-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Aerospace Sciences
2012; 1(1): 1-7
doi: 10.5923/j.aerospace.20120101.01
SDR Joint GPS/Galileo Receiver from Theory to Practice
1DELEN, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, 10129, Italy
2NAVSAS, Istituto Superiore Mario Boella, Torino, 10138, Italy
Correspondence to: Marco Rao , DELEN, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, 10129, Italy.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This paper deals with a Software Defined Radio (SDR) receiver capable to process GPS and Galileo signals jointly. A large set of possible solution can be implemented, with the main aim of assessing the performance of the receiver for the considered architectures. For this reason, software receivers, either real-time or non-real-time, are fundamental tools to enable research and new developments in the field of GNSSs. In this paper our intent is to discuss some of the choices one can face when implementing an SDR GNSS receiver, switching from the theory to the practice. We focus our attention on the pseudorange construction and the Position, Velocity and Time (PVT) estimation stage, discussing different algorithms to implement these blocks. Our aim is to offer an insight on the options to implement those stages of the receiving chain, in a practical vision which is difficult to find in the available literature.
Keywords: Software Defined Radio, Gnss Software Receiver, Galileo, Gp
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent times, particular attention has been directed toward the development of new Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs), as the European Galileo and the renewed Russian GLONASS. All these systems aim to be interoperable each other and with the GPS, and to be exploited all at once, to provide the user receiver with a large set of measurements, entailing better precision and robustness[1][2].Software Defined Radio (SDR) is a modern technology that allows to replace part of the hardware of a radio device with a software architecture running on an appropriate digital processor[3][4][5][6]. Such an approach allows the development of reconfigurable terminals, thanks to the ease of access to every single functional block implemented in software. This characteristic happens to be very useful for system designers that are provided with a valuable tool for testing and comparing algorithms and architectures, quickly implemented as simple software modulesIn this article we discuss the possibility to implement a SDR receiver capable to jointly process both the GPS and Galileo signals. In particular, we discuss some of the issues that may commonly arise in designing a joint GPS/Galileo software receiver for research purposes, taking as an example our real-time software receiver, N-Gene[7].Although abundant literature is available on architectures and algorithms for GNSS receivers (see for example[8]—[17] and references therein), it is often difficult and time-consuming to cope with the implementation options arising when passing from the theory to the practice, as itcan be seen even in the recent literature and research activities[15] —[18]. We discuss here implementation choices related to the tracking stage and to the Position-Velocity-Time (PVT) computation, since these are in our opinion the characterizing blocks in a joint GPS/Galileo receiver, when processing measurements from Galileo and GPS at the same time. Since the Galileo signal is not currently available, our tests relied on the signals produced with the Spirent GSS7700 and GSS7800 generators. The remainder of the paper is structured as follows: in Section II we discuss the architecture of the receiver: subsection A introduces the acquisition stage, while subsections B and C describe in details the tracking and PVT stages, emphasizing the issues that arise when dealing with a joint GPS/Galileo receiver. In Section III we show some results obtained processing the data collected using the Spirent signal simulators, comparing the results obtained using the different considered algorithms. Finally, in Section IV we draw the conclusions of this work
2. Receiver Architecture
- As one of the goals of the software receiver we consider in this paper is to be a research and investigation tool, its basic architecture, shown in Figure 1, is represented using a standard “educational” design, made up by the typical modules that constitute a GNSS receiver blocks chain. The shaded area represents the functionalities implemented in software from the Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) on. The overall software module resides on a PC and works in real-time with respect to the signal output by the ADC. The signal processing executed by the Back-end Section (opposite to the Front-end one, in the SDR language) after the Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) consists of several actions.Signal acquisition, in order to roughly align the received code with the internal replica; tracking of the received code and carrier, in order to align the incoming and local spreading codes, finely removing the frequency shifts due to the Doppler effect.Demodulation of the navigation data, in order to recover the ephemeris information, retrieve the satellite’s position and calculate the time offset between the satellite and system time. All the information regarding the data structure of both the Galileo and GPS can be found in[19] and[20] respectively; measurement of the code phases from the PRN sequences of the satellite signals, in order to estimate the pseudoranges; PVT computation in order to estimate the user’s position.
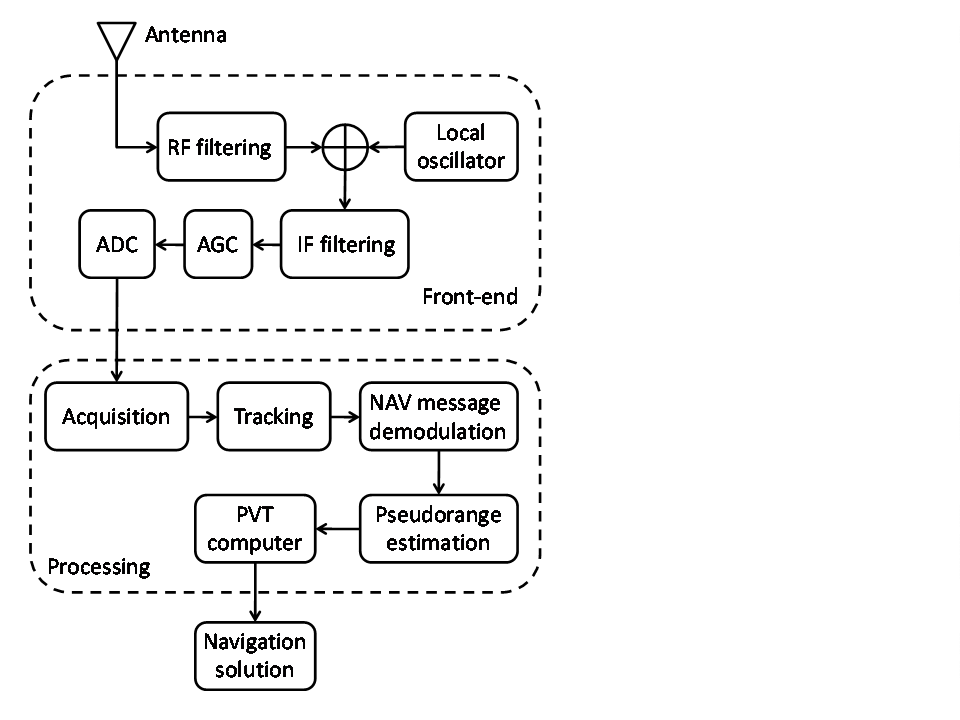 | Figure 1. Architecture of the considered software receiver |
2.1. Acquisition Stage
- In order to track and decode the information transmitted by the GNSS constellation, a generic receiver must at first detect the presence of the signal in space, performing the acquisition. The receiver must be able to search over a certain frequency range in order to cover all the expected Doppler frequency shifts on the received signal Once the acquisition algorithm detects the presence of the signal, two parameters must be estimated• the delay τ of the received code with respect to the local code,• the Doppler frequency shift fd of the received signal (due to the relative velocity between the transmitting satellite and the user receiver).The search space for acquisition operations must cover the full range of uncertainty in the code and Doppler offset. There are different methods to perform acquisition, based on the evaluation of the cross-correlation function of the received signal with a local signal, generated for each value of delay τ and Doppler shift fd under evaluation (Cross-Ambiguity Function, CAF). Serial search (i.e., the cell-by-cell evaluation of the 2-dimensional CAF) is suitable for hardware receivers, due to its simplicity in implementation. Instead, in the perspective of a fully-software implementation, we focus on the parallel search in frequency domain, which exploits the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), while serial search method is extremely slow for software-based implementation[21][22].Indeed, methods based on FFT can be used to efficiently evaluate the correlation function. In the hypothesis to observe one code period (pre-detection integration Tint time equal to the code period Tc), the incoming sampled signal sin[n] = sin(nTs) (where the sampling time Ts is chosen according to the GNSS signal specifications), is FFTtransformed, obtaining the sequence Sin[m] = Sin(m/Ts) = FFT{sin[n]}.A period of the current spreading code x is generated by the local code generator and it is stretched according to all the possible Doppler bins i, taking into account the minimum frequency resolution imposed by the time of observation Tint. The obtained signals
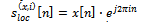 are FFT-transformed, obtaining the sequences
are FFT-transformed, obtaining the sequences 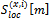 in the frequency domain.The multiplications
in the frequency domain.The multiplications 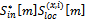 are then computed for each couple (x,i) in the frequency domain. After that, the inverse FFT (IFFT) is performed, so obtaining the circular correlation sequence. Its absolute value is computed and a possible peak in the delay domain is searched. This allows evaluating the relative delay of the spreading code for a certain Doppler shift step i.This procedure has been performed to acquire both GPS and Galileo satellite signals. Of course, the code period Tc is different between the aforementioned GNSS signals. In case of E1-B this procedure has been performed to acquire both GPS and Galileo satellite signals. Of course, the code period Tc is different between the aforementioned GNSS signals. In case of E1-B Galileo signal we have a code length equal to 4ms as reported in[19] while the Tc in case of L1 C/A for GPS is 1ms[20].
are then computed for each couple (x,i) in the frequency domain. After that, the inverse FFT (IFFT) is performed, so obtaining the circular correlation sequence. Its absolute value is computed and a possible peak in the delay domain is searched. This allows evaluating the relative delay of the spreading code for a certain Doppler shift step i.This procedure has been performed to acquire both GPS and Galileo satellite signals. Of course, the code period Tc is different between the aforementioned GNSS signals. In case of E1-B this procedure has been performed to acquire both GPS and Galileo satellite signals. Of course, the code period Tc is different between the aforementioned GNSS signals. In case of E1-B Galileo signal we have a code length equal to 4ms as reported in[19] while the Tc in case of L1 C/A for GPS is 1ms[20].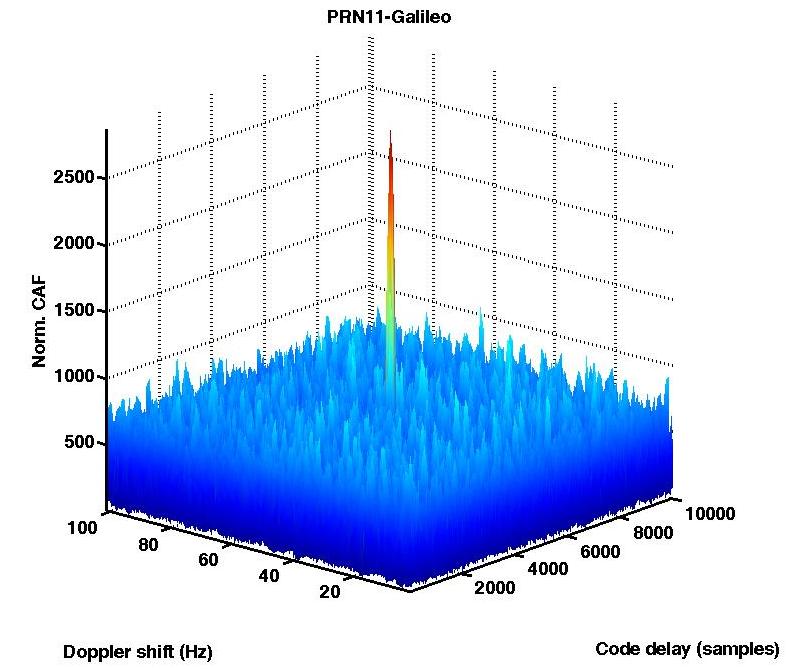 | Figure 2. Estimated CAF for Galileo PRN 11 |
2.2. Tracking Stage and Pseudorange Computation
- Once the acquisition phase has brought the received and the locally generated code within less than a half chip period residual offset, a fine synchronization, named tracking, takes over and keeps the two codes aligned, by means of closed loop operations. Generally, the tracking system in GNSS receivers consists of a Delay Lock Loop (DLL) for code tracking and a Phase Lock Loop (PLL) for carrier phase tracking.A detailed analysis of how a PLL and DLL work is out of scope of this paper and an exhaustive description can be found in[21]. The main aim of this Section is to stress the fundamental role played by the tracking stage in the correct and precise recovery of the code delay τ, which is necessary to measure the pseudoranges, and consequently the PVT solution, and to decode the navigation message. Focusing on the estimation of the pseudoranges, they are usually computed using two different methods.1) The first technique (named common transmission time) is based on the satellites transmission time. In fact, all satellites broadcast data synchronously but, due to different propagation delays, at a given time the user does not receive the same data from every satellite.Once each preamble is identified for all available channels, a comparison on their time of arrival is performed. In this case, in order to determine the set of pseudoranges for the first time, the channel with the earliest arriving subframe is assumed as a reference and a minimum travel time is assigned to the reference channel (e.g., its value, for GPS, is in a range between 65 and 85 ms). This concept is sketched in Figure 3.All other pseudoranges are then derived respect to the reference channel through proper time counters, that are continuously updated by the tracking structures of each channel. If we suppose that the start of the subframe is identified for all the tracked satellites, then the receiver measures the time difference between the starting points of the subframe and the reference one. This time difference δi can therefore been written as
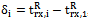 , where
, where 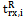 represents the time of reception of the subframe for the i-th satellite while
represents the time of reception of the subframe for the i-th satellite while 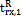 is the time relative to the reference satellite.The time difference δi for each i-th satellite can be computed by means of specific time counters. Although there are many time-keeping conventions, which depend on the specific receiver implementation, the system of counters has to accumulate the number of words (i.e.: in case of the GPS C/A code, 1 word = 0.6 s), data bits (i.e.: 1 data bit = 20 ms), code periods (i.e.: 1 GPS C/A code period = 1 ms), and samples (i.e.: 1 sample = 1/sampling frequency
is the time relative to the reference satellite.The time difference δi for each i-th satellite can be computed by means of specific time counters. Although there are many time-keeping conventions, which depend on the specific receiver implementation, the system of counters has to accumulate the number of words (i.e.: in case of the GPS C/A code, 1 word = 0.6 s), data bits (i.e.: 1 data bit = 20 ms), code periods (i.e.: 1 GPS C/A code period = 1 ms), and samples (i.e.: 1 sample = 1/sampling frequency 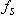 ). In the case of Galileo, the procedure is similar to the GPS case. The receiver has to store the following parameters, in order to compute a valid pseudorange: number of pages (i.e.: 1 page = 2 s), data bits (i.e.: 1 data bit = 4 ms), code periods (i.e.: E1-B code period = 4 ms) and samples (i.e: 1 sample = 1/sampling frequency where
). In the case of Galileo, the procedure is similar to the GPS case. The receiver has to store the following parameters, in order to compute a valid pseudorange: number of pages (i.e.: 1 page = 2 s), data bits (i.e.: 1 data bit = 4 ms), code periods (i.e.: E1-B code period = 4 ms) and samples (i.e: 1 sample = 1/sampling frequency where 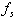 is the same as the GPS’s one, as the receiver uses a unique front end to collect and digitalize the incoming GNSS signals). It is important to stress that receivers are able to measure the time offset with a resolution on the order of a fraction of chip (i.e.: a fraction of microseconds).
is the same as the GPS’s one, as the receiver uses a unique front end to collect and digitalize the incoming GNSS signals). It is important to stress that receivers are able to measure the time offset with a resolution on the order of a fraction of chip (i.e.: a fraction of microseconds).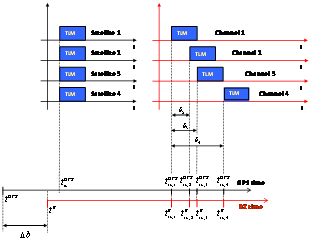 | Figure 3. Pseudorange computation based on transmission time |
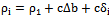 , where
, where 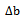 is the bias between the clock of the user and the ones on board of the satellites, c is the speed of light,
is the bias between the clock of the user and the ones on board of the satellites, c is the speed of light, 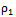 is the pseudorange relative to the reference channel and
is the pseudorange relative to the reference channel and 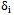 is the delay of the i-th satellite channel with respect to the reference satellite.This kind of approach has some disadvantages to be implemented in a real-time fully software receiver:a) Since the beginning of a given subframe transmitted by different satellites is received at different times, the receiver has to count for each tracked satellite the time elapsed from the reception of the subframe in the reference channel (i.e. the satellite with the shortest distance to the user’s receiver) to the beginning of same subframe for at least other three satellites. As a consequence, this kind of approach is not particularly suitable in a real-time implementation, since it requires to wait until all the channels have received the same data bit (e.g. the beginning of the same subframe) to compute the pseudoranges.b) In case of a joint GPS/Galileo scenario, this technique is unsuitable in real-time implementations, since the receiver would have to work with two independent satellite systems, characterized by different data structures and two separate reference channels (one for GPS and one for Galileo). This approach will force the receiver to keep a large amount of information into its buffer, with a significant waste of resources as well as a non-negligible delay in the PVT computation. For this reason, it is useful to consider a different method, that takes into account the status of every channel at a given, unique time, fixed by the receiver.2) The second approach (common reception time) performs the pseudoranges estimation by setting a common reception time over all the channels. In this case, which is sketched in Figure 4, the time elapsed from the reference bit (TLM in the Figure) to the bits currently considered in each channel (X, Y, Z, W in the Figure) is different for each channel, since the transmission time corresponding to the data message currently processed by the receiver is different for all the satellites.The different time offsets are computed measuring the time passed from the reception of the last subframe and the receiving time instant set by the receiver as shown in Figure 4.
is the delay of the i-th satellite channel with respect to the reference satellite.This kind of approach has some disadvantages to be implemented in a real-time fully software receiver:a) Since the beginning of a given subframe transmitted by different satellites is received at different times, the receiver has to count for each tracked satellite the time elapsed from the reception of the subframe in the reference channel (i.e. the satellite with the shortest distance to the user’s receiver) to the beginning of same subframe for at least other three satellites. As a consequence, this kind of approach is not particularly suitable in a real-time implementation, since it requires to wait until all the channels have received the same data bit (e.g. the beginning of the same subframe) to compute the pseudoranges.b) In case of a joint GPS/Galileo scenario, this technique is unsuitable in real-time implementations, since the receiver would have to work with two independent satellite systems, characterized by different data structures and two separate reference channels (one for GPS and one for Galileo). This approach will force the receiver to keep a large amount of information into its buffer, with a significant waste of resources as well as a non-negligible delay in the PVT computation. For this reason, it is useful to consider a different method, that takes into account the status of every channel at a given, unique time, fixed by the receiver.2) The second approach (common reception time) performs the pseudoranges estimation by setting a common reception time over all the channels. In this case, which is sketched in Figure 4, the time elapsed from the reference bit (TLM in the Figure) to the bits currently considered in each channel (X, Y, Z, W in the Figure) is different for each channel, since the transmission time corresponding to the data message currently processed by the receiver is different for all the satellites.The different time offsets are computed measuring the time passed from the reception of the last subframe and the receiving time instant set by the receiver as shown in Figure 4.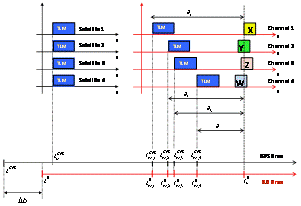 | Figure 4. Pseudorange computation based on transmission time |
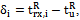 , where
, where  is the time when the receiver computes the pseudoranges and it is common to all the tracked signals.This method allows to obtain pseudoranges at any time, without waiting for a particular bit front on each channel, and it is often employed in commercial GPS receivers and is the technique that has been implemented in our joint GPS/Galileo receiver.The effect on the final PVT accuracy of implementing these two approaches will be analyzed in Section III.
is the time when the receiver computes the pseudoranges and it is common to all the tracked signals.This method allows to obtain pseudoranges at any time, without waiting for a particular bit front on each channel, and it is often employed in commercial GPS receivers and is the technique that has been implemented in our joint GPS/Galileo receiver.The effect on the final PVT accuracy of implementing these two approaches will be analyzed in Section III.2.3. PVT Computation
- The computation of the PVT can be demanded to many different algorithms. Nonetheless, this stage must be always provided with the following data, at least:• Pseudorange measurements• Doppler measurements• Satellites related data (positions, errors, etc.)The simplest method to implement the PVT stage of a GNSS receiver is to consider the Least Squares (LS) solution [21]. The rationale is to iteratively update the position solution at a given time, starting from a generic linearization point (usually the centre of the earth) and iteratively updating it to converge to the least squares estimate given by the current set of measurements. The linear equation stating the relation between the pseudorange prediction error vector,
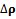 and the estimated position error,
and the estimated position error, 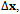 is the following:
is the following: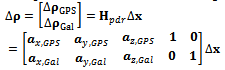 where
where 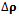 is the difference between the measured and estimated pseudoranges,
is the difference between the measured and estimated pseudoranges, 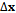 is the correction to be applied to the linearization point and the matrix
is the correction to be applied to the linearization point and the matrix 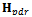 is the Direction Cosine Matrix (DCM), whose rows are made up by the unitary vectors pointing from the linearization point toward each one of the satellites in view; the subscript pdr stands for ‘pseudorange’.It must be noted that the pseudorange prediction error and the DCM are conceptually made of two parts. The upper part stores the values related to the GPS measurements, while the lower part stores the measurements related to Galileo. Moreover, the vector
is the Direction Cosine Matrix (DCM), whose rows are made up by the unitary vectors pointing from the linearization point toward each one of the satellites in view; the subscript pdr stands for ‘pseudorange’.It must be noted that the pseudorange prediction error and the DCM are conceptually made of two parts. The upper part stores the values related to the GPS measurements, while the lower part stores the measurements related to Galileo. Moreover, the vector 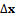 is made up by five elements:
is made up by five elements: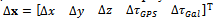 where the first three components are the corrections in meters to be applied to the ECEF components of the linearization point, the last two are the clock bias corrections in meters to be applied to the GPS and Galileo clock bias linearization point, since the receiver must take into account a clock bias with respect to the GPS (upper part) and a clock bias with respect to Galileo (lower part), and T points out the transpose of the vector.A similar result is obtained for the prediction of the velocity, when Doppler measurements are exploited [21]. In this case, the clock drift is the same for both the GPS and Galileo, so that the measurement matrix shows four columns:
where the first three components are the corrections in meters to be applied to the ECEF components of the linearization point, the last two are the clock bias corrections in meters to be applied to the GPS and Galileo clock bias linearization point, since the receiver must take into account a clock bias with respect to the GPS (upper part) and a clock bias with respect to Galileo (lower part), and T points out the transpose of the vector.A similar result is obtained for the prediction of the velocity, when Doppler measurements are exploited [21]. In this case, the clock drift is the same for both the GPS and Galileo, so that the measurement matrix shows four columns: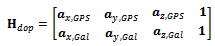 and the corrections vector to the estimated velocity has four components:
and the corrections vector to the estimated velocity has four components: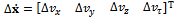 where the first three components are the ECEF corrections in meters per second and the last component is the local clock drift correction in meters per second; the subscript dop stands for ‘Doppler’. The linear relationship between the pseudorange-rate error vector,
where the first three components are the ECEF corrections in meters per second and the last component is the local clock drift correction in meters per second; the subscript dop stands for ‘Doppler’. The linear relationship between the pseudorange-rate error vector, 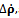 and the estimated velocity error is then
and the estimated velocity error is then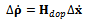 Whenever a PVT solution has to be delivered, the LS iterations run to resolve the two linear systems written above.Despite this method is simple, it has two main drawbacks. The first one is due to the complexity, since for each point the algorithm must usually iterate until the corrections are below a threshold and each time the pseudo-inverse matrix of
Whenever a PVT solution has to be delivered, the LS iterations run to resolve the two linear systems written above.Despite this method is simple, it has two main drawbacks. The first one is due to the complexity, since for each point the algorithm must usually iterate until the corrections are below a threshold and each time the pseudo-inverse matrix of 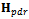 (and
(and 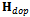 ) must be computed. This issue might be avoided introducing a model to make the linearization point evolve, as in a Kalman filter.The second drawback of the LS approach is due to the fact that the estimate is computed only on the basis of the current measurements, without any regards to the past trajectory and without weighting the available measurements. Despite the atter issue is solved using the Weighted LS (WLS), it is not possible to cope with the past trajectory using a LS-based method, ince it has no memory and at each time a solution is computed independently from the past.For this reason, it is useful to adopt other methods that rely on the representation of state-space models [23-26]. Among these, the algorithm that historically has shown the best compromise between performance and complexity in GNSS receivers is the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) [26], which is characterized by the following state-space equations:
) must be computed. This issue might be avoided introducing a model to make the linearization point evolve, as in a Kalman filter.The second drawback of the LS approach is due to the fact that the estimate is computed only on the basis of the current measurements, without any regards to the past trajectory and without weighting the available measurements. Despite the atter issue is solved using the Weighted LS (WLS), it is not possible to cope with the past trajectory using a LS-based method, ince it has no memory and at each time a solution is computed independently from the past.For this reason, it is useful to adopt other methods that rely on the representation of state-space models [23-26]. Among these, the algorithm that historically has shown the best compromise between performance and complexity in GNSS receivers is the Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) [26], which is characterized by the following state-space equations: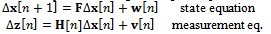 where
where 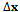 is the incremental state,
is the incremental state, 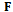 is the state transition matrix,
is the state transition matrix, 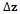 is the measurement prediction error,
is the measurement prediction error, 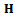 is the measurement matrix,
is the measurement matrix, 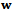 is the process noise and
is the process noise and 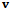 is the measurement noise. The notation is in part similar to the one adopted in the LS discussion. This is a voluntary choice, since the two algorithms are based upon similar concepts. The incremental states represent the increments (corrections) to be applied to an a priori estimate
is the measurement noise. The notation is in part similar to the one adopted in the LS discussion. This is a voluntary choice, since the two algorithms are based upon similar concepts. The incremental states represent the increments (corrections) to be applied to an a priori estimate 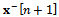 of the state, which acts as a linearization point. The state model adopted here is characterized by nine incremental states, the first five related to position and the last four related to velocity:
of the state, which acts as a linearization point. The state model adopted here is characterized by nine incremental states, the first five related to position and the last four related to velocity: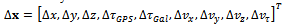 to which the following state-transition matrix is associated:
to which the following state-transition matrix is associated: Each time a new set of pseudorange and Doppler measurements is available, the Kalman filter is iterated once. The first step (prediction) allows to get the a priori estimate
Each time a new set of pseudorange and Doppler measurements is available, the Kalman filter is iterated once. The first step (prediction) allows to get the a priori estimate 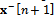 by using the last obtained estimate of the PVT in the state equation. This value is used to compute the prediction of the measurements and, together with the measurements, to compute the correction to be applied to the a priori estimate, as follows (update):
by using the last obtained estimate of the PVT in the state equation. This value is used to compute the prediction of the measurements and, together with the measurements, to compute the correction to be applied to the a priori estimate, as follows (update):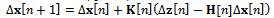 where
where 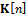 is the Kalman gain. Finally, the a posteriori estimate
is the Kalman gain. Finally, the a posteriori estimate 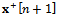 is obtained correcting the a priori estimate:
is obtained correcting the a priori estimate: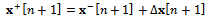 The main advantage of the EKF with respect to the LS is the introduction of a method to balance the contribution of the trajectory given by the model and the one obtained by the measurement. In this way, it is possible to obtain a smoother trajectory than the one obtained using the LS and to avoid the model trajectory to diverge. A complete definition of this model can be found in [26] and [27]. These results will be analyzed in the following section.
The main advantage of the EKF with respect to the LS is the introduction of a method to balance the contribution of the trajectory given by the model and the one obtained by the measurement. In this way, it is possible to obtain a smoother trajectory than the one obtained using the LS and to avoid the model trajectory to diverge. A complete definition of this model can be found in [26] and [27]. These results will be analyzed in the following section.3. Comparative Results
- In this Section we investigate the effects of the two different approaches to compute the pseudoranges discussed in Section II.B; then, we show some results we obtained by using both a LS and an EKF approach to resolve the PVT problem.Concerning the calculation of the pseudoranges, an example of their estimation results by using the two methods of Section II.B is depicted in Figure 5, taking as an example the GPS satellite with PRN 30.
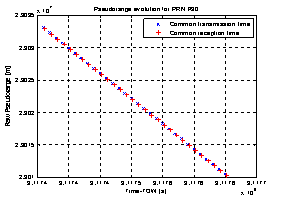 | Figure 5. Comparison between pseudoranges computed by using common reception time and common transmission time |
4. Conclusions
- This paper has discussed a receiver architecture that allows to simultaneously process the Galileo and the GPS signals in a software receiver. Despite this topic is known in literature, we focused our attention on some practical implementation details that are often disregarded when the theory is discussed.
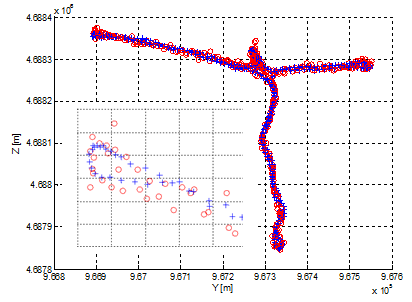 | Figure 6. Estimated trajectory, using both a LS (red circles) and an EKF (blue crosses) based receiver, and zoom of the north-western area. |
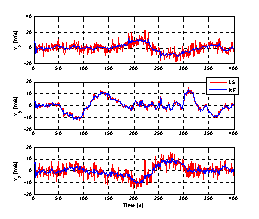 | Figure 7. Estimated trajectory, using both a LS and an EKF based receiver, and zoom of the north-western area. |
References
| [1] | B. Eissfeller, G. Hein, J.-Á. Ávila-Rodriguez, P. Hartl, S. Wallner, T. Pany, “Envisioning a Future: GNSS System of Systems, Part 1”, Inside GNSS, Jan.-Feb. 2007, pp. 58-67 |
| [2] | “Envisioning a Future: GNSS System of Systems, Part 2”, Inside GNSS, Mar.-Apr. 2007. pp. 64-72 |
| [3] | W.H.W. Tuttlebee, "Software-defined radio: facets of a developing technology," Personal Comm., IEEE , vol.6, no., pp.38-44, Apr 1999 |
| [4] | J. Mitola, “The software radio architecture,” IEEE Comm. Magazine, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 26–38, May 1995 |
| [5] | G. MacGougan, P. L. Normark, C. Ståhlberg, “The Software GNSS Receiver,” GPS World, Jan. 2005 |
| [6] | G. Hein, J.-H. Won, and T. Pany, “GNSS software defined radio: real receiver or just a tool for experts?” Inside GNSS, vol. 1, no. 5, 2006 |
| [7] | M. Fantino, A. Molino, M. Nicola, “N-Gene GNSS Receiver: Benefits of Software Radio in Navigation”, in proceedings of the ENC GNSS 2009, May 3-6 2009, Naples, Italy |
| [8] | M. S. Braasch and A. J. van Dierendonck, “GPS receiver architectures and measurements,”Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 48–64, 1999 |
| [9] | G. W. Hein, T. Pany, S. Wallner, J.-H. Won, “Platforms for a Future GNSS Receiver. A Discussion of ASIC, FPGA, and DSP Technologies,” Inside GNSS, March 2006, pp. 56-62 |
| [10] | F.Macchi andM. G. Petovello, “Development of a one channel Galileo L1 software receiver and testing using real data,” in Proceedings of the 20th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GNSS ’07), vol. 2, pp. 2256–2269, FortWorth, Tex, USA, 2007 |
| [11] | M. G. Petovello, C. O’Driscoll, G. Lachapelle, D. Borio and H. Murtaza, “Architecture and Benefits of an Advanced GNSS Software Receiver,” Journal of Global Positioning Systems (2008), Vol. 7, No. 2 : pp. 156-168 |
| [12] | H. Hurskainen, J. Raasakka, T. Ahonen, and J. Nurmi, “Multicore Software-Defined Radio Architecture for GNSS Receiver Signal Processing,” EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems, vol. 2009, Article ID 543720, 10 pages, 2009. doi:10.1155/2009/543720 |
| [13] | M. Sahmoudi and M. G. Amin. 2009. Robust tracking of weak GPS signals in multipath and jamming environments. Signal Process. 89, 7 (July 2009), 1320-1333. doi=10.1016/j.sigpro.2009.01.001 |
| [14] | M. Zahidul, H. Bhuiyan and E. S. Lohan, “Advanced Multipath Mitigation Techniques for Satellite-Based Positioning Applications,” International Journal of Navigation and Observation, vol. 2010, Article ID 412393, 15 pages, 2010. doi:10.1155/2010/412393 |
| [15] | F.Macchi, “Development and testing of an L1 combined GPS-Galileo software receiver”, PhD Thesis , Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada, 2010 |
| [16] | C.Mongrédien, “GPS L5 Software Receiver Development for High Accuracy Applications”, PhD Thesis, Department of Geomatics Engineering, University of Calgary, Canada, 2008 |
| [17] | P.Berglez, “Development of a GPS, Galileo and SBAS receiver”, Proceedings of 50th, International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 10-12 Sept. 2008 |
| [18] | F. Principe, G. Bacci, F. Giannetti, and M. Luise, “Software-Defined Radio Technologies for GNSS Receivers: A Tutorial Approach to a Simple Design and Implementation,” Int. J. of Navigation and Observation, Vol. 2011, Article ID 979815, doi:10.1155/2011/979815 |
| [19] | Galileo.ICD,“http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/policies/satnav/galileo/open-service/index_en.htm” |
| [20] | GPS.ICD,“http://www.navcen.uscg.gov/pubs/gps/icd200/default.htm” |
| [21] | E.D. Kaplan and C.J. Hegarty, “Understanding GPS: principles and applications”, Artec House, 2006 |
| [22] | J. Bao and Y. Tsui, “Fundamentals of GPS receivers – 2nd edition”, Wiley, 2006 |
| [23] | A. Gelb. Applied Optimal Estimation. 1974. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press |
| [24] | M. West and P.J. Harrison, Bayesian Forecasting and Dynamic Models. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1997 ( First edition 1989) |
| [25] | G. Welch, G. Bishop, An introduction to the Kalman filter, SIGGRAPH 2001, Course 8, Los Angeles, CA. Available at: http://www.cs.unc.edu/~tracker/media/pdf/SIGGRAPH2001_CoursePack_08.pdf (accessed: 07.2011) |
| [26] | R.G. Brown and P.Y.C. Hwang, “Introduction to random signals and applied Kalman filtering”, John Wiley and Sons, 1997 |
| [27] | E. Falletti, M. Rao, S. Savasta, “The Kalman Filter and its Applications in GNSS and INS”, in S. A. (Reza) Zekavat, and R. M. Buehrer, Editors, “Handbook of Position Location - Theory, Practice and Advances,” in publication by Wiley-IEEE Press; Oct. 2011 |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML