| [1] | Agrawal A, Tratnyek P G. Reduction of nitro aromatic compounds by zero-valent iron mental. Environ Sci Technol, (1996), 30(1): 153-160. |
| [2] | Agrawal, A. and Tratnyek, P. G. Reduction of nitro aromatic compounds by zero-valent iron metal. Environmental Science & Technology. (1996), 30, 153-160. |
| [3] | Belkhadem F., Maldonado A., Siebenhaar B., Clacens J.M., Perez Zurita M.J., Bengueddach A., Figueras F. Micro calorimetric measurement of the acid properties of pillared clay prepared by competitive cation exchange, Appl. Clay Sci. (2008) 39: 28–37. |
| [4] | Bigg T, Judd S J. Kinetics of reductive degradation of azo dye by zero-valent iron. Process Saf Environ, (2001), 79(B5): 297-303. |
| [5] | Brown MA, DE VITO SC. Predicting azo dye toxicity. Critical Reviews. Environmental Science and Technology, (1993), 23/3: 249-324. |
| [6] | Cao J, Wei L, Huang Q, Han S. Reducing degradation of azo dyes by zero- valent iron in aqueous solution. Chemosphere, (1999), 36(3): 565-571. |
| [7] | Carliell CM, Barclay SJ, Naidoo N, Buckley CA, Mulholland DA, Senior E. Microbial decolourisation of a reactive azo dye under anaerobic conditions. Water SA (1995); 21(1): 61-9. |
| [8] | Chang M C, Shu H Y, Yu H H, et al. Reductive decolorization and total organic carbon reduction of the diazo dye CI Acid Black 24 by zero-valent iron powder. J Chem Technol Biot, (2006), 81: 1259–1266. |
| [9] | Chen J, Zhu L. Heterogeneous UV-Fenton catalytic degradation of dyestuff in water with hydroxyl-Fe pillared pillared clay e. Catal Today, (2007), 126: 463–470. |
| [10] | Cheng R, Wang J L, Zhang W X. The research process on degradation of halogenated organic compounds by nano iron. Process Chem, (2006), 18(1): 93-99. |
| [11] | Churchman G.J. Gates W.P., B.K.G. Theng, G. Yuan, Clay and clay minerals for pollution control Handbook of Clay Science, Developments in Clay Science, (2006), vol.1, pp. 625–675. |
| [12] | Dickinson, M.; and Scott, T.B. The application of zero –valent iron nano particles for the remediation of a uranium –contaminated waste effluent. J. Hazard. Mater, (2010), 178, 171-179. |
| [13] | Eykholt G R, Davenport D T. Dechlorination of the hloroacetanilide herbicides alachlor and metolachlor by iron metal. Environ Sci. Technol, (1998), 32(10): 1482-1487. |
| [14] | Fan J, Guo Y, Wang J, et al. Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J Hazard Mater, (2009), 166: 904–910. |
| [15] | Feng J Y, Hu X J, Yue P L, Zhu H Y, Lu G Q. Degradation of Azo-dye Orange II by a photoassited fenton reaction using a novel composite of iron oxide and silicate nanoparticles as a catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res, (2003), 42(10): 2058-2066. |
| [16] | Fiedor J N, Bostick W D, Jarabek R, Farrell J. Understanding the mechanism of uranium removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Environ Sci Technol, (1998), 32(10): 1466-1473. |
| [17] | Hou M, Li F, Liu X, et al. The effect of substituent groups on the reductive degradation of azo dyes by zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater, 145: (2007), 305-314. |
| [18] | Huang C P, Wang H W, Chiu P C. Nitrate reduction by metallic iron. Water Res, (1998), 32(8): 2257-2264. |
| [19] | Khan A A, Husain Q. Decolorization and removal of textile and non-textile dyes from polluted wastewater and dyeing effluent by using potato (Solanum tuberosum) soluble and immobilized polyphenol oxidase. Bioresource Technol, (2007), 98 (5): 1012-1019. |
| [20] | Li J Y, Chen C C, Zhao J C, Zhu H Y, Ding Z. Photo degradation of dye on the pillared clay e impregnated TiO2 under UV irradation. Sci China Ser B-Chem (in Chinese), (2002), 32(3): 268-270. |
| [21] | Li J., Li Y., Lu J. Adsorption of herbicides 2,4-D and acetochlor on inorganic–organic pillared clay e, Appl. Clay Sci. (2009), 46:314–318. |
| [22] | Li J., Li Y., Q. Meng, Removal of nitrate by zero valent iron and pillared pillared clay e, J. Hazard. Mater. (2010), 174:188-193. |
| [23] | Li M Y, Xiong L, Chen Y Y, Zhang N, Zhang Y M, Yin H. Studies on Photo-electro-chemical catalytic degradation of acid scarlet 3R dye. Sci China Ser B-Chem. (in Chinese), (2005), 35 (2): 144-150. |
| [24] | Li Y, Li J, Zhang Y. Mechanism insights into enhanced Cr(VI) removal using nanoscale zero valent iron supported on the pillared pillared clay e by macroscopic and spectroscopic studies. J Hazard Mater (2012); 227–228: 211–8. |
| [25] | Masciangioli T, Zhang W X. Environmental technologies at the nanoscale. Environ Sci Technol, (2003), 37: 102A– 108A. |
| [26] | Mezohegyi G, Kolodkin A, Castro U I, et al. Effective anaerobic decolorization of azo dye acid orange 7 in continuous up-flow packed-bed reactor using biological activated carbon system. Ind Eng Chem Res, (2007), 46: 6788–6792. |
| [27] | Nam S, Tratnyek P G. Reduction of azo dyes with zero-valent iron. Water Res, (2000), 34: 1837–1845. |
| [28] | Noubactep, C.; Care, S.; and Crane, R. 2012. Nanoscale Metallic Iron for Environmental Remediation: Prospects and Limitations, Water Air Soil Pollut. (223): 1363–1382. |
| [29] | Pereira W S, Freire R S. Azo dye degradation by recycled waste zero-valent iron powder. J Brazil Chem Sci, (2006), 17(5): 832-838. |
| [30] | Perey J R, Chiu P C, Huang C P, Cha D K. Zero-valent iron pretreatment for enhancing the biodegradability of azo dyes. Water Environ Res, (2002), 74(3): 221-225. |
| [31] | Perey J R, Chiu P C, Huang C P, et al. Zero-valent iron pretreatment for enhancing the biodegradability of azo dyes. Water Environ Res, 74: (2002), 221-225. |
| [32] | Phenrat, T., N. Saleh, K. Sirk, R.D. Tilton and G.V. Lowry, Aggregation and sedimentation of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions. Environ. Sci. Technol., (2010), 41(1): 284-290. |
| [33] | Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P .Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. (2001), 77: 247-255. |
| [34] | Scott J P, Ollis D F. Integration of chemical and biological oxidation process for water treatment: Review and recommendations. Environ Prog, (1995), 14(2): 88-103 . |
| [35] | Sezer K., H. I., Determination Of Disperse Azo Dyes In Industrial Textile Wastewater. University Of Plovdiv “Paisii Hilendarski“ – Bulgaria Scientific Papers, (2005), Vol. 33, Book 5, Chemistry. |
| [36] | Shu H Y, Chang M C, Yu H H, et al. Reduction of an azo dye Acid Black 24 solution using synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron particles. J Colloid Interface Sci, (2007), 314: 89–97. |
| [37] | Sun,Y. P.; Li, X. Q.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W. X. and Wang, H. P. Characterization of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles, Advances in Colloid and Interface Science (2006), (120): 47–56. |
| [38] | Tan, N. C. G, et al. Biodegradation of Azo Dyes in Co cultures of Anaerobic Granular Sludge with Aerobic Aromatic Amine Degrading Enrichment Cultures. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, (1999), 51.6: 865-71. |
| [39] | Wang, C.B. and Zhang, W.X. Synthesizing Nanoscale Iron Particles for Rapid and Complete Dechlorination of TCE and PCBs, Environ. Sci. Technol. (31): (1997), 2154–2156. |
| [40] | Weber E J. Iron-mediated reductive transformation: Investigation of reaction mechanism. Environ Sci Technol, (1996), 30(2): 716-719. |
| [41] | Zhang W. X. Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview, J. Nanopart. Res., (2003), (5): 323-332. |
| [42] | Zhang Y, Li Y, Li J, Hu L, Zheng X. Enhanced removal of nitrate by a novel composite: nanoscale zero valent iron supported on pillared clay. Chem Eng J (2011); 171:526–31. |
| [43] | Zhang, W. H.; Quan, X.; Wang, J. X.; Zhang, Z. Y. and Chen, S. Rapid and Complete Dechlorination of PCP in Aqueous Solution Using Ni–Fe Nano particles under Assistance of Ultrasound, Chemosphere (2006), (65): 58–64. |
| [44] | Zhang, Z.; Cissoko, N.; Wo, J. and Xu, X. Factors Influencing The Dechlorination of 2, 4-dichlorophenol by Ni–Fe Nano particles in The Presence of Humic Acid, J. Hazard. Mater. (2009), (165): 78–86. |
| [45] | Zhu L., Zhu R. Simultaneous sorption of organic compounds and phosphate to inorganic–organic pillared clay es from water, Sep. Purif. Technol. (2007), 54: 71–76. |
| [46] | Jing, F.; YanHui, G.; JianJi, W.; and Fan, M.H. Rapid decolorization of azo dye methyl orange in aqueous solution by nanoscale zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. (2009), 166, 904-910. |


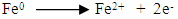
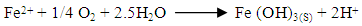

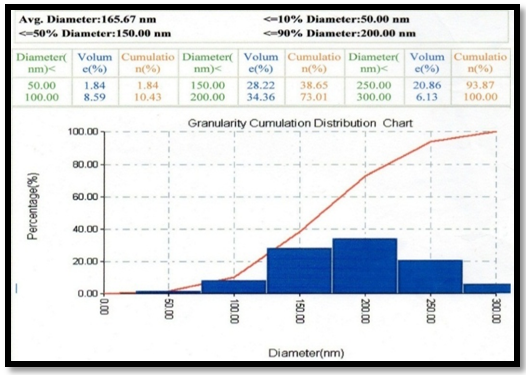
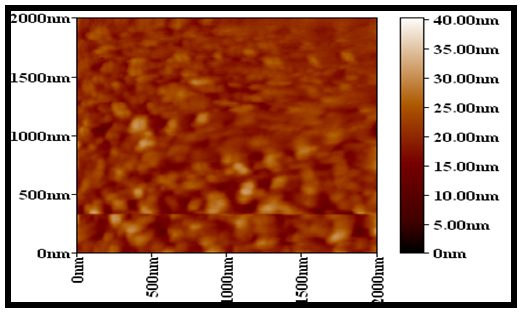

 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML