-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2016; 6(1A): 71-76
doi:10.5923/c.nn.201601.14

Photovoltaic Performance of (Al, Mg)-Doped CuCrO2 for p-type Dye-sensitized Solar Cells Application
Ursu Daniel 1, 2, Bănica Radu 1, 2, Vaszilcsin Nicolae 1
1Politehnica University Timisoara, Timisoara, Romania
2National Institute for Research and Development in Electrochemistry and Condensed Matter, Timisoara, Romania
Correspondence to: Vaszilcsin Nicolae , Politehnica University Timisoara, Timisoara, Romania.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Delafossite materials like CuCrO2 are promising p-type semiconductor materials for elaboration of future tandem dye sensitized solar cells. In this paper, we report the successful hydrothermal synthesis of Mg2+ and Al3+ doping nanocrystalline CuCrO2 with very small size and a high surface area of 107 m2/g for CuCrO2, 110 m2/g for CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and 122 m2/g for CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2. The specific surface area of our CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 nanocrystalline is the biggest ever reported compared with other materials with delafossite structure used for dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) applications. We show that after Al3+ and Mg2+ doping, the optical bandgap is shifted with 0.05 eV for Al3+ doping and 0.27 eV for Mg2+ doping. From Mott–Schottky plot the acceptor density is NA= 1.10 × 1021 cm−3 for undoped sample, NA= 1.22 × 1021 cm−3 for Al3+ doped and NA= 1.56 × 1021 cm−3 for Mg2+ doped. The performance of p-type DSSCs based on CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 photocathodes was made using two type of dye: Coumarin C343 and Ruthenium N719. Using Coumarin C343 as dye the short-circuit density (Jsc) is notable increased by approximately 11% for Al3+ doping and 16% for Mg2+ doping.
Keywords: Delafossite, Dye sensitized solar cell, Nanotechnology
Cite this paper: Ursu Daniel , Bănica Radu , Vaszilcsin Nicolae , Photovoltaic Performance of (Al, Mg)-Doped CuCrO2 for p-type Dye-sensitized Solar Cells Application, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 6 No. 1A, 2016, pp. 71-76. doi: 10.5923/c.nn.201601.14.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- One of the challenging problems confronting mankind in the last decade is due to the energy crisis [1]. This is confirmed in according to the International Energy Outlook 2011, where the total world energy consumption will increase with 53% before 2035, driven not only by the economic growth but also by increasing population in developing countries [2]. According to Grätzel, the energy provided by the sun is approximately 10,000 times more than the global demand (i.e., 3 x 1024 J/year). Thereby, the sun provides a considerable amount of energy for our planet. If it covering 0.1% of the earth's surface with solar cells that have an efficiency of 10% would fulfill our present needs [3]. Until now the photovoltaic cells are commonly classified as first-, second-, and third- generation devices depending on the underlying technology. First-generation wafer technology is identified by high production costs and has an average efficiency of 20%. Second generation thin film technology offers lower production costs and moderate efficiency (presently 5±10%) [4]. The third generation is dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) which present themselves as a very promising photovoltaic technology. They are made of cheap components that are non-toxic and world-wide available and offer distinctive features such a semi-transparency, multi-color range possibilities, flexibility and light weight applications but also good performance under low light conditions and different solar incident angles [5]. Until now, all the reported regarding at high performance of DSSCs is based on dye-sensitized n-type nanocrystalline semiconductors, such as TiO2, ZnO, etc. [6], and are known as n-DSSCs. The highest efficiency of n-DSSCs is 12% by introducing a porphyrin dye with broad light harvesting range [7], and more recently 13% [8]. Therefore, are few studies that are focused on p-type semiconductor based DSSCs, and the reported efficiencies were much lower than those of their n-type counter parts. According to the literature NiO has been the most frequently reported p-type photocathode material in the past [9, 10]. Thereby, major efforts are made to find new nanostructurated p-DSSCs to favor higher open-circuit voltage (VOC), short-circuit current (JSC), and fill factor (FF) [11]. In order to improve these parameters, the photocathode for p-type DSSC should be required to have some special features: wide band gap, large surface area, high surface chemical affinity, suitable valence band potential and suitably high hole mobility. In addition to these parameters, an important step in the fabrication of DSSCs is to enhance the electron transport and reduce the interfacial charge recombination in photocatodes [12]. Cu (I)-based delafossite compounds, CuMO2 (M= Al, Ga or Cr) are shown very promising performances in p-DSSCs because of their intrinsic advantages over NiO such as: high hole conductivity (10-2 - 102 S cm-1), wide band gaps (3.0-3.6 eV) and decent optical transparency (50-80%) [13-18]. One of the disadvantages of the CuCrO2 compound is a color, compared to CuAlO2 and CuGaO2, which are colorless and have full d-orbitals of M site elements, therefore they are more advantageous for p-type DSSCs applications. It is very hard to synthesize nanocrystalline CuAlO2 or CuGaO2 with small enough sizes that still remains a great challenge [19]. To increase the efficiency of CuCrO2 nanocrystals based p-DSSCs can choose to decrease particle size which leads to a higher adsorption of dye on their surface, and by increasing the conductivity due to doping to favor the flow of injected charges (and to limit consequently the electron−hole recombination). Up to now the highest photoconversion efficiency for CuCrO2is 0.132 % if using 4-(Bis-{4-[5-(2,2-dicyano-vinyl)-thiophene-2-yl]-phenyl}-a mino)-benzoic acid (P1) dye under optimized conditions [20]. According to the theory of semiconductors the trivalent ion substitution with divalent cations, such as Mg2+, Mn2+, Ca2+, is considered a direct and effective route for improving p-type conductivity. Even if the substitution with trivalent cations cannot directly increase the hole concentration, this investigating may provide insight into the complex conduction mechanism in this structure. Until now, only a few studies involving trivalent cation doping have been reported and their use as cathodes in dye sensitized solar cell.In this work, we report the effect of Mg2+ and Al3+ doping nanocrystallineCuCrO2 with high surface area and we discuss the impact of the photovoltaic performances with two types of dye, Ruthenium-based (N719), and Coumarin C343, using I-/I3- dissolved in acetonitrile as redox couple.
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2
- The hydrothermal synthesis procedure of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 was performed according to our previous work [21], using the following reagents: 1 mmol copper(I) oxide (Cu2O, Sigma-Aldrich, 99%), 0.095 mmol chromium (III) hydroxide (Cr(OH)3 amorphous was precipitate in aqueous media from Cr(SO4)3 • 12H2O in the presence of NaOH, 0.05 mmol aluminum chloride (AlCl3 Sigma-Aldrich, 99%) and magnesium oxide (MgO Sigma-Aldrich, 99%) respectively. Sodium hydroxide has been dissolved in 42 mL deionized water to obtain 2.5 M solution, and stirred for 20 min. Temperature was increased to 250ºC for 60 h. The autoclave was cooled down to room temperature naturally. The precipitate was filtered and washed with deionized water and then, the product was dried at 80ºC for 5h. The structure of products was determined by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD) Panalytical X'pert Pro/PW 3040/60 using Cu-Kα radiation with (λ=1.5418Å), in the range 2θ = 10-80°. The morphology of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 nanocrystals was observed using a transmission electron microscope (TEM, Titan G2 80-200). Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis was used to determine the surface area measurements were achieved by using Quantachrome Nova 1200e device in nitrogen at 77 K temperature. First, all the samples were degassed, in vacuum, at room temperature for 4 hours. The diffuse reflectance spectra (DSR) was obtained using a Lambda 950 UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer with 150 mm integrating sphere in the wavelength range of 300–800 nm. All the measurements were performed at room temperature.The electrochemical investigations were performed using a Voltalab potentiostat model PGZ 402, with Volta Master 4 (version 7.09) software. A single compartment three-electrode cell was employed along with a platinum wire as counter electrode and the Ag/AgCl/KCl saturate electrode coupled to a Luggin capillary as reference electrode. Thin film of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 was used as working electrodes (area 0.28 cm2). All potentials were referenced to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE).The Mott–Schottky (MS) plot was recorded by the electrochemical workstation using the ac impedance method. The principle of this method is to measure the impedance at fixed frequency during a potential. The capacitance of the interface was measured in 0.5M KOH aqueous solutions, in the potential range: 0 ÷ 1 V; with a 20 mV potential step; at fixed frequency: 3 kHz and amplitude of ac potential: 20 mV.
2.2. Preparation of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 Films and DSSCs
- CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 paste used for film obtaining was made by adding 200 μL distillated water, 200 μL (1 %) acetic acid in water and 250 μL (1%) Triton - 100 polymer in isopropanol as surfactant into about 50 mg of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 aqueous colloid. This mixture was ultrasonated for 30 minutes in order to disperse the agglomerate particles. After that, the aqueous colloid was heated at 90°C and mixed with a magnetic stirrer. Resulting paste with suitable viscosity was deposited on FTO-coated glass substrates using Doctor Blade (DB) method. For CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 photocathodes fabrication, FTO coated glass was cleaned using an ultrasonic bath in deionized water, acetone and ethanol, each for 15 min successively. After air drying, the films were sintered under air flow at 350°C for 1 hour [22] to burn off the organic binder. After cooling to about 100°C, films were immersed into two type of ethanolic dye solution 0.5 mM Ruthenium N719 dye and 0.5 mM Coumarin C343 dye solution under dark for 48 hour. Catalytic counter electrodes were produced by the thermal decomposition of H2PtCl6 solution on FTO-coated glasses using a hot-wind gun set at 400ºC for 15 minutes. CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 photocathodes were sandwiched together with the platinized counter electrodes using the electrolyte containing 0.5 M LiI/0.1 M I2 dissolved in acetonitrile and its were transferred into the cell. Solar cell performances were recorded on a DMM 7352 Series Digital Multimeter, under AM 1.5G simulated sunlight (100 mW/cm2).
3. Results and Discussions
- XRD patterns forCuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 nanoproducts prepared by using hydrothermal method are shown in figure 1a. All studied samples have a single rhombohedral (R-3m) delafossite structure. All diffraction peaks are consistent with the standard JCPDF card (No. 00-039-0247) of CuCrO2. Impurity phase could not be detected. From XRD patterns using the Scherrer equation can be calculate the average crystal size which indicates that the crystal size decreases with Al3+ and Mg2+ doping from 21 nm to 20 nm and 17 nm respectively. The decrease in the crystal size could be assigned to the stabilizing effect of Al3+ and Mg2+ on the delafossite crystal structure and the corresponding obstruction of the crystal growth by this resistant impurity [23]. The biggest advantages of CuCrO2 nanocrystalls used in DSSCs applications is the ultra small size which leads to a large amount of adsorbed dye on the semiconductor surface and subsequently to a greater amount of light absorbed. The specific surface area (SSA) of Mg2+ and Al3+ doped CuCrO2, determined by the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method, was found to be 107 m2/g for CuCrO2, 110 m2/g for CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and 122 m2/g for CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2. Based on literature data the specific surface area of our CuCr0.95Al0.05O2 and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 nanocrystals is the biggest ever reported compared with other materials with delafossite structure used for DSSCs applications [15, 24]. This high value of surface area is due to the fact that besides nanoparticles with hexagonal shape that is very well defined, there is also a form of long bars morphology which increases the specific surface. Those morphologies can be seen from the transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images (figure 1 b,c and d) where the nanocrystals with hexagonal shape are around 17-20 nm and their thicknesses are around 5 nm, consistent with XRD, and the bars morphology has a length of 20-40 nm.
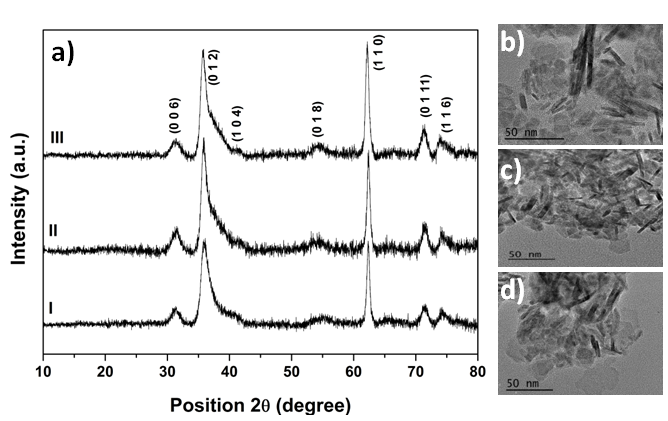 | Figure 1. a) XRD patterns for I) CuCrO2, II) CuCr0.95Al0.05O2, III) CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2, b) TEM image of CuCrO2, c) TEM image of CuCr0.95Al0.05O2, d) TEM image of CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 |
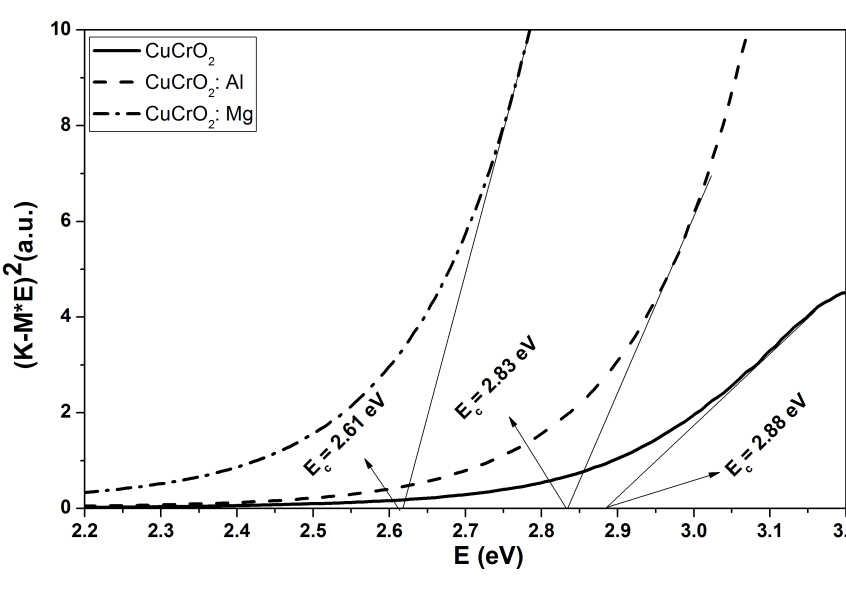 | Figure 2. Extracted direct optical band gaps of CuCrO2, CuCr0.95Al0.05O2, and CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 films |
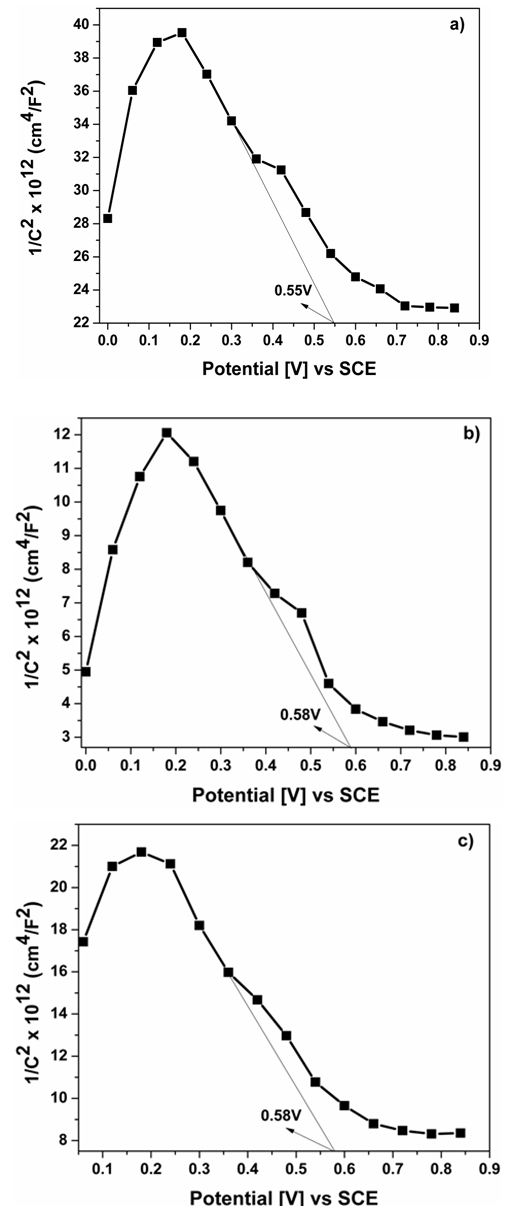 | Figure 3. Mott–Schottky plot for a) CuCrO2, b) CuCr0.95Al0.05O2, c) CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 |
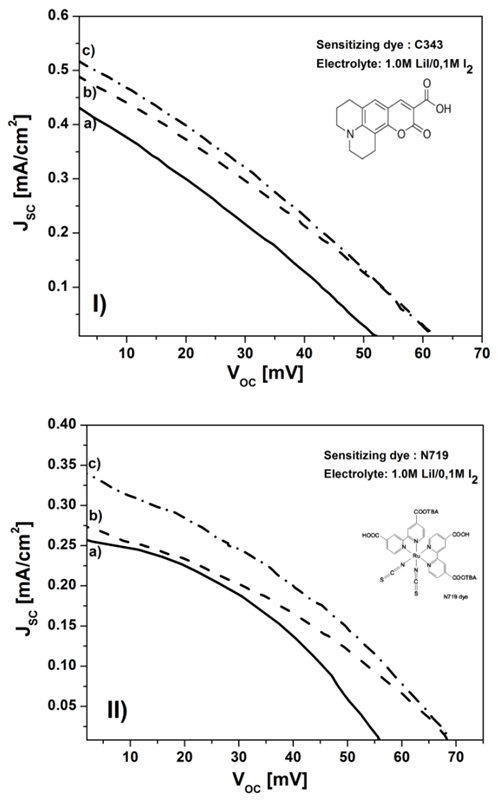 | Figure 4. Photocurent-voltage (J-V) curve of a) CuCrO2, b) CuCr0.95Al0.05O2, c) CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2 based p-type DSSCs using I) C343 dye and II) N719 dye (molecular structure show as insert) |
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, we report the hydrothermally synthesis effect of CuCrO2 doped with Al3+ and Mg2+ with ultrasmall nanocrystals, having high surface area, the highest ever reported for materials with delafossite structure used in DSSCs. The nanosized particles play a crucial role in the enhancement of cathodic current efficiency. Their applications as photocathodes were first demonstrated, using two type of dye:Coumarin C343 and Ruthenium N719, and I-/I3- as redox couple thus being obtained yield conversion efficiencies similar to those commonly reported for NiO. In the case of used Coumarin C343 as dye, the short-circuit density (Jsc) is notable increased from 0.44 mA/cm2 for undoped sample to 0.52 mA/cm2 for CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2. This increase of Isc with 29% for CuCr0.95Mg0.05O2, compared with CuGaO2 [16], is due to the small width of the particle resulting in a high specific surface area.In future investigations, our attention will be focused to further optimize the dye and the redox mediators, to improve the photovoltaic performances of the p-type DSSCs. In addition, we try to increase the VOC using the “surface passivation” with different materials.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This paper is partial supported by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOP HRD), financed from the European Social Fund and by the Romanian Government under the projects numbers POSDRU/159/1.5/S/134378 and POSDRU/159/1.5/S/ 137070 and by a grant of the Romanian Ministry of National Education, CNCS – UEFISCDI, project number PN-II-ID-PCE-2012-4-0398.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML