-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
p-ISSN: 2163-257X e-ISSN: 2163-2588
2016; 6(1A): 18-24
doi:10.5923/c.nn.201601.03

Ionic Substituted Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Prepared by Sponge Replication Technique for Bone Regeneration
1Department of Materials & Metallurgical Engineering, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India
2Dr. S.S. Bhatnagar University Institute of Chemical Engineering & Technology, Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
Correspondence to: Uma Batra , Department of Materials & Metallurgical Engineering, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Porous metallic implants used for replacement in fractures have well-documented fixation problems, and like natural bone, cannot self-repair or adapt to changing physiological conditions. As a consequence, the implant becomes loose over time. Bioactive ceramic alternatives have shown excellent potential in repair and regeneration of bone defects due to their ability to support bone cell growth and form strong bonds to both hard and soft tissues. This work deals with synthesis and characterization of biodegradable scaffolds with nano-hydroxyapatite (HA), zinc substituted nano-hydroxyapatite (ZnHA) and fluorine substituted nano-hydroxyapatite (FHA) particles for bone regeneration. The nanoparticles were synthesized via wet chemical method and scaffolds were fabricated using sponge replication technique. The elemental composition of nanoparticles was determined using XRF. The crystallography and functional groups were evaluated by XRD and FTIR spectroscopy, respectively. TEM images exhibited the as-synthesized nanoparticles size below 50nm. Zinc/fluorine substitution could affect the ratio of HA and β-TCP (β-tricalcium phosphate) phases in scaffolds. SEM images showed the presence of both macroporosity and microporosity in the scaffolds, with total porosity in the range of 65-75%. From the in-vitro study, it was confirmed that the obtained scaffolds were biomimetic, bioactive, and osteoconductive. Other than bone regeneration, the obtained scaffolds can have a wide array of applications, including tissue engineering, filtration, and catalyst support. The use of ionic substituted hydroxyapatite also opens new possibilities in the field of bone regeneration, utilizing the easily tailored bioactivity and biodegradation rates.
Keywords: Hydroxyapatite, Tricalcium phosphate, Scaffolds, Bioactivity, Bone regeneration, In-Vitro
Cite this paper: Uma Batra , Seema Kapoor , Ionic Substituted Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds Prepared by Sponge Replication Technique for Bone Regeneration, Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, Vol. 6 No. 1A, 2016, pp. 18-24. doi: 10.5923/c.nn.201601.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The bone tissue engineering has focused on the use of natural or synthetic materials in the form of scaffolds as conduits to guide new bone growth in vivo (in the body). The success of tissue engineering is highly dependent upon the properties of the scaffold materials. As such there are four desired characteristics for an ideal material used for making scaffold including osteointegration, osteoconduction, osteoinduction, and osteogenesis [1]. The first three characteristics can be achieved in both biological and synthetic materials, but it is the fourth characteristic that is currently only satisfied by apatitic scaffolds. Pore size, pore structure, surface topography, chemical composition and surface energy are other considerations [2]. The success of scaffolds in-vivo relies on their ability to induce surrounding tissue to invade, grow, and replace the implanted material [3]. In this context, various scaffolds such as HA, tricalcium phosphate (TCP), collagen, chitosan, polycaprolactone (PCL), and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA), have been used [4], [5]. Biphasic calcium phosphate consists of a bioactive mixture of HA and β-TCP. An optimum balance of the more stable phase of HA and the more soluble β-TCP in scaffold material helps in gradual dissolution in the body, inducing bone regeneration at the expense of biphasic mixture. Moreover, such materials closely resemble natural bone; therefore, foreign body reactions are avoided and bone cells recognize the material. They can also be produced artificially with relative ease and their composition can be varied to alter the degree of biodegradability or to more accurately mirror the chemical composition of bone mineral. Zinc substitution, for example, has shown significant increase in bioactivity in-vitro and improved bone regeneration both in-vivo and clinically. Porous structures have been shown clinically to allow bone in-growth and to provide genuine solutions for the repair of bone defects. Various modifications such as substitution of desirable ions in apatite, addition of bioactive molecules or nanoparticles can enhance attachment and proliferation of stem cells on the scaffold [6-8]. These scaffolds are more bioactive and responsive to changes in their surrounding environment [9]. Biological apatites attract special interest for the development of scaffolds because of the proven fact that bioactivity of pure HA is inferior to biological apatite. Thus, the substitutions at the Ca2+, PO43- and OH- sites of HA with several trace elements such as Na+ (1.0 wt.%), Zn2+ (39 ppm), Mg2+ (0.60 wt.%), Cl− (0.10 wt.%), and F− (0.10 wt.%) may hold the key to improve the biological performance, without altering the basic crystallographic characteristics of HA [10], [11]. Fluorine substitution improves the stability of HA, thus helps in controlling its dissolution rate in physiological environment. Zinc substituted HA nanoparticles containing 1.6 wt.% Zn have been found to enhance bioactivity to human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and antimicrobial capability [12]. Another research also suggests that Zn substituted HA nanoparticles have antibacterial activity and are non-toxic to osteoprogenitor cells [13]. In the present work, an attempt has been made to create scaffolds from zinc substituted and F substituted HA nanoparticles which will possess a good combination of physico-chemical properties, bioactivity and biodegradation.
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Synthesis of HA, ZnHA and FHA Nanopowders
- HA nanoparticles were synthesized by sol-gel route using calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (CNT, Merck, Germany) and potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP, Merck, Germany). 1.0 M solution of CNT and 0.6 M solution of KDP in deionised water was taken in such amounts that Ca/P molar ratio was maintained at 1.67. CNT was added drop by drop gradually to KDP under vigorous stirring using mechanical stirrer (2500 rpm) for one hour. The pH of the solution was maintained at 10 with addition of ammonia solution. In case of ZnHA nanoparticles, 2% zinc nitrate tetrahydrate (ZNT) was added to CNT. (Ca+Zn)/P molar ratio was maintained at 1.67. In case of FHA, a stoichiometric amount of ammonium fluoride (NH4F, Merck, India) was mixed with KDP solution to maintain P/F ratio at 6 to obtain Ca10(PO4)6OH2–xFx for x=1. Gels were obtained and were aged at room temperature for 24 hours. Gelatinous precipitates formed were filtered by a centrifuge and washed thoroughly by double distilled water. The precipitates were dried in an oven at 70°C for 24 hours and the powders were prepared by crushing them with a mortar and pestle. All powders were calcined at 900°C.
2.2. Preparation of HA, ZnHA and FHA Scaffolds
- For the synthesis of scaffolds, sponge replication method was used, where polymer sponge of 40 ppi, was cut into pieces of about 10x10x10 mm3. For the preparation of ceramic slip, the calcined powders were mixed with water containing polyvinyl alcohol, and the latter was varied from 3-10 wt%. The coating was performed by immersing the sponge pieces in the slurry, squeezing them to expel the excess slip. The calcined nanoparticle content was 50 wt. %. The green body was dried for 24 hours at 80°C and heated at a rate of 3°C/min to 800°C for 3 hours, and then further heating at a rate of 3°C/min to the final temperature i.e. 1250°C, where was held for 3 hours to achieve sintering of the mass.
2.3. Characterization of Scaffolds
- The morphology and size of nanopowders were observed using Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM, Hitachi, 7500) with resolution of 0.2 nm, operated at an accelerating voltage of 80-100 KV. The powders were ultrasonically dispersed in ethanol to form a dilute suspension and then a drop of suspension was dropped on carbon coated copper grid of 300 mesh for observation. The elemental composition of nanoparticles was determined using wavelength dispersive X-ray Fluoresence Spectroscopy (XRF, Make Bruker, Germany).The porosity was evaluated using the Archimedes method. The BET surface area of scaffolds was evaluated by N2 adsorption using Quantachrome Instruments NOVA 2200e Surface Area Analyser using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method [14]. The linearized form of BET equation is expressed by:
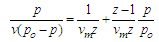 | (1) |
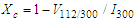 | (2) |
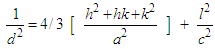 | (3) |
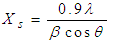 | (4) |
3. Results and Discussion
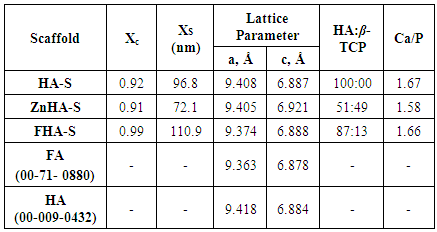
- In Figure 1, TEM micrographs show that HA and ZnHA had flake-like morphology with an average particle size of 34 ± 6 nm and 21 ± 3 nm, respectively; whereas, FHA nanoparticles consisted of rod-like particles having average length as 29 ± 7 nm, and diameter as 4.2± 0.4 nm, respectively. Due to F- incorporation in HA lattice, the morphology changed from flake-like to rod-like.
 | Figure 1. TEM images of HA, ZnHA, and FHA nanoparticles |
 | Figure 2. HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds prepared in present work |
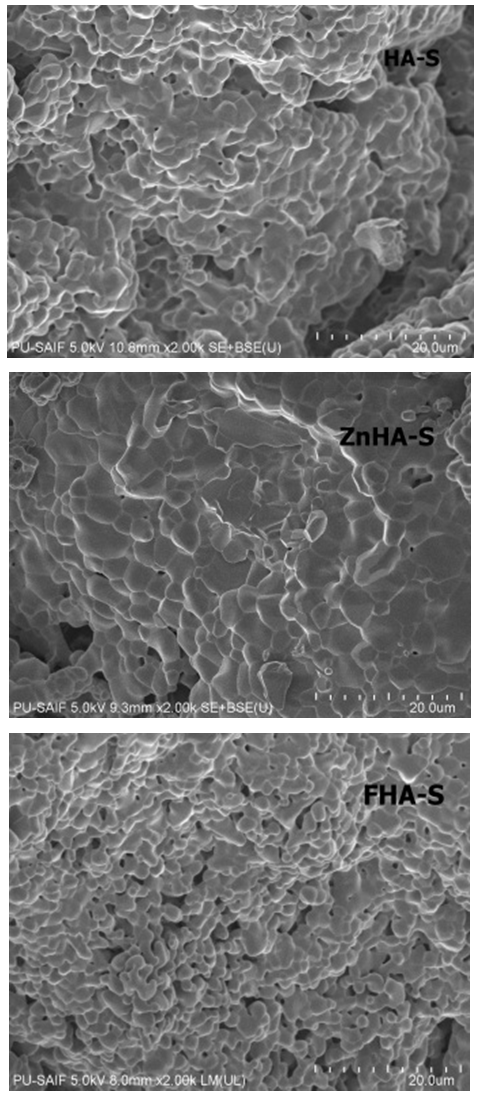 | Figure 3. SEM images of HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds |
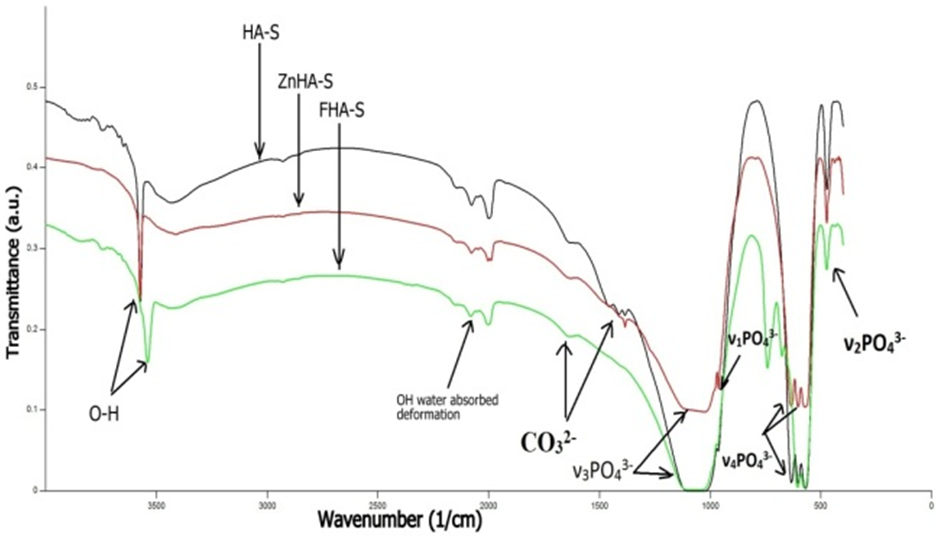 | Figure 4. FTIR spectra of HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds |
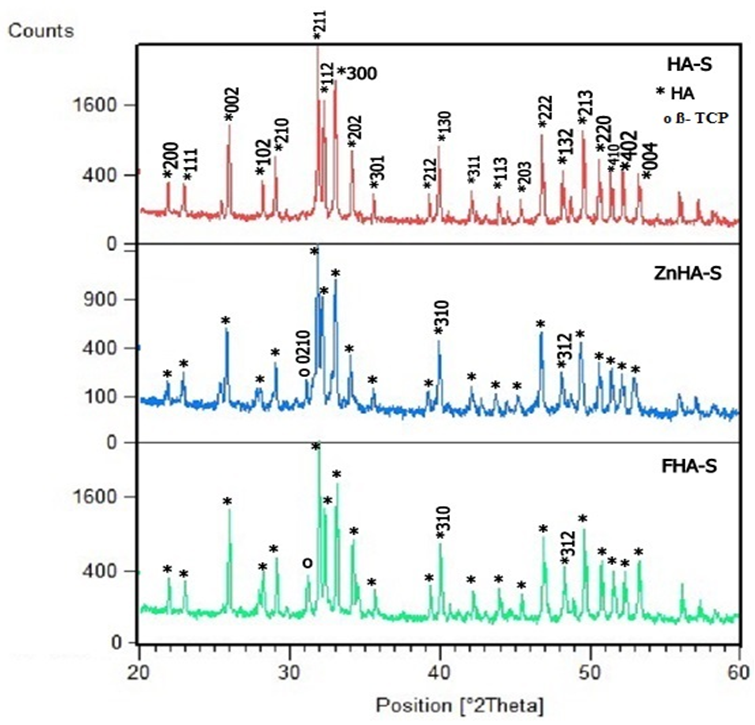 | Figure 5. XRD patterns of HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds |
|
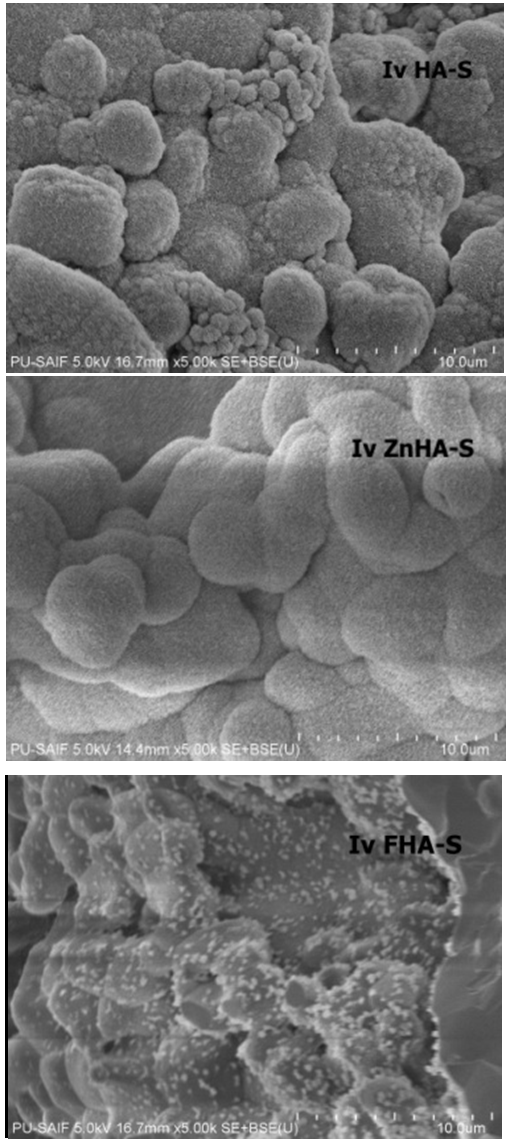 | Figure 6. SEM images of HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds after immersion in SBF for 12days |
 | Figure 7. FTIR spectra of HA-S, ZnHA-S, and FHA-S scaffolds after immersion in SBF for 12 days |
4. Conclusions
- This paper has proposed a new strategy for smart scaffold manufacturing, combining sponge replication technique with ionic substitution in nano-hydroxyapatite particles. The process is easy to carry out and does not require specialized equipments. The scaffolds have porosities of 65-75%. Increase in PVA led to decrease in porosity of the material. The scaffolds had macroporosity in the range of ~100-200μm and the pores were inter-connected. Microporosity was in the range of ~ 1-10μm. An appreciable amount of hydroxyapatite growth on these scaffolds formed when immersed in SBF for 12 days. In case of ZnHA-S apatite, growth was the most uniform. The biphasic mixture of 49% HA and 51% TCP in ZnHA-S appeared to have optimum balance and responsible for controlled resorbability. Thus, it can be concluded that the bone intrusion can possibly be tailored in calcium phosphate based scaffolds by adjustment of amounts of HA (biocompatible phase) and TCP (bioresorbable phase). The obtained scaffolds have the combined features of macroporosity, microporosity, apatite forming ability; therefore can be believed to possess the essential characteristics of a smart scaffold such as biomimicry and osteoinductive/ osteopromotive, bioactivity and osteoconductivity. Thus it can be concluded that the “smart scaffolds” can be created for bone regeneration applications by the proposed integrated approach.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML