-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Analytical Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-2839 e-ISSN: 2163-2847
2018; 8(2): 15-21
doi:10.5923/j.aac.20180802.01

Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of V(IV), Ag(I) and Cd(II) Complexes with Mixed Ligands Derived from Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim
Maysoon M. Abdul Hassan1, Adnan H. Abbas1, Eman H. Abed1, Entisar E. Abodi2
1Ministry of Science and Technology, Environment and Water Directorate, Baghdad, Iraq
2Department of Chemistry, College of Education for Pure Science (Ibn El-Haithm), University of Baghdad, Baghdad, Iraq
Correspondence to: Maysoon M. Abdul Hassan, Ministry of Science and Technology, Environment and Water Directorate, Baghdad, Iraq.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

A series of new metal complexes were prepared by mixing 4-amino-N-(5-methylisoxazole-3-yl)-benzene -sulfonamide (L1) as a chelating ligand in the presence of the co-ligand trimethoprim (L2), with Vanadium (V), Cadmium (Cd) and Silver (Ag) ions in alcoholic medium. The complexes were characterized in solid state by using flame atomic absorption, elemental analysis C.H.N.S, FT-IR, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, conductivity and magnetic susceptibility measurements. Tetrahedral geometry was suggested for CdL1L2, AgL1L2 complexes, while VL1L2 complex has a square pyramidal. The ligand L1, with the metal ions, was clearly behaving as a bidentate through O and N atoms of sulfonylamid, while L2 behaves as a bidentate ligand through N and N atoms for all the complexes. Conductivity has shown that all the preparations complexes are ionized, and the nature of bonding between the metal ion and the donor atoms of the ligands was demonstrated by calculating the ligand field parameters by using suitable Tanaba-Sugano diagrams. Biological activity of V(IV), Cd(II), Ag(I), TMP, and SMX, with different concentrations (50, 100, 250, 500, and 1000)ppm, were studied respectively, complexes with chelating ligand and co-ligand were evaluated against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, after incubating for 24hr at 37ºC. Results showed that L1 and L2 enhance effect of (V) against growth of (Staph. aureus and E. coli) with concentration (50, 100, 250, 500, and 1000)ppm, while Ps. aeruginosa was sensitized to (Cd) and (Ag) with concentration more than (250)ppm, after incubated for 24hr at 37ºC. Whereas, the SMX is exposed to a failure in its efficiency against Staph. aureus, Ps. aeruginosa, and E. coli.
Keywords: Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim, Chelating agent, Antibacterial activity
Cite this paper: Maysoon M. Abdul Hassan, Adnan H. Abbas, Eman H. Abed, Entisar E. Abodi, Synthesis, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of V(IV), Ag(I) and Cd(II) Complexes with Mixed Ligands Derived from Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim, Advances in Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 8 No. 2, 2018, pp. 15-21. doi: 10.5923/j.aac.20180802.01.
1. Introduction
- Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) (4-amino-N-(5-methylisoxazol -3-yl)-benzenesulfonamide) belongs to the sulfonamides group of chemotherapeutics, with formula C10H11N3O3S and molecular weight 235.3gm/mol (Fig. 1) (Barragry, 1994), while Trimethoprim (TMP) 5-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxybenzyl) pyrimidin-2,4-diyldiamine, with formula C14H18N4O3 (TMP) and molecular weight 290.3gm/mol (Fig. 2) (Goodman and Gilman, 1980). The medicinal use of SMX is for treatment of tuberculosis, malaria and urinary tract infections (Katzung, 1998), while TMP is a synthetic broad spectrum antibiotic used in treating urinary tract infections, respiratory infections and middle ear infections (Brogden et al., 1982; Bax et al., 2000; Margassery and Bastani, 2002). SMX was inhibited dihydrofolic acid bacterial synthesis by competing with paraaminobenzoic acid, whereas TMP blocks the production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase. The synergistic activity of a combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim against a wide variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria has been well established (Soheilian et al., 2005). The presence of donor atoms (N,S,O) at various positions in sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim molecules enable them to behave as multidentate ligands and thus form chelates of diverse structural types with a wide range of metal ions (Rothova et al., 1993). The chemistry of metal complexes with heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen, sulfur, and /or oxygen as ligand atoms has attracted increasing attention which exhibit enhanced bactericidal, fungicidal, herbicidal, and insecticidal activities in addition to their application as potential drugs (Srivastava, 1989).The research goal to study antibacterial activity of Vanadium, Cadmium and Silver complexes with ligands derived from Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim.
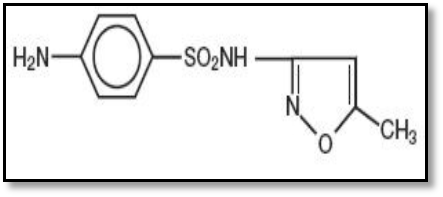 | Figure (1). Structural formula of (SMX) |
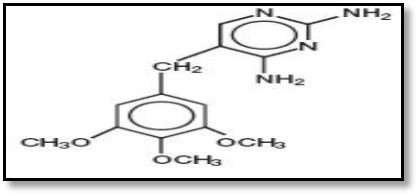 | Figure (2). Structural formula of (TMP) |
2. Experimental
- Physical measurementElemental C.H.N.S analysis were carried out on a EM-017mth instrument, the FT-IR spectra in range (4000-400 cm-1) and (400-200 cm-1) were recorded by using KBr and CsI respectively, discon IR-Prestige-21, Single beam path Laser, Shimadzu Fourier Transform infrared Spectrophotometer, UV-Visible spectra were measured using UV-1650PC Shimadzu, range (200-1100)nm. The magnatic susceptibility values of the complexes were obtained at room temperature using Magnatic Suscceptibility Balance of Johanson mattey catalytic system division, while atomic absorption measurements were obtained by using Shimadzu Atomic Absorption at (680) Flame Spectrophotometer. The conductivity values of the complexes were measured by using 0.001M DMF as a solvent, (WTW) Conductometer. Melting point apparatus of Barnstead Electrothermal BI was used to measure melting points for all the compounds.Materials and methods synthesis of metal complexesAn ethanolic solution of the sulphamethoxazole as a primary (L1)1mmole (0.2533)gm and 1mmole (0.29032)gm of trimethoprim (L2) as a co-ligand, were added slowly, into warm ethanolic solution of metal salts 1mmole [VOSO4.H2O (0.1809gm), AgNO3 (0.16987gm) and Cd(NO3)2.4H2O (0.3084gm)]. The mixture solution was heated and refluxed with stirring for about (2.5-3)hr. The colored precipitates were filtered, washed several times with ethanol and finally ether, and dried using desiccators. The ligands and their metal complexes were characterized by physical and analytical methods such as flame atomic absorption, elemental analysis C.H.N.S, FT-IR, UV-Vis Spectroscopy, conductivity and magnetic susceptibility measurements.Antimicrobial assayThe antimicrobial activity of the ligands and synthesized complexes were studied using the agar diffusion technique. The surface of Moller-Hinton agar in a petri dish (90mm diameter) was uniformly inoculated via spreading 100μl of bacterial suspension (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli) (24hr old), with concentration (1×109) cells/ml, approximately (Macfarland solution). Then 0.1 ml of each concentration (50, 100, 250, 500 and 1000)ppm of (L1), (L2), and complexes with metals (V), (Cd), and (Ag) preparing by DMSO were submerged into the wells (5mm diameter), the plates were leaved for 30min before incubation at 37°C for 24hr, then inhibitory zone (mm) were measured indicating to antibacterial activity.
3. Results and Discussion
- ChemistryStable complexes were isolated in all cases based on the metal analysis, spectroscopic data, molar conductance and magnetic susceptibility studies. The general formula of the complexes can be depicted as:[VOL1L2]SO4. H2O,[AgL1L2](NO3). H2O and [CdL1L2] (NO3)2. H2O.The analytical data together with some physical properties of the complexes are summarized in (Table 1).
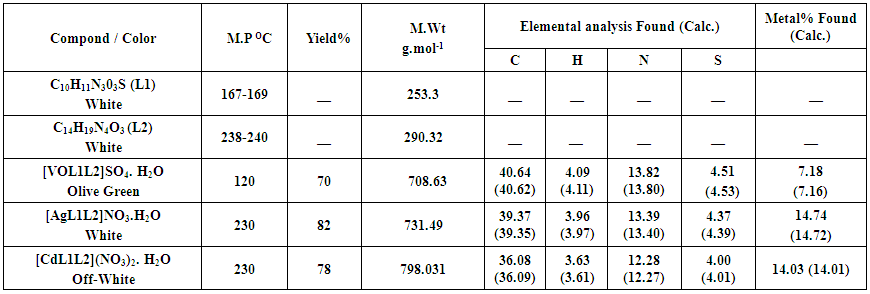 | Table (1). Some analytical and physical data of primary ligand (L1) with co-ligand (L2) and their metal complexes |
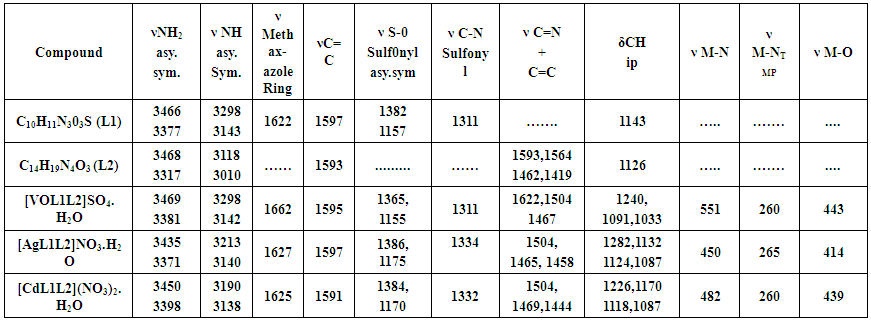 | Table (2). The most diagnostic FTIR bands of the mixed ligand SMX as primary ligand (L1) and TMP as co-ligand (L2) and their metal complexes in (cm-1) |
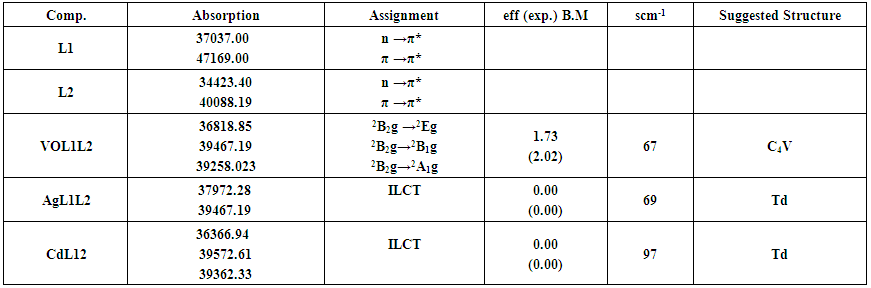 | Table (3). Electronic spectra, conductance in DMF solvent and magnetic moment (B.M) for the prepared ligand L1, co-ligand L2 and their metal complexes |
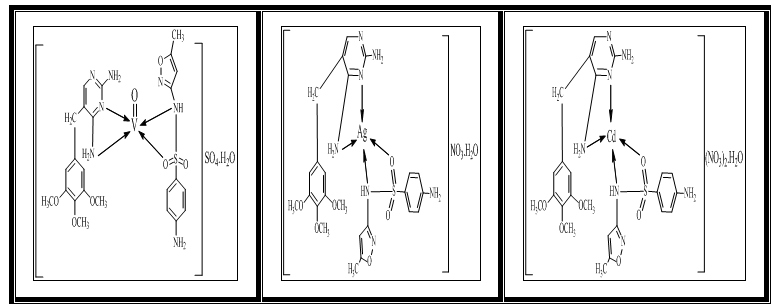 | Figure (3). Suggested structure of the prepared complexes |
4. Antimicrobial Activity
- Antibacterial activity of ligands and there metal complexes vanadium, cadmium, and silver, complexes have been tested by disc diffusion technique. The various gram positive bacteria (Staph. aureus) and gram negative bacteria (Escherichia coli and Ps. aeruginosa), were used for antimicrobial activity. Inhibition zone (mm) were measured after incubating for 24hr at 37°C. Results showed that (SMX) is exposed to a failure in its efficiency against Staph. aureus, Ps. aeruginosa, and E. coli (Fig. 4).
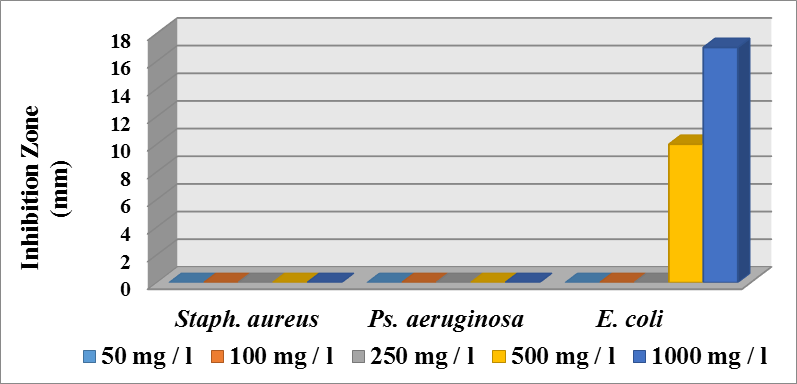 | Figure (4). Effect different concentration of SMX on the various genus of bacteria |
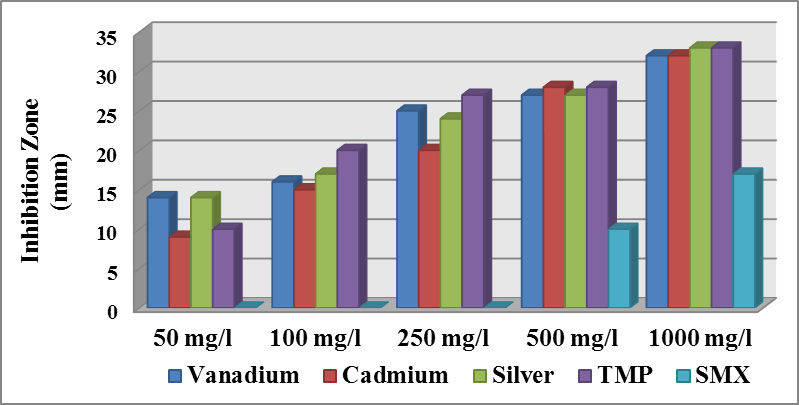 | Figure (5). Effect different concentration of materials on the growth of Staph. aureus |
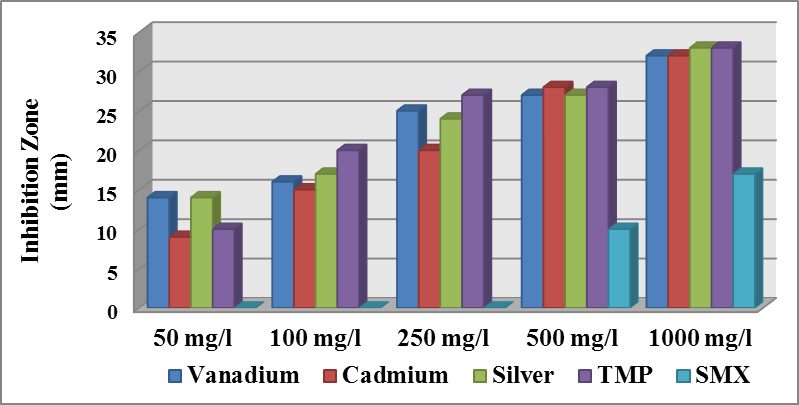 | Figure (6). Effect different concentration of materials on the growth of E. coli |
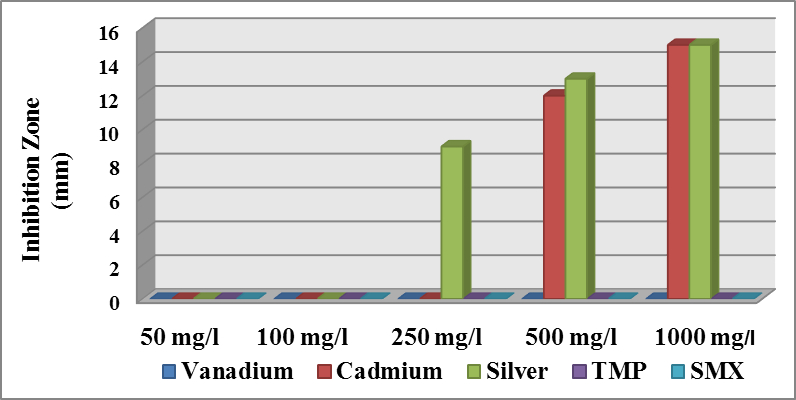 | Figure (7). Effect different concentration of materials on the growth of Ps. aeruginosa |
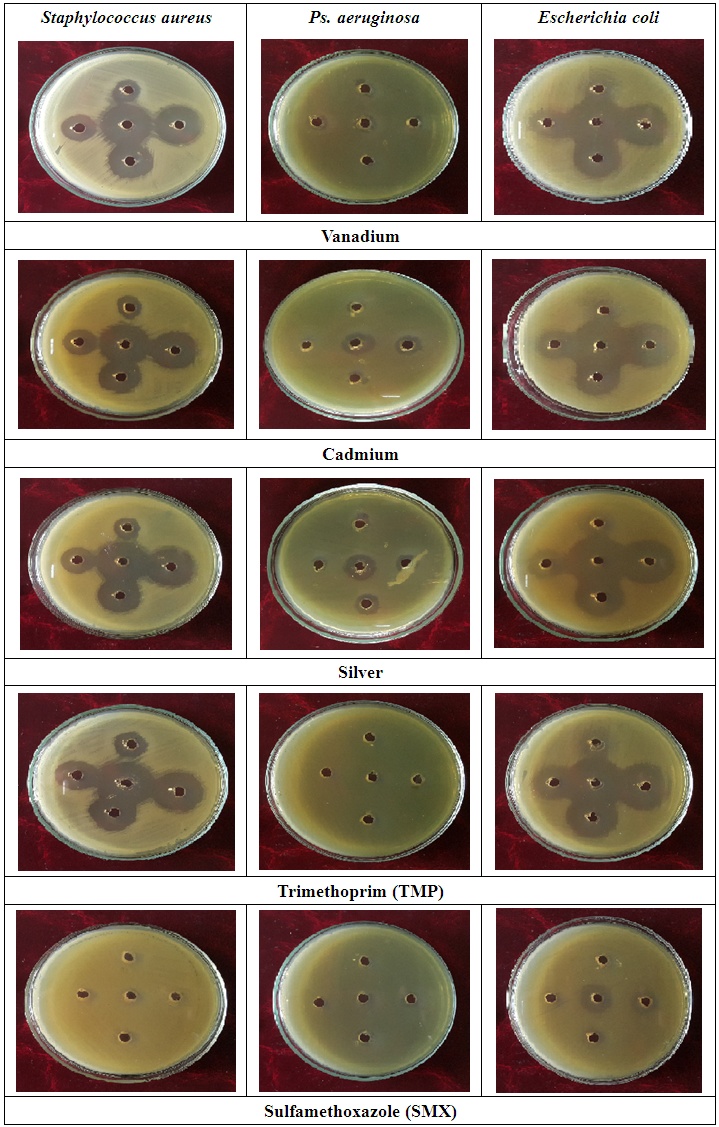 | Figure (8). Inhibition zone (mm) of metal ions complexes with (L1) and (L2) against bacteria |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML