-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Advances in Analytical Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2163-2839 e-ISSN: 2163-2847
2014; 4(1): 9-12
doi:10.5923/j.aac.20140401.02
Determination of Flouride Ions in Resource and Mineral Waters of the Van Region by Using Ion-Selective Electrode Method
1Karamanoğlu Mehmetbey University, Department of Chemistry, Science Faculty, Karaman
2Batman Üniversity, Department of Chemistry, Art and Science Faculty, Batman
Correspondence to: Fevzi Kiliçel, Karamanoğlu Mehmetbey University, Department of Chemistry, Science Faculty, Karaman.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Factors that have a significant negative effect of ecological research on species alive, especially human beings are very important. A most important danger for environment is called pollution that threaten human beings and nature since it is seen at the start of the second half of the twentieth century, due to technological development and a great increasing the population. As a result, toxic wastes accumulate continuously in the rivers, lakes and seas, cross-contamination of water leads to an important extent. Some of the water and soil with toxic and carcinogenic elements, concentrations exceed certain forms of pollution. Toxic and carcinogenic elements in waters and soils in any region, whether or not pollution, with research is exposed. With different ways some elements (Pb, Ni, Cd, As and Bi) reach to organisms, the body exhibit a direct toxic effect. Even though some of the elements (Cu, Mn, Zn, Co and Se, etc.) are the nutrients, increasing concentrations of these substances show a toxic effect [1]. The amount of fluoride in water is 1.0 mg/L as useful, as it is expressed on the concentrations of toxic and carcinogenic [2]. Because of the importance mentioned above, the source and the mineral waters of the Van region, the water samples were collected from 30 centers in 4 seasons. After some preparatory phase for the measurement of fluoride ion, the water samples were prepared. Examples were analyzed with ion-selective electrode method [3]. The values were compared with the standard values. The values in the samples vary according to the collection centers. Generally, the values are in the range of standard values. Fluoride in 2 samples taken from the centers of 9 and 17 has been found to exceed the standard.
Keywords: Water Pollution, Determination of Fluoride, Ion-Selective Electrode
Cite this paper: Fevzi Kiliçel, Beşir Dağ, Determination of Flouride Ions in Resource and Mineral Waters of the Van Region by Using Ion-Selective Electrode Method, Advances in Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 4 No. 1, 2014, pp. 9-12. doi: 10.5923/j.aac.20140401.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Fluor is very reactive element and because of that it easily binds to the other elements. Fluoride (F-) is an important anion, present in water, air and food. Fluorides come naturally into water by dissolving minerals that contain fluor, such as fluorite (CaF2), cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorapatite (Ca5(PO4)3F). Fluoride is found more frequently in different sources of water but with higher concentrations in groundwater due to the presence of fluoride-bearing minerals. Average fluoride concentrations in seawater are approximately 1.3 mg/L. Water is vitally important to every aspects of our lives. Water is a risk because of possible input and transmission of infectious pathogens and parasitic diseases. We use clean water to drink, grow crops for food and operate factories. The most commen pollutants in water are chemicals (pesticides, phenols, heavy metals and bacteria) [4].Fluoride is found in several minerals such as apatite, and mica. Fluoride is an essential element for the formation of healthy tooth enamel. For this purpose, fluoride-free drinking water in some of the city 1.5-2.5 mg/L fluoride will need to participate. However, fluoride is harmful is something more. Fluoride concentration of 5 mg/L can cause tooth decay more than the case. And use of fluoride in drinking water at 1.5 mg/L limit was put into the value. Fluoride in the water, but it cleared up with the anion holders. Fluoride in soil is in the form of both elements and minerals. Terms of volume, average 0.3 g/kg as the most common minerals in the fluoride Florist and Fluorspar. Naturally, the soils in the 30-300 ppm level fluoride generally reported to be harmless to plants and animals. 950 ppm of fluorine, the Earth's crust, sea water is around a 1.3 ppm [5]. Stagnant water, lake, river and spring waters have the different concentrations of fluoride ion. 1-25 mg/L of underground waters, in freshwater and 0.01-0.3 mg/L level of fluoride in sea water, these values are found to 0.8-1.4 ppm, 0.5 ppm in the lake and river waters, the concentration of fluoride in drinking water should have found to be in the range 0.8-1.7 mg/L. Fluoridated drinking water containing 0.8 ppm of fluoride needed is defined [6]. In a 10 years period, a study conducted in 1989, in Newburn fluorinated dental caries in children who use drinking water has been demonstrated for a reduction in the rate of 20-35%. Fluorinated is done in different ways. These are direct fluorinated of water, the use of NaF tablets, fluoridated milk and milk powder, cooking salt, fluoridated, fluoride drops and the use of gels, fluoride varnish, and pastries is a direct application of tooth.
2. Materials and Methods
- Water samples were collected from 30 different centers, 4 seasons of the year and received by the public of the alleged source and the mineral waters of different properties of material.The studied water samples were taken from different locations in Van Region (such as city central, villages and townships) can be divided into 2 groups: resource waters and mineral waters. When necessary, water samples (1.0 L) were filtered through a blue band filtered paper to separate insoluble materials and 5 ml % 65 HNO3 were added in each sample. Water samples were collected at the middle of every season and fluoride ion concentrations were measured in the same season using ion-selective electrode method.
2.1. Ion-Selective Electrode Method
- While determining the fluoride ion with selective electrode method, in principle, the solution inside the cell in the crystal of lanthanum fluoride forming a potential with fluoride ion. Fluoride ion activity, the solution depends on the total ionic strength and pH. Providing a suitable buffer medium, fluoride, and pH by sequestering agents provides a force on the uniform sets. The force is breaking previously formed complexes. Then the concentration is measured with fluoride ion-selective electrode, especially multivalent cat ions such as aluminum and iron complexes. Shape, solution pH, amount of fluoride ion and metal depends on the kinds of complex constructive. To avoid complex formation, CDTA (cyclohexylene diamine tetra acetic acid) is used. The constructive interference of complex forming cations frees fluoride ions [3]. The use of ion-selective electrodes enables the determination of very low concentrations of desired ions (to 10-6 mol/L). The amount of fluoride present naturally in non-fluoridated drinking water is highly variable, being dependent upon the individual geological environment from which the water is obtained. It is well known that fluoridation of drinking water is an important tool in the prevention of tooth decay. Adequate fluoride ingestion is helpful to avoid caries, but over ingestion induces dental and skeletal fluorosis, wich may result in malfunction of the bone and joint system [7, 8].Analysis were carried out using a ORION BENCHTOP pH/ISE METER 720 A Model pH Meter and ORION 96-09 BN COMBİNE FLUORIDE ELECTRODE as an ion-selective electrode. In Figure 1, the connection of fluoride ions activity or concentration in aqueous solutions and electrode potential is shown. Activity of fluoride ions in the solution of this electrode is measured directly. This electrode is for the analysis of waters, the amount of fluoride, fluoride complexes in solution of an examination of the metabolism of fluoride in the study of plants and animals. This electrot is used no longer controlling the amount of fluoride in waters. This electrode in titrations to determine the equivalence point (or the solution is titrated, to determine the amount of solution) is available.The only difficulty for fluoride ion electrode is the presence of OH- ions. This is resolved by keeping the pH of a solution close to neutral.
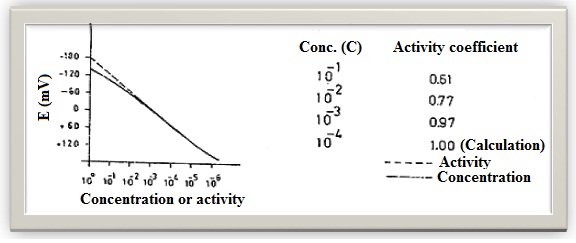 | Figure 1. Fluoride ion electrode |
3. Results
- Fluoride ion concentrations were measured by ion-selective electrode method in Table 1 and in Figure 2, in Figure 3 are given.
|
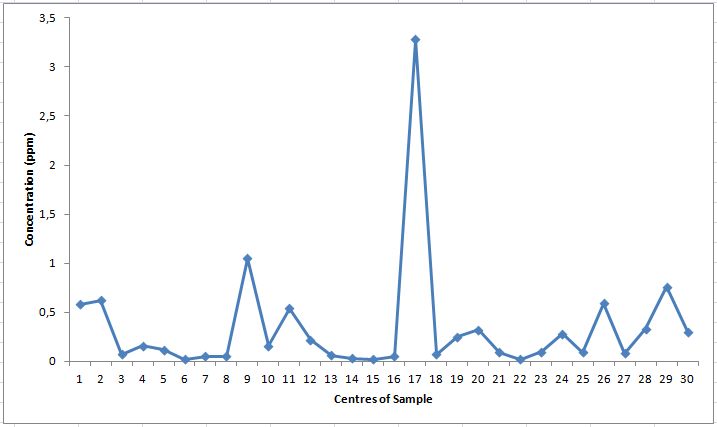 | Figure 2. Resource and mineral waters of the Van region received 30 different point mean fluoride ion concentration (ppm) |
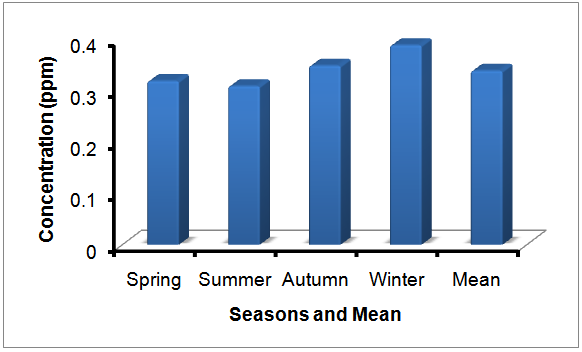 | Figure 3. Resource and mineral waters of the Van region received 30 different point according to seasons and mean fluoride ion concentration (ppm) |
4. Discussion and Conclusions
- Primary drinking water standards are those that must be enforced. Secondary drinking water standards are non-enforceable guidelines regulating contaminants that may cause cosmetic effects (such as skin or toorh discoloration) or aesthetic effects (such as as taste, odour or colour) in drinking water [9]. The WHO maximum guideline value of 1.5 is higher then the recommended value for artificial fluoridation of water supplies, which is usually 0.5-1.0 mg/L [10]. Electroanalytical methods based on potentiometry with ion-selective electrode seem to be the most popular and convenient methods of fluoride ion determination. Fluoride selective electrode can be used to determine fluoride concentration in resource and mineral water due to its high selectivity, specificity and low detection limit. The advantages of this study include a short analysis time, elimination of sample pretreatment, simplicity of the measuring system and relatively low instrument cost. The concentration of fluoride ion was determined in 30 resource and mineral water samples. Some samples that could not be read in the observed values are very low. Sample No. 17, Van-House Kapıköy thermal water fluoride concentration was found to be over 5 times of the normal value. Other centers had been identified in general terms water is poor in terms of the concentration of fluoride ion in the water below 0.7 ppm would be appropriate to giving fluorine with this method should be considered in the tablets. The concentration of fluoride ion in 29 samples is within allowed concentration according to World Health Organisation (WHO) [8]. Our experimental data give evidence that the concentration in these samples are within the allowed concentration according to World Health Organisation except the concentration of fluoride in sample 17. Therefore, determining of fluoride ion in water samples is of great significance for human healt because of daily consumption in certain amounts.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML