Keisuke Katsura1, Fumiko Harada2, Hiromitsu Simakawa1
1Ritsumeikan University Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering, Kusatsu, Japan
2Connect Dot Ltd., Kyoto City, Japan
Correspondence to: Keisuke Katsura, Ritsumeikan University Graduate School of Information Science and Engineering, Kusatsu, Japan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
The decline of traditional culture is regarded as a problem in Japan. In addition, Japanese with sufficient knowledge of traditional culture are required in order to disseminate Japanese traditional culture to the world. In order to increase Japanese who have sufficient knowledge of traditional culture, it is necessary to cause young people interested. In this research, we propose a method that stimulates user's interest by using a guide avatar in a VR space to provide background knowledge of Japanese culture. The guide avatar is a famous historical figure. The topic that the guide avatar introduces to users is the events related to both the historical figures and traditional crafts. Utilizing story marketing, the guide avatar explains the knowledge for understanding the charm of the traditional crafts to users, thereby stimulating the user's interest. As a result of examining the usefulness of the method, it became clear that compared to the audio guidance provided at a museum, the guide avatar introducing traditional culture can more strongly stimulate the subject's interest in traditional culture. It became clear that, by allowing the well-known person speak the episodes related to both himself and traditional culture, the user’s interest in traditional culture is more strongly evoked. Since young people are interested in VR technology, the method can make them learn traditional culture through story marketing.
Keywords:
Interest, Virtual Reality, Guide Avatar, User Behavior
Cite this paper: Keisuke Katsura, Fumiko Harada, Hiromitsu Simakawa, Stimulating Interests in Traditional Culture Using Guide Avatar Narrating Story in VR Space, Advances in Computing, Vol. 8 No. 1, 2018, pp. 1-9. doi: 10.5923/j.ac.20180801.01.
1. Introduction
Recently, more and more foreigners visit Japan. According to a survey by the Japan National Tourism Organization, the number of foreigners visiting Japan exceeded 20 million in 2016 [1]. Due to increase of the number of foreign visitors, there is increasing interest in Japanese traditional culture in the world. It is necessary to further develop the traditional culture industry and its information dissemination to foreign countries to increase demands. Japanese with sufficient knowledge of traditional culture are required in order to disseminate Japanese traditional culture to the world.On the other hand, the decline of traditional culture is regarded as a problem in Japan. According to announcement of the Japan Policy Council, it is said that nearly 40% of temples will disappear from about 77,000 temples nationwide in the next 25 years [2]. One of the reasons is young people's lack of interest in traditional culture. Because of influence of the changing social needs, opportunities for young people to experience traditional culture are decreasing. By reduction of opportunities to contact traditional culture, young people are losing interest in traditional culture. In order to increase Japanese who have sufficient knowledge of traditional culture, it is necessary to cause young people interested.The value of traditional culture is intensified through understanding of the historical background [3]. Therefore, it is difficult to be interested in traditional culture without understanding the background knowledge. In order to stimulate interest in traditional culture, it is necessary to give effective knowledge of historical background. As a method to arouse interests of consumers for what we want to promote, many companies have used the story marketing [4]. The story marketing does not appeal what we want to promote with its value, but with a story explaining the process where it gets attractive. We consider that utilization of the story marketing can provide knowledge of historical background that arouses interest. In addition, experience promotes understanding of traditional culture. Recently, advance of VR(virtual reality) technology has brought VR consumer products of high quality and low cost. The spread of inexpensive VR products such as headsets and handsets has attracted attention in the tourism field. For example, experiences of VR tourism may make people feel like having experienced without actual visit to the sight-seeing areas [5]. With the VR technology, it is easy to make a pseudo sightseeing and experience of various traditional cultures.In the existing work [8], in order to deepen the knowledge of traditional culture, the cultural facilities were recreated in the VR space and the exhibits were introduced. Also, in the existing work [6], the user learned cultural behavior like bowing in VR space. However, these methods do not provide effective knowledge that arouses interest.This study proposes a method to make users interested in traditional culture using VR. Many people hear the story when famous people speak to themselves. In this study, a guide avatar representing celebrities in history is set in the VR space. The avatar talks to the user about the introduction of traditional culture. According to story marketing, the method introduces the traditional culture in the explanation of historical events relating to the well-known person the avatar represents. This method stimulates user's interest by avatar introducing traditional culture. Thereby, the user is able to deepen the background knowledge and to be interested in traditional culture. Therefore, it can contribute to maintenance and development of traditional culture.
2. Related Works
2.1. Interest Arousing Method by Story Marketing
There is story marketing as a method to stimulate interest [4]. Story marketing is a marketing method that creates empathy by appealing emotional added value such as experience and worldview rather than appealing superiority of performance or function itself of goods and services. In other words, by introducing products and services by tailoring stories, it is possible to give consumers empathy to the stories and to stimulate purchasing behavior. For example, when the main character of a story is in trouble, listeners can easily empathize by feeling that they want to cheer. Empathy to the main character of the story brings about empathy for the story, which leads to interest and purchase willingness. In traditional culture, by introducing the historical background as a story focusing on people, it is considered that the user's interest can be aroused.
2.2. Current Problems in Traditional Culture
Many of young people do not show their interest in traditional culture. This paper aims to arouse them to be interested in traditional culture. We can understand the real value of traditional culture if we deepen historical background knowledge [3]. In order to arouse interest in traditional culture, it is required to give information involving the background knowledge of traditional culture. It means, if we do not know the background knowledge of traditional culture, we cannot have interest. Even if we learn background knowledge for shallow interest items, we are likely to lead to frustration. It is necessary to give effective background knowledge in order to arouse interest to young people who are not interested in traditional culture.
2.3. Virtual Reality and Tourism
Recently advance in VR technologies brings VR products of high quality at low cost. VR headsets are available even in home. The technology revolution in VR has attracted attention in the tourism field [10]. There are existing works to arouse interest in traditional culture using VR [5, 9, 17]. Realistic images in the VR space give users sensations because they feel as if real objects were actually presented in the space. Even users who do not have sufficient time, opportunity, or money can enjoy the sightseeing without actual visit. In addition, by previewing the travel destination in the VR space, the user can easily plan sightseeing routes and meaningful sightseeing becomes possible.
2.4. Existing Works Using Virtual Reality
VR technology is useful as a means to promote understanding of traditional culture [12-14]. Therefore, there are existing works utilizing VR in traditional culture. The works in [7] and [15] reproduced a museum in the VR space and encourage interest in exhibits by allowing users to walk around the hall. In addition, Adri et al. reproduced cultural heritage such as Buddha statue in VR space [16]. They developed a system that detects well-viewable angle and allows users to view the cultural heritage from an angle that they cannot actually see. However, these studies do not consider providing effective background knowledge.There are existing works that focus on the acquisition of knowledge by using the VR technologies. Alan et al. built a tool to learn languages along with cultural behavior using VR [6]. The work sets an avatar in a VR space and teaches cultural behavior such as bowing and language learning through interaction with the avatar. The work reported that there was a significant difference in acquisition of cultural behavior and learning motivation for linguistics compared to non-VR. However, there was no significant difference in language learning. Dylan et al. built a tool to learn languages in VR space [11]. Through pleasure obtained from the use of VR content, useful results were obtained for user's language learning. Language learning is exciting because they can communicate in that language. Acquisition of knowledge of traditional culture is usually not exciting. If we do not stimulate interest in traditional culture, we will not attract sightseeing areas and practical fields.
3. Invitation to Traditional Culture Using VR
3.1. The Method Overview
In this paper, we propose a method to evoke an interest in Japanese traditional culture using the VR. People who do not have knowledge of traditional culture do not have an interest even if we convey the appeal to them about charm of traditional crafts. However, when presented as a story as to why the item has made its charm, people easily absorb knowledge in understanding traditional crafts. With this knowledge acquisition, users are interested in traditional crafts. In this study, we use story marketing for stimulating user's interest in traditional culture.The method stimulates user's interest by using a guide avatar in the VR space to provide background knowledge of the Japanese culture. The outline of the method is shown in Fig 1. The method targets users with poor knowledge about Japanese traditional culture. We prepare a 3-dimensional VR space in which Japanese traditional crafts are scattered in a Japanese old-style room. We set a guide avatar representing a historical figure in this 3-dimensional space. The guide avatar introduces historical backgrounds of the traditional crafts scattered in the VR space to users. The topic that the guide avatar introduces to the users is events related to both the historical figure and traditional crafts. Utilize the story marketing method that the historical person tells the reason why the cultural products have attracted, as an explanation of the event. Utilizing story marketing, the guide avatar explains the knowledge for understanding the charm of traditional culture to the users, thereby stimulating the user's interest. By raising the user's interest in the traditional culture, it enhances the desire for real experience and contributes to attracting sightseeing spots and actual locations. | Figure 1. Method overview |
3.2. How to Stimulate Interest by a Guide Avatar
The method gives knowledge of traditional culture and stimulates user's interest, by utilizing avatar and story marketing method. From the discussion in Section 2.1, people often show strong empathy with stories that focus on persons. Because traditional culture has a historical background, there are abundant topics related to historical figures. Therefore, a guide avatar is a historical person in Japan who is deeply related to introducing traditional culture. In addition, the guide avatar introduces the knowledge about traditional culture to users in the experience story focusing on historical events related to the person corresponds to the guide avatar. Therefore, users can enjoy virtual experiences of listening to personal experiences on traditional culture from a historical figure.In this study, we define a guide avatar simulating a historical figure as a great avatar. We appoint a famous person as the historical figure used for a great avatar. If users have no prior knowledge on a topic, it is difficult for them to interest in it because they have difficulty to understand the story [19]. Therefore, explanation from a person whom users cannot recognize is less interesting. On the other hand, if the historical figure is enough famous among many people, users have a certain level of prior knowledge even if they are not familiar with history or culture. It is considered that user never suffer from understanding by receiving explanations from the famous figures so that it is easy for users to have an interest. Therefore, the method gives users knowledge of traditional culture through a story focused on famous historical figures. Thereby, it is considered that the user harbors a strong empathy and get interested.
3.3. Interests Appearing in Behavior
This study aims at attracting a user to an actual location when the user's interest in the traditional culture is stimulated in the VR space. Therefore, it is necessary to identify the traditional culture of user's interest target.It is considered that the user's interest appears in the user behavior in the VR space. For example, a user who becomes interested in introduced tea utensils will ask for introduction of the tea utensils again when he / she misses the explanation. Furthermore, it may be expected to request further disclosure of information. On the other hand, in case of not interested, the user will interrupt the tea utensil introduction midway and select introductions of other traditional cultures. The method assumes that if the user becomes interested in a specific traditional crafts, he / she asks for the introduction again or request disclosure of deeper information in the VR space. The method calculates the frequency of these requests from the operation log of the user.
4. VR Space for Introducing Traditional Culture by a Guide Avatar
We constructed the VR space where users can receive introductions of traditional culture by a great avatar. In this VR space, all operation logs are recorded. By analyzing the operation logs, it is discriminated which kind of traditional culture in the VR space the user is interested in.
4.1. Physical Devices
Oculus Rift and Oculus Touch [8] were used as the devices by that users can enjoy the VR function. The situation where the user wears these devices and uses the VR space is shown in Fig. 2.  | Figure 2. The tools for the VR space |
Oculus Rift is a head mount display for virtual reality. Users can enjoy the VR function by wearing Oculus rift on their heads. Oculus Touch is an input device for Oculus Rift, and reproduces the movement of the hand in the VR space by wearing it on both hands. By manipulating the hands of the VR space according to the movement of the hand in the real world, the user can operate the tool.
4.2. Physical Devices
The user's field of view in the VR space when the user uses this tool is shown in Fig. 3. The camera angle adopts the first-person viewpoint which makes it easy for users to feel immersion. In order to remove unnaturalness in the situations of introducing Japanese traditional culture, we built a virtual space of Japanese houses. A room is placed in a traditional Japanese house. The room consists of an artistic column, wooden pillars, soil walls, and tatami mats. It also equips with Japanese traditional objects including Japanese sword, hanging scroll, and Japanese paintings.  | Figure 3. The user's field of view in the VR space |
An example of the great avatar used in this tool is shown in Fig. 4. In this method, two-dimensional image is used for a great avatar. Users can listen to the introduction of traditional culture by the great avatar voice. We use the lip-sync function to move the mouth and eyes of the great avatar according to voice. With this function, users can get the feeling that they are spoken to from the great avatar.  | Figure 4. An example of the great avatar used in this tool |
4.3. User’s Operation
When the great avatar introduces traditional culture, this VR space has two functions to acquire which the user's interest appears in the behavior. The first one is the function of rewinding. Users would want to receive introduction again, when they miss some parts of narration of interested objects. It is considered that the user's interest appear in behavior. Therefore, in this research we have a function to rewind introduction of traditional culture by the great avatar for 10 seconds. Secondly, it is a function to present detailed information on traditional culture. The user wants to know more about the traditional culture of interest. Therefore, this VR space has a function that users can request detailed information on the traditional culture introduced by the great avatar.Also, the user operates the VR space by movement of the arm and hand. A pseudo hand is displayed in the VR space so that the user can easily understand which object is the target of operation. In order to receive introduction of traditional culture from the great avatar, hand movement and button input are required. First, in order to a user receives an introduction of traditional culture from the great avatar, user selects a specific traditional culture object, using the laser pointer output from on the right hand. By selecting the traditional culture objects, it moves to the position where traditional cultural objects are in front of user. After moving, by pushing the button of Oculus Touch on the left hand, the user can view the guide avatar and receive introduction of the selected traditional culture.In order to present detailed information on the traditional culture introduced by the great avatar, we set up a button to present detailed information in the VR space. By selecting the button, information on the target traditional culture can be viewed with sentences. The rewind function can rewind the introduction explanation for 10 seconds by pressing the button of Oculus Touch on the left during the introduction of the traditional culture by the great avatar.
5. Experiment
In order to evaluate the usability of the method, we experimented to verify whether the user's interest can be stimulated using the VR system based on this method.
5.1. Experiment Environment
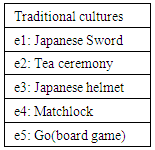
The great avatar used in this experiment is Nobunaga Oda [18]. For that reason, we prepare five traditional cultures deeply related to the great avatar (Nobunaga Oda). The traditional cultures used in this experiment are shown in Table 1. Each traditional culture and story about the great avatar were extracted from literature [18].Table 1. Traditional cultures in this experiment
 |
| |
|
In the experiment, as a comparison target of the traditional culture introduction method by the great avatar, we prepared a method of introducing traditional culture by audio. In the introduction of traditional culture by audio, cultural goods are introduced only by audio, like the audio guidance that is provided at cultural facilities. When a great avatar introduces himself and episodes related to traditional culture, it explains with a subjective expression. On the other hand, in the introduction by audio, episodes related to historical figures and traditional culture are explained with objective expression. For example, in case of the great avatar, we use subjective expressions using a first-person words such as “I figured out a three-step method in that shooting shooters are divided into three groups”. On the other hand, in the case of the audio guide, we use objective expressions such as “Nobunaga figured out a three-step method in that shooting shooters are divided into three groups”. The subjects experience two patterns of the introduction methods. In this experiment, the introduction methods by the great avatar and the audio guide are called as the great avatar version and the audio guide version, respectively.
5.2. Experimental Method
In this experiment, we investigate the following points.1. Would subject interest in traditional culture be stimulated by the great avatar introducing traditional culture in VR space?2. Can the method estimate interests from user's behavior?3. Is the great avatar useful?We had 26 Japanese subjects from 20 to 26 years of age.The experimental procedure is shown in below. First, the subjects answer the pre-questionnaire. In the pre-questionnaire, we confirmed the current interest in the five traditional cultures introduced in the VR space. Then, subjects receive introduction about the five kinds of traditional culture from the great avatar in the VR space. At this time, the subjects randomly experience to receive introduction by the audio guide version for from 1 to 3 objects out of the five traditional cultures objects. Subjects may get tired if they receive all five types of the audio guide version. In order to avoid deteriorating evaluation on the audio guide version due to fatigue, we let the subject experience two introduction methods. After using this tool, we carry out questionnaires in both cases of audio guide version and great avatar version, and interviews about the five traditional cultures that have been introduced. In the post-questionnaire, we confirmed the current interests in the introduced traditional culture. The pre-questionnaire and post-questionnaires were conducted on the Likert scale with 7 grades in all items, where 7 is treated as the highest rating while 1 as the lowest rating. In the interview, we surveyed the factors of change in interest, the behavior in which interest appears, and the effectiveness of the great avatar.
5.3. Result
5.3.1. Verification of Stimulating User Interest
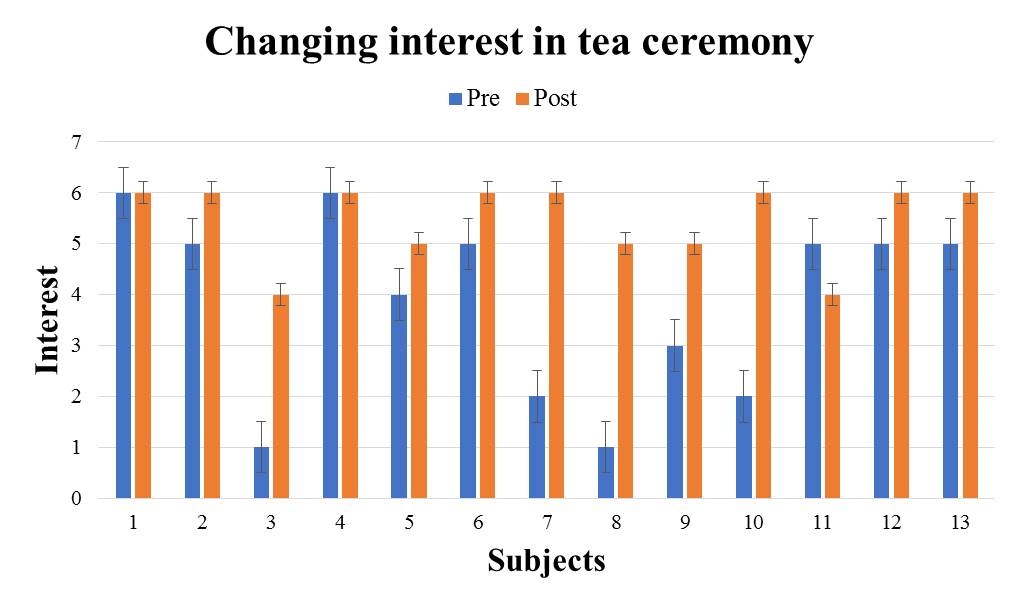
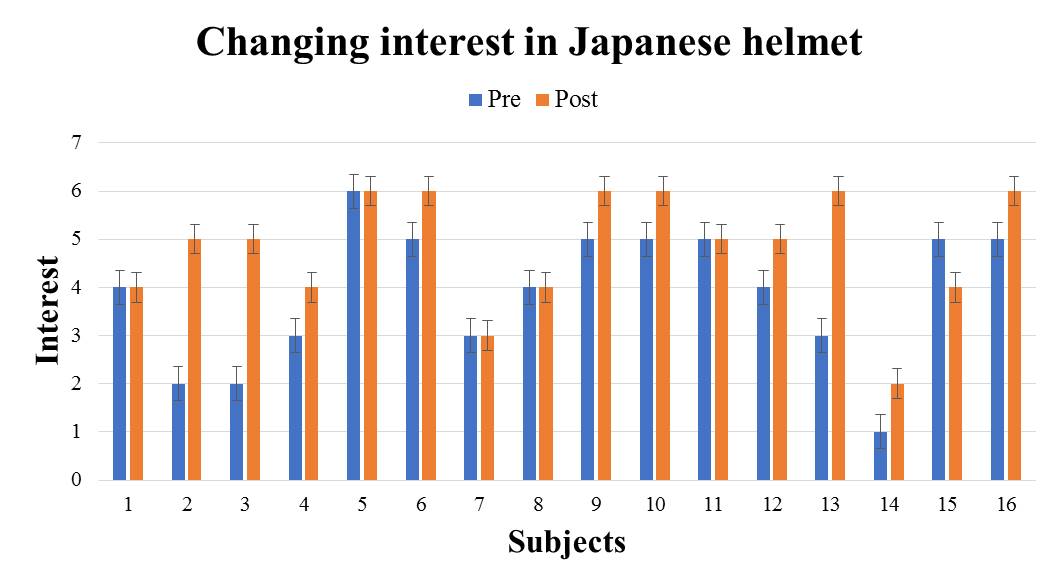
We evaluate the subject's interest in the introduced traditional culture from the differences in questionnaire results between the two introduction methods. We evaluate changes in interest before and after using the VR system using the Wilcoxon signed-rank sum test. When conducting the test, the significance level shall be 5%. For each traditional culture, we show the questionnaire result of the subjects who experienced the great avatar version in Fig. 5-9 (The subjects randomly experienced to receive introduction by the audio guide version and the great avatar version, so there are variations in the number of subjects.). It shows the test results by the method for introducing the great avatar version in Table 2. From the results in Table 2, there were significant differences for the four traditional cultures except "Go" between before and after using the system. In addition, from the results in Fig. 5-9, there are more than 53% of subjects who have improved the value of interest before and after using the system. Therefore, it was shown that the four types of traditional culture in which significant difference was recognized are easy to stimulate the subject's interest by using this method.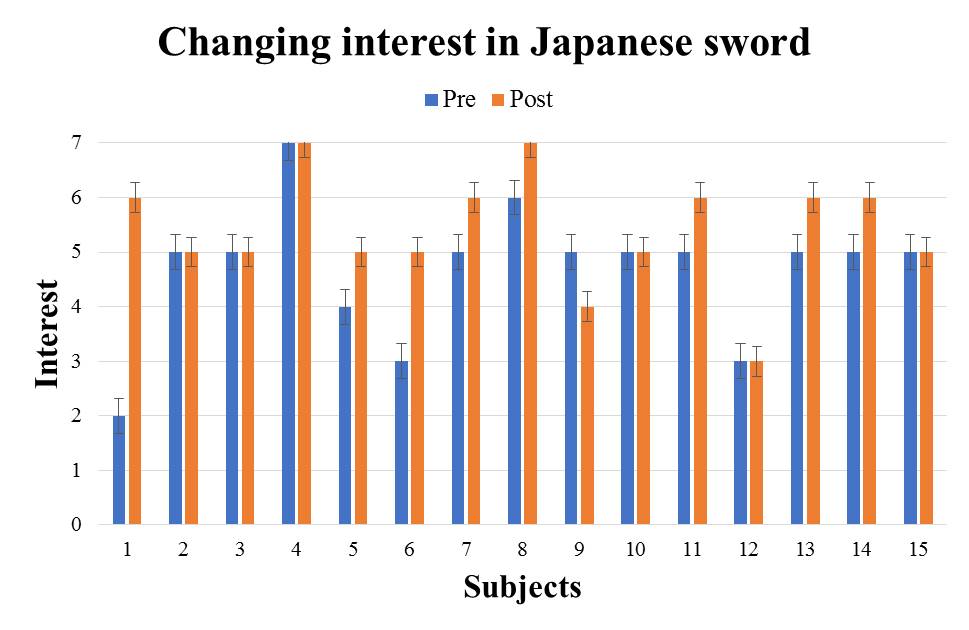 | Figure 5. e1: The great avatar version questionnaire result |
 | Figure 6. e2: The great avatar version questionnaire result |
 | Figure 7. e3: The great avatar version questionnaire result |
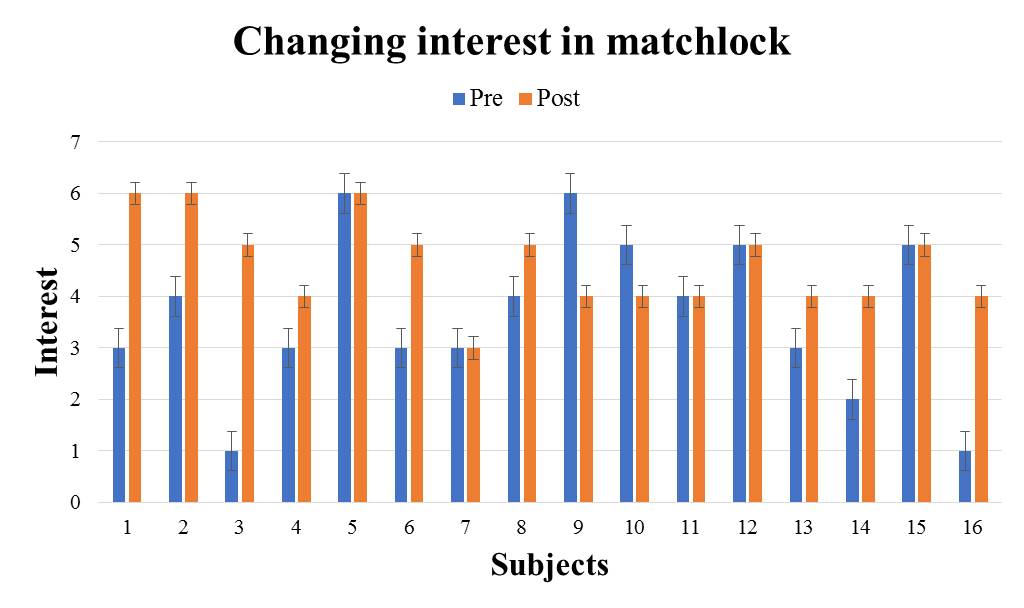 | Figure 8. e4: The great avatar version questionnaire result |
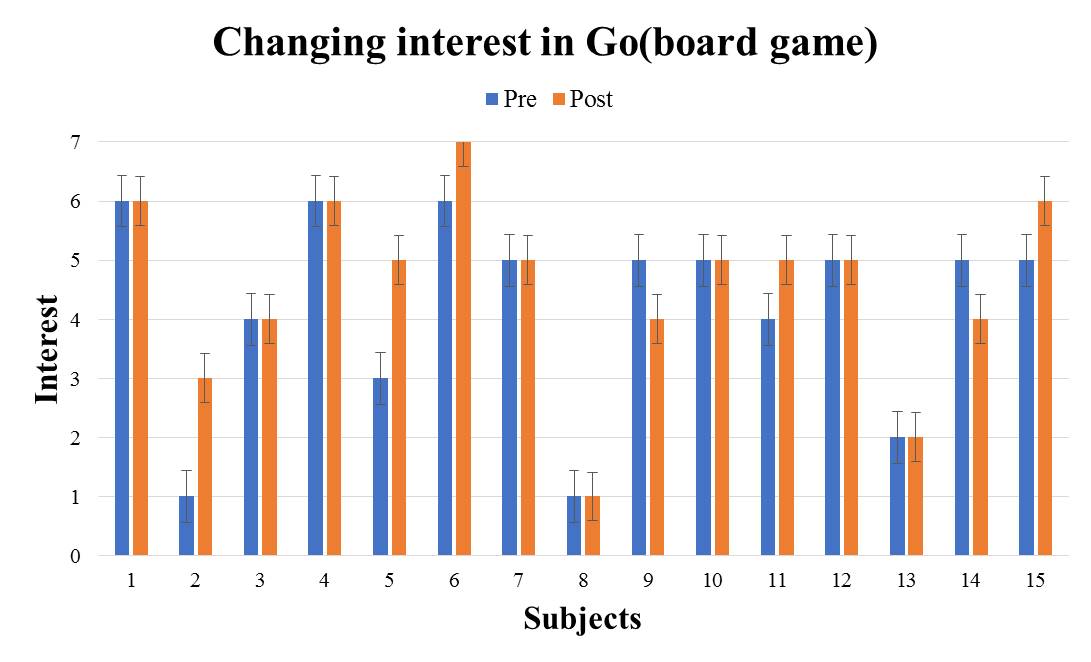 | Figure 9. e5: The great avatar version questionnaire result |
Table 2. Examination result of the great avatar version
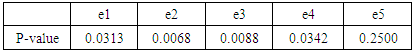 |
| |
|
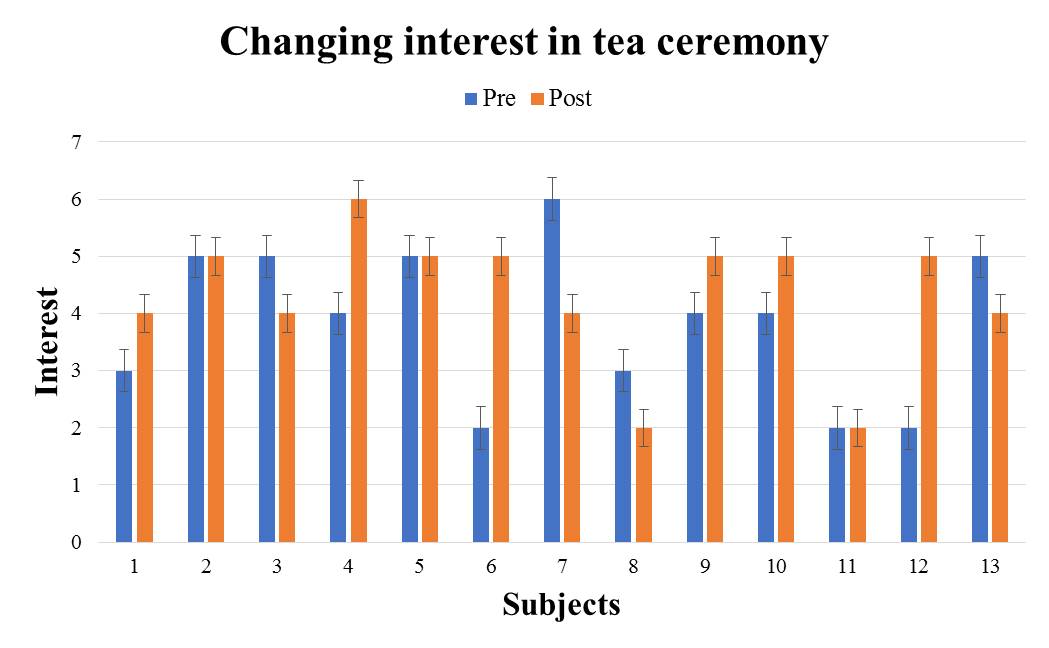
Next, the questionnaire result of subjects who experienced the audio guide version is shown in Fig. 10-14. It shows the test results of the audio guide version in Table 3.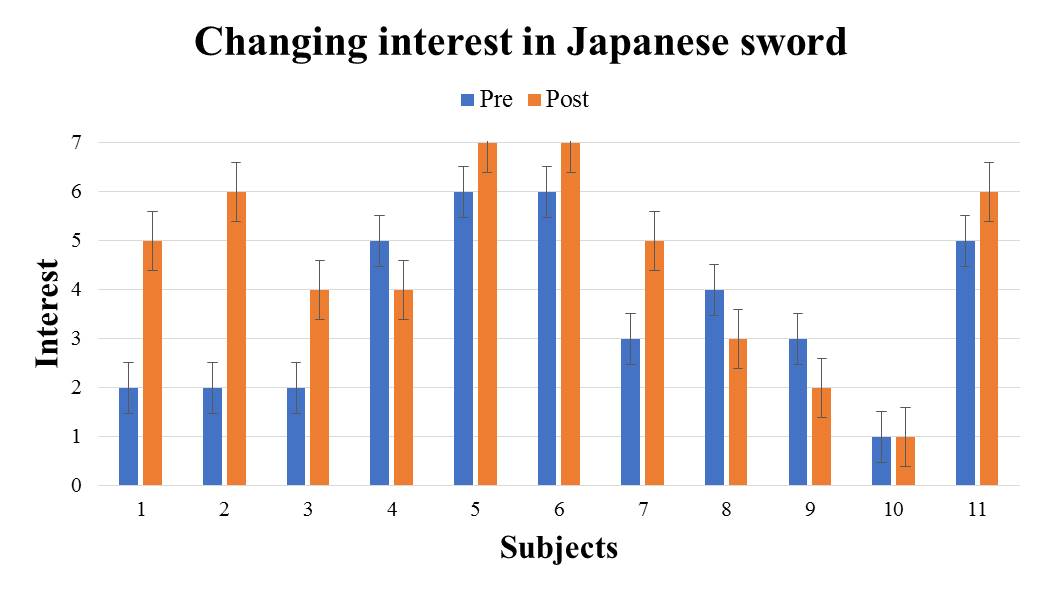 | Figure 10. e1: The audio guide version questionnaire result |
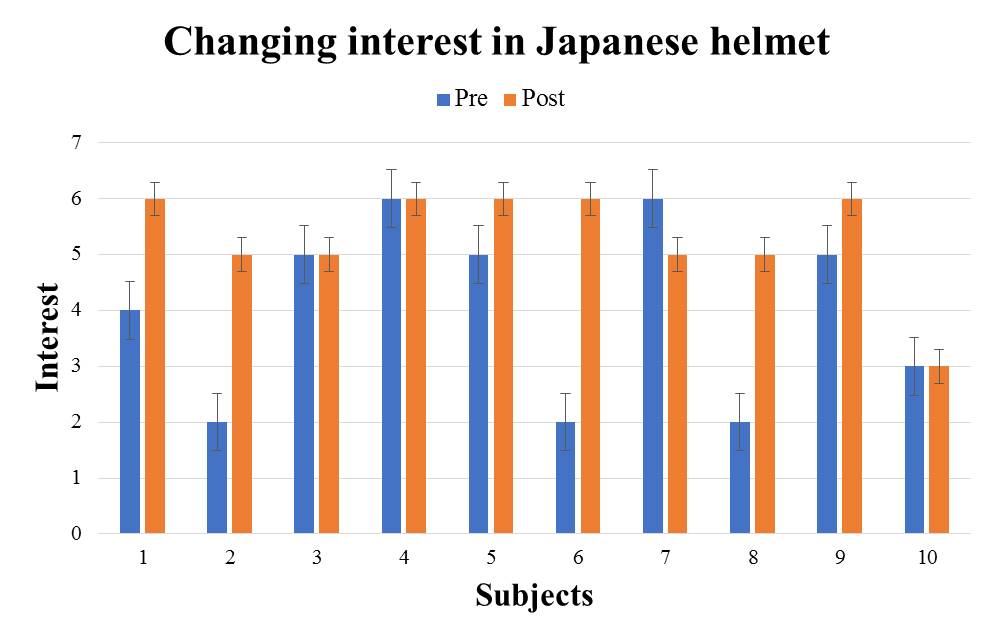
 | Figure 11. e2: The audio guide version questionnaire result |
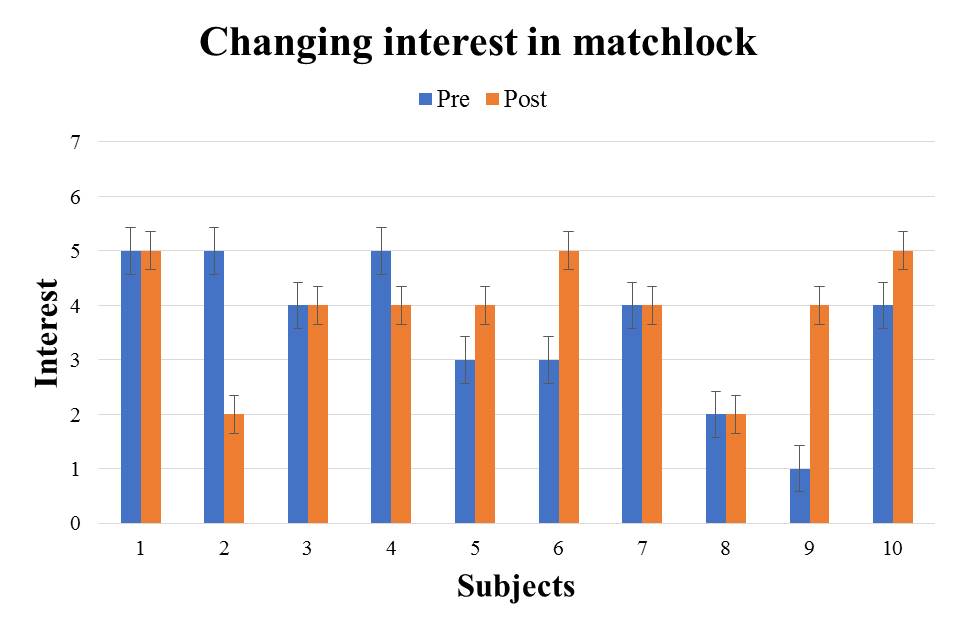
 | Figure 12. e3: The audio guide version questionnaire result |
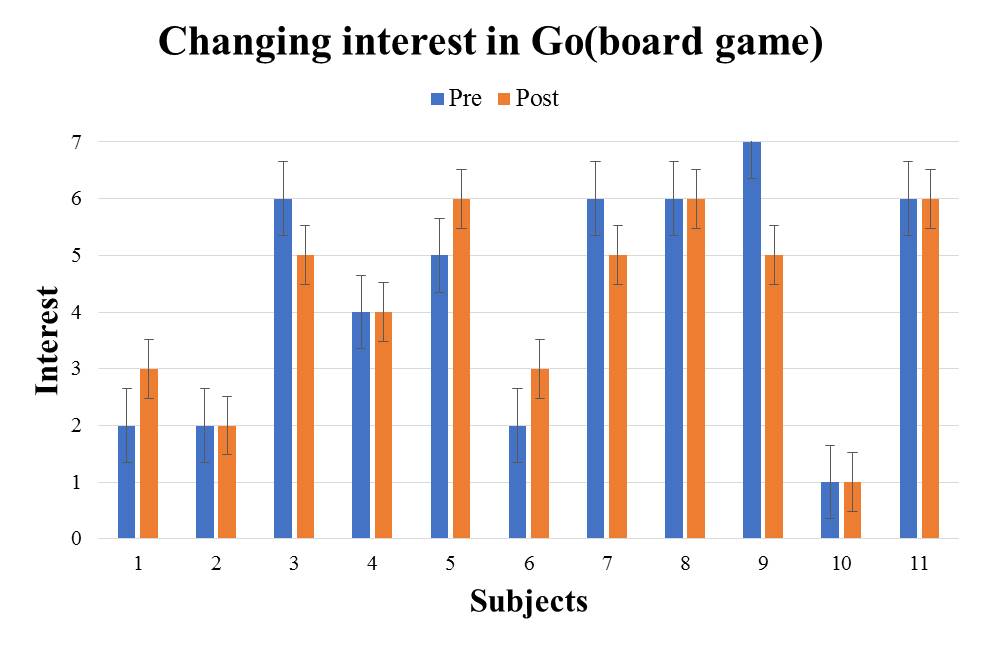
 | Figure 13. e4: The audio guide version questionnaire result |
 | Figure 14. e5: The audio guide version questionnaire result |
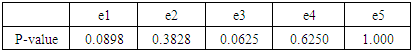
Table 3. Examination result of the audio guide version
 |
| |
|
From the results in Table 3, significant difference was not observed in all traditional cultures. It turns out that the method of introducing traditional culture by audio cannot be said to stimulate the subject's interest.From the test result of the 2 types of introduction methods, introducing traditional culture by the great avatar is strongly arousing the interest in traditional culture more compared with the existing method. Therefore, it can be said that the introduction of the traditional culture by the great avatar is effective as a method to stimulate interest.
5.3.2. Verification of Behavior in which Interest Appears
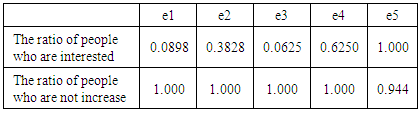
We examined whether it is possible or not to distinguish interesting targets based on the presence or absence of browsing detailed information and the usage count of rewind function. These are acquired from Oculus Touch log data. In each of the traditional culture, Table 4 shows the ratio of the subjects who viewed detailed information for each difference in interest (e1 to e5 are five traditional cultures.).Table 4. Percentage of browsing detailed information
 |
| |
|
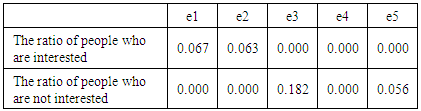
Next, in each traditional culture, Table 5 shows the percentage of the subjects who used the rewind function for each difference in interest. From the results in Table 4, most subjects viewed detailed information regardless of changes in interest. Moreover, from the results in Table 5, most subjects did not use the rewind function regardless of change in interest.Table 5. Percentage of the rewind function
 |
| |
|
From the above results, it was impossible to distinguish subjects' interest targets from the two kinds of functions.
6. Discussion
6.1. Discussion of VR System Improvement
From the experimental results, it was possible to stimulate users' interest in the four traditional cultures introduced by the great avatar. Within the five kinds of traditional culture, there is no significant difference in "Go". This section discuss why interest in "Go" was not stimulated.In this experiment, we interviewed the subjects after the post-questionnaire. As a result of the interview, the reason why the subjects’ interest was stimulated about the four traditional cultures excluding "Go" has been pointed out that "I was enjoy because I was able to receive introduction while seeing the real thing". On the other hand, the reason why the subjects' interest could not be stimulated for “Go” is " I think that “Go” is a board game to play, not objects to enjoy seeing", "It was not interested only by looking at the go board". Go is widely known as a board game, and it is considered to be able to interest people by its actual experience. In the VR space provided by this method, it is impossible to experience touching or using cultural items introduced by the great avatar. In addition to providing knowledge by this method, it is considered that users' interest can be stimulated by giving user experience of traditional culture where the interest is easily aroused by experiencing. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the VR space considering the traditional culture where the interest is easily stimulated by the experience.
6.2. Discussion on Behavior in which Interest Appears
From the experimental results, it was impossible to distinguish the user's interest targets based on the presence or absence of browsing detailed information and the usage count of rewind function. In this subsection, we consider the reason why it was not able to distinguish users' interests based on each of the functions, and the effective behavior in which the users' interest appear.First, we discuss the function of browsing detailed information. The reasons why the subjects whose interest were stimulated by the introduction of traditional culture browsed detailed information are clear. However, despite the fact that the value of interest has not increased, there were many subjects who viewed the detailed information. Through the interview after the experiment, there were many opinions that these subjects viewed the detailed information as “I thought the topic that will stimulate interest might be in the detailed information. So, I have browsed the detailed information”. Many subjects requested detailed information to find interesting topics. Therefore, many subjects browsed detailed information regardless of the change in interest.Only a small number of subjects used the rewind function among the subjects who were interested in the introduced traditional culture. We recorded the situation in which the subjects use the tools with video. As a feature of the subjects whose interest was aroused from the movie, many of such the subjects looked at the great avatar and had little movement of hands and bodies. This indicates that the subjects were attracted to the topic the great avatar speaks, and were focused. Interested users try not to miss the topics to be introduced. Because they will not miss it, they can fully understand the topics introduced without using the rewind function. As a result, few subjects used the rewind function.From the above, it was impossible to distinguish the user's interest targets based on the presence or absence of browsing detailed information and the usage count of rewind function. On the other hand, it is considered that interested target can be distinguished using gazed objects and movement of hands and bodies as behavior in which interest appears.
6.3. Discussion on the Usefulness of the Great Avatar
Based on the interview, we consider the factors that stimulated interest by the great avatar. In the interview, we investigated the subjects' opinions when experiencing the great avatar version for the subjects who answered that the interest increased in the questionnaire. As a result, there were many opinions that "I felt like I was talking with the great avatar", "It was easy to concentrate on talking because I could narrow the focus of the eye to one great avatar". The subjects who recognized the introduction of traditional culture by the great avatar as 1 on 1 dialogue seems to actively try to understand the contents. Compared with knowledge transmission for ubiquitous classes such as lecture-based teaching, knowledge transmission in 1 on 1 is not established without understanding by the listener. Therefore, It is considered that the user whose interest was stimulated by trying to positively understand the contents that the great avatar speaks in order to establish a 1 on 1 dialogue.Also, in the case of audio guide version, since there is no speaker, the user focuses on understanding the contents with only hearing sense. In the case of the great avatar version, it is easier to understand the contents compared to the audio guide version because the word that the great avatar speaks is easy to interpret by the lip-sync function. By feeling that the contents are easy to understand, it is considered that the user easily deepened knowledge about traditional culture and their interest was easily stimulated.From the above, it can be said that the great avatar is useful for stimulating user's interest by providing knowledge of traditional culture. It is considered that adding more vigorous interaction function such as avatar responds to the question that the user threw will bring more stimulated interest.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we have proposed a method to make young people interested in traditional culture by using VR technologies. The method stimulates VR user's interest by using a guide avatar in the VR space to provide background knowledge of Japanese culture. The guide avatar introduces historical backgrounds of traditional crafts scattered in the VR space to users. The guide avatar is a famous historical figure. The topic that the guide avatar introduces to users is the events related to both him and the traditional crafts. Furthermore, in this study, we utilize the story marketing method, in which avatar tells the reason why the traditional crafts have attracted as an explanation of the events. Utilizing the story marketing, the avatar explains the knowledge for understanding the appeal of traditional culture to users, thereby stimulating the user's interest. As a result of examining the usefulness of the method, in the four kinds of traditional culture introduced by the guide avatar, the proposed method was able to encourage the subject's interest in the traditional culture. This experiment also demonstrated that the proposed method can evoke the subjects’ interest in the traditional culture more strongly, compared with existing methods. On the other hand, the method was impossible to identify user's interest targets from usage frequency of the detailed information browsing and the rewinding. In future works, we aim that interested target can be distinguished using gaze objects and movement of hands and bodies as behavior in which interest appears.
References
| [1] | Japan National Tourism Organization. Number of foreign visitors to Japan (total number).: https://www.jnto.go.jp/jpn/statistics/since2003_tourists.pdf, last accessed 2017/11/30. |
| [2] | Hidenori Ukai.: Temple disappearance. Nikkei Business Publications, (2015). |
| [3] | METI Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.: Report of the community activation study group using cool Japan resources for tourism, http://www.meti.go.jp/press/2015/06/20150630005/20150630005a.pdf, (2015). |
| [4] | Jerome Bruner.: Making stories: law, literature, life. Harvard University Press, (2002). |
| [5] | TOPPAN PRINTING CO., LTD.: Street Museum (Locationed VR), https://0x9.me/eiW93. |
| [6] | Alan Cheng, Lei Yang, Erik Anderson.: Teaching language and culture with a virtual reality game. CHI’17 Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Pages 541-549 (2017). |
| [7] | Suzanne Beer.: Virtual Museums: an innovative kind of museum survey. VRIC '15 Proceedings of the 2015 Virtual Reality International Conference, Article No. 19 (2015). |
| [8] | Oculus VR.: https://www.oculus.com/rift last accessed 2017/11/30. |
| [9] | Leigh Ellen Potter, Lewis Carter, Alexandra Coghlan.: Virtual reality and nature based tourism: an opportunity for operators and visitors. CHI '16 Proceedings of the 28th Australian Conference on Computer-Human Interaction, Pages 652-654 (2016). |
| [10] | Daniel Guttentag.: Virtual reality: applications and implications for tourism. Tourism Management, Vol.31, No.5, Pages 637-651 (2010). |
| [11] | Dylan Ebert, Sanika Gupta, Fillia Makedon.: Ogma: A virtual reality language acquisition system. PETRA '16 Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Pervasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Article No. 66 (2016). |
| [12] | Bernadette Flynn.: Augmented visualisation: designing experience for an interpretative cultural heritage. IV’08 Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Information Visualisation, Pages 447-452 (2008). |
| [13] | Maria Roussou.: Virtual heritage: from the research lab to the broad public. Proceedings of the VAST Euroconference, Pages 93-101 (2000). |
| [14] | Champion, E.: Augmenting the present with the past. In playing with the past. London: Springer London, Pages 157–176 (2011). |
| [15] | Inception Inc..: Inception: VR & 360 Videos. https://0x9.me/lG6Qu. |
| [16] | Adri Gabriel Sooai, Surya Sumpeno, Mauridhi Hery Purnomo: User perception on 3D stereoscopic cultural heritage ancient collection. CHIuXiD '16 Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference in HCI and UX Indonesia 2016, Pages 112-119 (2016). |
| [17] | Google LLC, https://vr.google.com/earth/, last accessed 2018/1/20. |
| [18] | Ota, Ushikazu and Tadachika Kuwata.: Shintyoko-ki. Shin Jimbutsu Ōraisha (1997). |
| [19] | Hunt, J. McV.: Motivation inherent in information processing and action. In O.J. Harvey (Ed.) Motivation and Social Interaction. New York: Ronald Press, Pages35-94, (1963). |

















 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML



