB) levels (g/dl) and ages of underground current miners and previous miners |
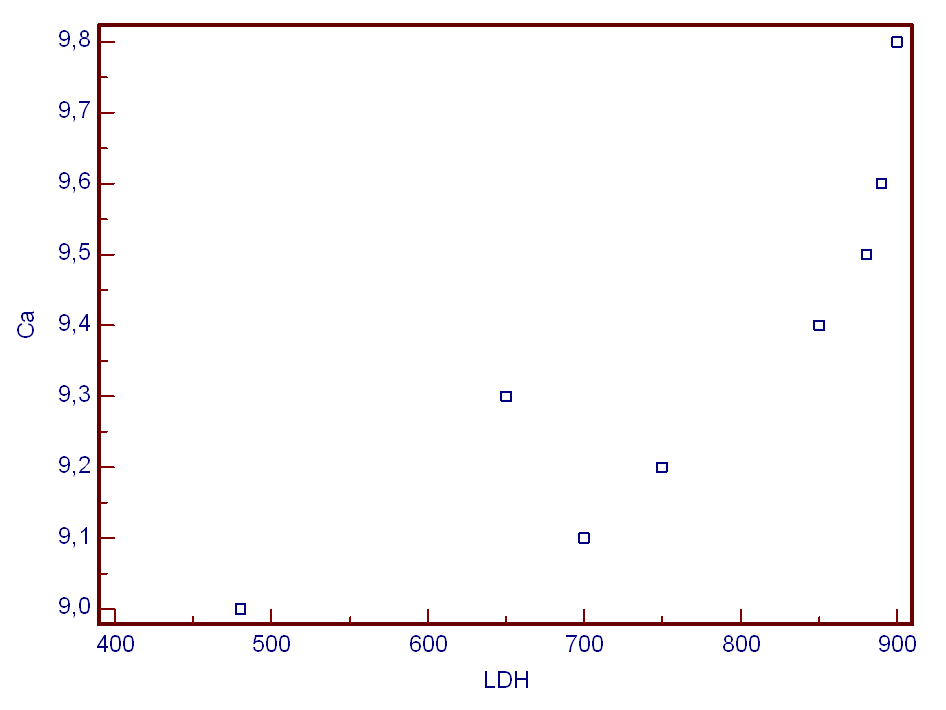 | Figure 2. Scatter plot showing main relationships found between Calcium (Ca) (mg/dl) and Lactat Dehydrogenase (LDH) (U/L) |
4. Discussion
- Coal is a fossil fuel mined throughout the world. The generation of coal mine dust during underground coal mining is the most significant source of coal dust exposure. Dust exposure at the workplace can be many times higher. The average cumulative exposure to respirable coalmine dust in Great Britain was 174 gh/m3, which corresponds to an average concentration of more than 3 mg/m3 over 30 years underground[7]. Among the occupations listed by the U.S. Census industry code, coal mining is the highest risk job associated with asthma and COPD death, with a proportionate mortality ratio of 1.98 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.84–2.12, adjusted for age, sex, and race), compared with the second highest risk job of trucking service of 1.29 (95% CI, 1.22–1.37). There are two basic types of coal mining operations, surface mining and underground mining, producing distinctively different exposure variables and disease entities. Under- ground coal miners are at greater risk of developing CWP than strip or surface miners because of the higher dust levels in the underground environment[4]. Levels of bioavailable iron (BAI) in the coals correlated with the prevalence of CWP. The prevalence and severity of CWP was shown to differ markedly among coal mines despite exposures comparable with respirable dust. CWP prevalence in coal mine regions was shown to be significantly correlated with the levels of BAI from the same region[3].There is genotoxic risk of occupational exposure to coal mine dust. Reactive oxygen species have been implicated in the pathogenesis of its toxicity. Cellular damage was seen to be associated reactive oxygen. Species with ROS that was occurred by the exposure of coal dust[17]. The high level of HGB means the increase of lung symptom in these patients[11]. Blood levels of HGB and prolactin did not show a normal symmetrical distribution. The differences in prolactin levels were releated with levels of Haemoglobin, ferritin and anemia. The increase of prolactin levels causes irritation of chest wall[18]. The increase of Ca+2 levels in miners was demostrated to be the result of an increased production of LDH. This change in LDH levels is an inducer of plasma membran damages[19,20].In previous studies, coal is determined to induce cellular damages. The toxicity of elements in coal results from the ability to catalysing occurence of free-radical derived from oxygen interacting with cytoplasmic component and cellular membran. These interactions not only modify potantially functional wholeness, but also occur toxic product modifing various cellular functions[5].Red blood cell antioxidant parameters were shown to decrease in some stages of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis[21, 22]. Erythrocyte glutathione s-transferase activity and glutathione concentration were decreased in the early stages of pneumoconiosis[23]. Coal dust exposure also affects some serum enzymes. For example, LDH activity increased with this exposure[24-26]. Serum enzymes such as ALT, AST, CK, GGT and LDH levels was showed to be a statisti- cally significant increase (p _ 0.05)[17]. Pinho et al., (2005) [25] were determined high LDH activity in the fluid obtained from the bronchoalveolar lavage following coal instillation. Castranova and Vallyathan (2000)[4] reported that direct cytotoxicity of silica or coal mine dust exhibits significant response for Lipid peroxidation, Hemolysis, LDH release from alveolar macrophages, Chemiluminescence, Nitric oxide. Cytogenetic analysis at previous studies have showed coal workers have sister chromatid exchanges, chromosomal aberration and micronucleus occurrence. The induction of oxidative DNA damage by long-term exposure to coal dust suggests the oxidative stress as early effect of respirable dust and quartz followed by direct DNA damage due to DNA strand-breaks[10,19,26].
5. Conclusions
- This study determined that coal dust exposure caused imbalance at biochemical parameters in blood of coal work- ers. Measurements of these parameters make an attractive approach for monitoring dust induced biologycal phenom- ena in coal workers. Smoking miners had higher risks of physician-dignosed chronic bronchitis and had a tendency to more respiratory symptomes[27,28]. Coal dust together with aging factor effect accelerates to catch respiratory symptoms in the retired coal miners and working miners.
References
| [1] | Donbak, L., Rencuzogulları,R., Yavuz, A,. and Yopaktaş, M., 2005, The genotoxic risk of underground coal miners from Turkey, Mutation Research, 588, 82-87 |
| [2] | Jorjani, E., Chelgani, S.C., and Mesroghli, S.H., 2007, Prediction of microbial desulfurization of coal using artificial neural Networks, Mineral Engineering, 2, 1285-1292 |
| [3] | Huang, X., Li, W., Attfield, M.D., Nadas, A., Frenkel, K., and Finkelman, R.B., 2005, Mapping and Prediction of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis with Bioavailable Iron Content in the Bituminous Coals, Environmental Health Perspective, 113(8), 964-968 |
| [4] | Castranova, V., and Vallyathan, V., 2000, Silicosis and Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis, Environmental Health Perspec- tives, 108, 200 675-684 |
| [5] | Altin, R,. Savranlar, A., Kart, L., Mahmutyazıcıoğlu, K., Ozdemir, H., Akdağ, B., Gündoğdu, S., 2004, Presence and HRCT quantification of bronchiectasisin coal worker, European Journal of Radyology , 52,157-163 |
| [6] | Sari, M., Duzgun, H.S.B., Karpuz, C., Selcuk , A.S., 2004, Accident analysis of two Turkish underground coal mines, Safety Science, 42,675-690 |
| [7] | Morfeld, P., Noll, B., Büchte, S.F., Derwall, R., Schenk, V., Bicker, H.J., Lenaerts, H., Schrader, N., and Dahmann, D., 2009, Effect of dust exposure and nitrogen oxides on lung function parameters of German coalminers: a longitudinal study applying GEE regression 1974–1998, International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 483-489 |
| [8] | Kleinerman, J., Green, F.H.Y., Harley, R., Lapp, N.L., Laqueur, W., Naeye, R.L., Pratt, P., Taylor, G., and Wyatt, J. 1978, Pathology Standards for Coal Workers' Pneumoc- oniosis: Report of the Pneumoconiosis Committee of the College of American Pathologists to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Arch Pathol Lab Med., 103, 375-431 |
| [9] | Green, F.H.Y., Vallyathan, V., 1998, Coal workers' pneumoconiosis and pneumoconiosis due to other carbonaceous dusts. In: Pathology of Occupational Lung Disease. 2nd ed (Churg A, Green FHY, eds). Philadelp- hia:Williams and Wilkins, 129-208 |
| [10] | Fanizza,C., Ursini, C.L., Paba, E., Ciervo, A., Di Fancesco, A., Maiello, R., P. De Simone and D. Cavallo, 2007, Cytotoxicity and DNA-damage in human lung epithelial cells exposed to Respirable Quartz, Toxicology, 2,586- 594 |
| [11] | Karakaya, A., Ates, I., Yücesoy B., and Suzen, S.H., 2006, Cytokine genes in susceptibility at coal wolkers’ pneum- oconiosis, Abstract/Toxicology Letters, 164S, S1-S324 |
| [12] | Tarnok, A., Schlüter, T., Berg I., and Gercken, G.., 1997, Silica induced changes in cytosolic free calcium, cytosolic PH, and plasma membrane potential in bovine alveolar macrophages, Analytical Cellular Pathology, 15,61-72 |
| [13] | Chang, C.L., Tseng, J.C., Hua, C.C., Liu, Y.C., Shieh, W.B., and Wu, HP., 2006, Gene Polymorphisms of Fibrinolytic Enzymes in Coal wolkers’ pneumoconiosis, Archives of Environmental and Occupational Health, 61,61-66 |
| [14] | Hedlund, U., Jarvholm, B., and Lundback, B., Respiratory Symptoms and obstractive lung diseases in 2004, iron ore miners:Report from the obstractive lung disease in northern Sweden studies, European Journal of Epidemiology, 19, 953-958 |
| [15] | Geeson, N.A., Abrahams, P.W., Murphy, M.P., and Thorm- ton, I., 1998, Flourine and metal enrichment of soils and pasture herbage in the old mining areas of Derbysire, UK. 8, 217-231 |
| [16] | Armutcu, L., Gurel, A., and Aker, A., 2004, Serum iron concentration, lipid peroxidation and superoxide dismutase activity in Turkish iron miners, Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26, 1-4 |
| [17] | Tuluce, Y., Ozkol, H., Koyuncu, İ., Ine, H., 2011, Increased occupational coal dust toxicity in blood of central heating system workers, Toxicology and Industrial Health, 27(1), 57–64 |
| [18] | Montes, S., Rodriges, H.R., Pedraza, E.S., and Rios, C., 2008, Biomarkers in manganese exposure in a population living close to a mine and mineral processing plant in Mexico, En-vironmental Research, 106, 89-95 |
| [19] | Cavallo, D., Fanizza, C., Ursini, C.L., Paba, E., Ciervo, A., Di Francesco, A., Maiello, R.,and De Simone, P., 2006, DNA damage and Cytotoxic effects induced by respirable quartz in humanlung epithelial cells, Abstract/Toxicology Letters, 164S,S1-S324 |
| [20] | Chen, J., Lucas, C., Armstrong, L.C., Joan, E., Gerriets, J.E.A., and Last, A., 1997, Silica induced changes in cytosolic pH and plasma membrane potential in bovine alveolar macrophages, Analytical Cellular Pathology, 15, 61-72 |
| [21] | Borm, P.J.A, Meijers, J.M.M., and Swaen, G.M.H., 1990, Molecular epidemiology of coal worker’s pneumoconio- sis:application to risk assessment of oxidant and monokine generation by mineral dusts, Experimental Lung Research, 16, 57–71 |
| [22] | Engelen, J.J., Borm, P.J., Van-Sprundel, M., and Leenaerts, L., 1990, Blood anti-oxidant parameters at different stages of pneumoconiosis in coal workers, Environmental Health Perspectives, 84, 165–172 |
| [23] | Evelo, C.T.A., Bos, R.P., and Borm, P.J.A., 1993, Decreased glutathione content and glutathione s-transferase activity in red blood cells of coal miners with early stages of pneumoconiosis. British Journal of Industrial Medicine 50, 633–636 |
| [24] | Fan, W.D., Wang, Z.C., Fu, D., Yan, J.L., Li, X.D., and Wu, Y., 1994, The change of Zinc and Zinc enzyme in skeletal fluorosis. Proceedings of the 20th International Congress of Fluoride Research; 5-9 September, Beijing, PR China |
| [25] | Pinho, R.A., Silveira, P.C.L., Silva, L.A., Luiz Streck, E., Dal-Pizzol, F., and Moreira, J.C., 2005, Acetylcysteine and deferoxamine reduce pulmonary oxidative stress and inflammation in rats after coal dust exposure. Environmental Research, 99, 355–360 |
| [26] | Bansal, S.K., and Kaw, J.L., 1981, Lactate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in macrophages and serum during the development of pulmonary silicosis in the rat, Toxicology Letters, 7 ( 4-5), 279- 283 |
| [27] | Kim, K.A., Lim, Y., Kim, J.H., Kim, E.K., Chang, H.S., Park, Y.M., and Ahn, B.Y., 1999, Potential biomarkersof coal workers’pneumoconiosis, Toxicology Letters, 108,297-302 |
| [28] | Chen, J., Armstrong, L.C,. Liu, L., Gerriets, J.E., and Last ,A., 1991, Slica increases cytosolic free calcium ion concentration of alveolar macrophages in vitro, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmocol. 53, 14-23 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML