-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Materials Science
p-ISSN: 2162-9382 e-ISSN: 2162-8424
2015; 5(3C): 38-42
doi:10.5923/c.materials.201502.08
A Study on Manufacturing Processes and Compressive Properties of Zinc-Aluminium Metal Foams
Sonika Sahu , Mohd. Zahid Ansari
PDPM-Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing (IIITDM) Jabalpur, Khamaria, Jabalpur, India
Correspondence to: Mohd. Zahid Ansari , PDPM-Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing (IIITDM) Jabalpur, Khamaria, Jabalpur, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of this paper is to discuss mechanical properties of different zinc-aluminium alloy foams that can be used as a substitute metal foam in place of aluminium and other low temperature metal alloy foams. ZA alloys have better wear resistance and self lubricating properties than aluminium and therefore can be used in automobile applications. Different fabrication processes that are adopted to manufacture ZA alloy and the compressive stress-strain characteristics of these are discussed. A comparison between energy absorption abilities of ZA12, ZA22 and ZA27 is presented. And, the compressive strength and energy absorption features of ZA22, ZA22/SiCp and ZA22/Al2O3 was compared. It was observed that ZA27 has high energy absorption capacity. And, ZA22 composite foams, i.e. ZA22/SiCp and ZA22/Al2O3, have better compressive strength and energy absorption features.
Keywords: Zinc-Aluminium foam, Stir casting, Relative density, Strain-Rate sensitivity, Energy absorption capacity
Cite this paper: Sonika Sahu , Mohd. Zahid Ansari , A Study on Manufacturing Processes and Compressive Properties of Zinc-Aluminium Metal Foams, American Journal of Materials Science, Vol. 5 No. 3C, 2015, pp. 38-42. doi: 10.5923/c.materials.201502.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Foams belong to a special class of engineering materials called cellular solids that exhibit the unique combination of lightweight and high compressive energy absorption characteristics. Some other forms of cellular solids include honeycomb, wood, cork and sponge. Foams can be open-cell or closed-cell depending on the interconnections between the foam cells. Open-cell foams mostly have strut or beam connections whereas closed-cell foams have membrane or plate connections. Typical cell size of metal foams ranges between one mm and eight mm. Almost any material can be foamed. Foams can be made of metals, polymers, ceramics and glass. Relative density (ρ*/ ρs) is the single most important feature of a cellular solid. It is defined as the ratio of density of the cellular material (ρ*) to the density of the solid material from which the cell walls are made of (ρs). Typical relative density values for polymeric foams vary between 0.05 and 0.2 whereas those for metal foams are generally less than 0.1 [1]. In general, metal foams follow the power law relation between elastic modulus (E) and relative density. And, the relation between elastic modulus and relative density for foams with relative densities less than 0.2 can be approximately given as [1]:
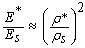 for open-cell, and
for open-cell, and for closed-cell foams while neglecting the internal gas pressure inside closed cells. Metal foams have attracted substantial attention for their simple manufacturing as well as easy composition variation features. These foams are used in construction, transportation and aerospace industry because of their high specific strength, energy absorption capacity, thermal insulation, flame resistance and sound absorption characteristics [1-3, 9-19]. Metal foams are commonly used as the soft core material of a sandwich composite material or the filler material in tubular impact crash energy absorber metal columns. In case of sandwich composite materials, the foams mainly support the shear stress produced during bending loads. In contrast, the foams support the compressive load during the impact loads. Most of the work on metal foam has been focused on usual engineering materials such as aluminium, magnesium and titanium alloys [4-5]. Zinc-Aluminium (ZA) alloy foams are special type of metal foams that have some additional advantages over other metal foams like high wear resistance and lubrication features [9-19]. ZA alloys family comprises ZA12, ZA22 and ZA27 which differ in the percentage of Al content. Several researchers have reported that ZA alloys can be substitute material for bronze, cast iron and Al for use in bearing and bush [6-8]. Among the three classes of ZA alloys, ZA27 posses excellent yield strength, better mechanical properties [6, 8]. Due to its good mechanical properties, researchers are focusing their attentions towards producing ZA foam and characterize its mechanical properties. K. Kitazono et al. [10] observed that strain-rate sensitivity exponent and absorbed energy of the ZA22 foams was much larger than those of the conventional aluminium foams having same density. It should be noted that although zinc alloys have low melting point due to which it is easy to handle and excessive burning of metal hydride is not problematic through melt foaming route. A Daoud [11] produced syntactic ZA12 foam by stir casting method and observed that energy absorption capacity and plateau stress increases with increased strain rate and larger energy absorption capacity than those of conventional foams. In addition, the compressive behaviour of ZA12 syntactic foam showed ductile behaviour and higher strength than ZA12 foam. It was the first attempt of making syntactic foam through liquid metallurgy route. Syntactic foams are composite materials synthesized by filling a metal, polymer, or ceramic matrix with hollow particles called microballoons. The author observed that ZA12 Syntactic foam relative density marginally decreased with increasing in micro balloons volume fraction so increased in micro balloons content were decreased in plateau stress and energy absorption capacity. The presence of hollow particles results in lower density, higher specific strength (strength divided by density), lower coefficient of thermal expansion, and, in some cases, radar or sonar transparency. Mondal et al. [16-18] developed ZA27/SiCp composite foam using CaH2 as a foaming agent by melt foaming method and characterised the mechanical properties at room temperature as well as high temperature and observed that energy absorption capacity and plateau stress follows the power law relation with relative density whereas densification strain follows linear relation with relative density.This paper presents an overview of the different manufacturing processes that are used to produce ZA foams in its normal as well as composite material form. Since these foams are mostly used to support compressive mechanical load and impact energy absorption, these properties of the foams are also discussed. In addition, since relative density of the foam is its single most important physical property, its effect on compressive strength and energy absorption is also presented. Finally, the compressive strength and energy absorption features of different ZA foams are compared.
for closed-cell foams while neglecting the internal gas pressure inside closed cells. Metal foams have attracted substantial attention for their simple manufacturing as well as easy composition variation features. These foams are used in construction, transportation and aerospace industry because of their high specific strength, energy absorption capacity, thermal insulation, flame resistance and sound absorption characteristics [1-3, 9-19]. Metal foams are commonly used as the soft core material of a sandwich composite material or the filler material in tubular impact crash energy absorber metal columns. In case of sandwich composite materials, the foams mainly support the shear stress produced during bending loads. In contrast, the foams support the compressive load during the impact loads. Most of the work on metal foam has been focused on usual engineering materials such as aluminium, magnesium and titanium alloys [4-5]. Zinc-Aluminium (ZA) alloy foams are special type of metal foams that have some additional advantages over other metal foams like high wear resistance and lubrication features [9-19]. ZA alloys family comprises ZA12, ZA22 and ZA27 which differ in the percentage of Al content. Several researchers have reported that ZA alloys can be substitute material for bronze, cast iron and Al for use in bearing and bush [6-8]. Among the three classes of ZA alloys, ZA27 posses excellent yield strength, better mechanical properties [6, 8]. Due to its good mechanical properties, researchers are focusing their attentions towards producing ZA foam and characterize its mechanical properties. K. Kitazono et al. [10] observed that strain-rate sensitivity exponent and absorbed energy of the ZA22 foams was much larger than those of the conventional aluminium foams having same density. It should be noted that although zinc alloys have low melting point due to which it is easy to handle and excessive burning of metal hydride is not problematic through melt foaming route. A Daoud [11] produced syntactic ZA12 foam by stir casting method and observed that energy absorption capacity and plateau stress increases with increased strain rate and larger energy absorption capacity than those of conventional foams. In addition, the compressive behaviour of ZA12 syntactic foam showed ductile behaviour and higher strength than ZA12 foam. It was the first attempt of making syntactic foam through liquid metallurgy route. Syntactic foams are composite materials synthesized by filling a metal, polymer, or ceramic matrix with hollow particles called microballoons. The author observed that ZA12 Syntactic foam relative density marginally decreased with increasing in micro balloons volume fraction so increased in micro balloons content were decreased in plateau stress and energy absorption capacity. The presence of hollow particles results in lower density, higher specific strength (strength divided by density), lower coefficient of thermal expansion, and, in some cases, radar or sonar transparency. Mondal et al. [16-18] developed ZA27/SiCp composite foam using CaH2 as a foaming agent by melt foaming method and characterised the mechanical properties at room temperature as well as high temperature and observed that energy absorption capacity and plateau stress follows the power law relation with relative density whereas densification strain follows linear relation with relative density.This paper presents an overview of the different manufacturing processes that are used to produce ZA foams in its normal as well as composite material form. Since these foams are mostly used to support compressive mechanical load and impact energy absorption, these properties of the foams are also discussed. In addition, since relative density of the foam is its single most important physical property, its effect on compressive strength and energy absorption is also presented. Finally, the compressive strength and energy absorption features of different ZA foams are compared.2. ZA Foam Fabrication Processes
- ZA foams are generally manufactured by molten metal stir casting and using physical or chemical blowing agents to create the voids and cells. Physical blowing agents use an inert gas such as carbon dioxide or nitrogen which is bubbled into the melt by mechanical stirring. In contrast, chemical blowing agents use a chemical like CaCO3 and CaH2 into the melt which generally decomposes on heating to release gas. In addition, powder metallurgy is also sometimes used to make ZA foams. Many manufacturing routes are available in the literature for manufacturing of ZA alloys foam [1-3, 10]. Table 1 summarizes some of the popular routes to manufacture ZA foam.
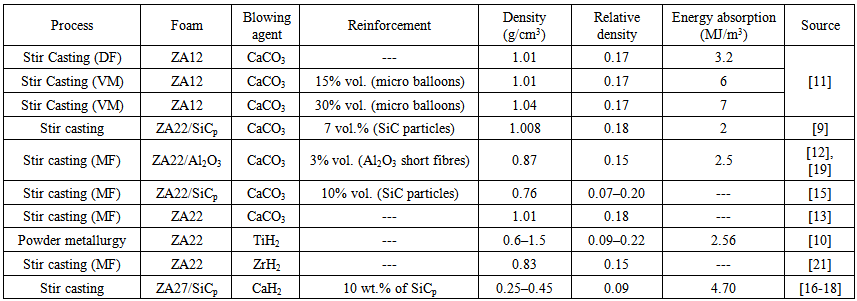 | Table 1. Different manufacturing processes for ZA foams and their properties (DF: Direct foaming, VM: Vortex method and MF: Melt foaming) |
 | Figure 1. ZA foam cubical sample [18] |
3. Structural Behaviour of ZA Foams
- In most of the structural applications, the foams are almost invariably sandwiched between two thin but stiff skins that are normally made of high strength alloys or advanced composites. The compressive load applied to the structure is transferred to the foams through the skin. Metal foams have poor mechanical properties in tension load because of the inherent material flaws and imperfections that occur during their fabrication. Therefore, metal foams are generally used to support compressive and shear loads. Accordingly, the compressive properties are the most important characteristics of metal foams. As mentioned before, relative density is the single most important feature of a foam. The different mechanical properties like elastic modulus, compressive strength, energy absorption and thermal conductivity are a strong function of relative density. In addition, the size and the type of cell like open or closed is also influential. Mondal et al. [16] reported that ZA27/SiCp foam the plateau stress, energy absorption follows power law relation with relative density and linearly with densification strain.
3.1. Compressive Strength
- Figure 2 shows the compressive stress-strain behaviour of plain ZA22 foam and its two composite configurations. The curves show a behaviour typical of foams. The behaviour can be divided into three distinct regions: linear, plateau and densification. The linear region extends approximately up to the strain value of 0.02, plateau region up to about 0.4 and thereafter densification starts. Linear region represents the linear elastic deformation behaviour of the foam under compressive load that occurs due to elastic bending of the struts and the plates that form the intracellular bridge and walls. The deformation is recoverable in this zone. The peak stress in this zone defines the compressive strength of the foam. The plateau region starts once the applied compressive load is higher than the yield strength of the foam material. In this region, plastic bending of the hinges of the struts and the plates takes place and the foam yield at almost constant stress. The plateau stress defines the energy absorption characteristics of the foam. Finally, in the densification region, the buckling and collapse of the intercellular connections and therefore of the cells takes place and the stress increases very rapidly for the given amount of strain.
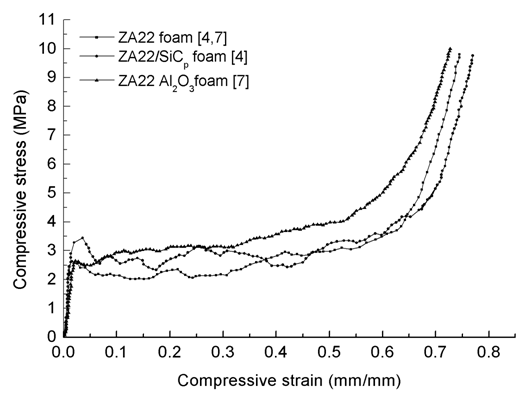 | Figure 2. Compressive stress – strain curve of ZA22 foam with or without reinforced material |
3.2. Energy Absorption Capacity
- Other than the compressive strength characteristics of foams when used in static loading, energy absorption capacity is the most important feature when the foams are used in dynamic loading conditions like impact loading and fatigue. Such a load conditions arise when the foam are used as shock absorbers in automotives, safety devices and packaging. The energy absorption capacity of a foam is defined mainly by the area under the plateau region in the compressive stress-strain tests. The higher the area, the greater the absorption ability will be. For shock absorption, the average plateau stress should be high, whereas for packaging purpose the plateau stress should be low. In both the applications, the foams should deform at constant plateau stress and the plateau strain range should be high.The energy absorption ability of the ZA foams is presented in Figure 3. The composite ZA22 foams have higher energy absorption capacity than plain ZA22. The absorption ability increases with strain because the higher the strain the higher the area under the stress-strain curve would be. It can be seen in the figure that ZA22/SiCp foams have high absorption capacity at low plastic strains, where as ZA22/Al2O3 foams have high absorption capacity at high plastic strains. Liu et al. [9] reported that energy absorption capacity of ZA22/SiCp foam was significantly higher than the ZA22 foam due to the dispersion of SiC particle on the cell wall which makes the wall hard to resist buckling and collapse. J. Liu et al. [12] further observed that ZA22/Al2O3 foams show higher energy absorption capacity than ZA22 foam due to presence of Al2O3 fibre having additional dissipating energy mechanism and debonding between fibre- matrix interface. Mondal et al. [16] reported that ZA27/SiCp foam shows higher energy absorption rate among all ZA alloys foam because of high yielding strength (Table 1).
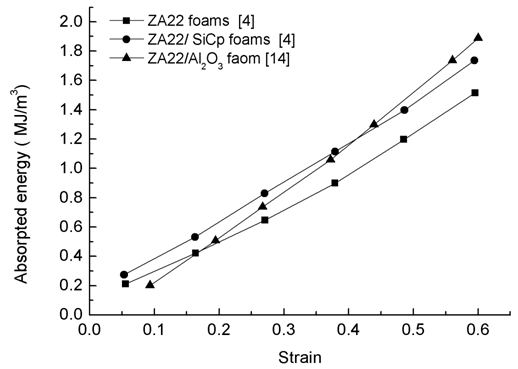 | Figure 3. A plot between energy absorbed and plastic strain in ZA foam |
4. Conclusions
- Metal foams are cellular solids that have some special blend of mechanical properties. ZA foams have certain advantages over plain Al foams in terms of better surface properties. In addition, these alloys have low melting point which makes these easy to handle and economic to fabricate. ZA22/SiCp and ZA22/Al2O3 composite foams have better mechanical properties as compared to the plain ZA22 foam. The compressive strengths of ZA22 is about 2.6 MPa and that of ZA22/SiCp and ZA22/Al2O3 is about 3.5 MPa and 2.6 MPa, respectively. Similarly, the elastic modulus of ZA22 is about 290 MPa and that of ZA22/SiCp and ZA22/Al2O3 is about 290 MPa and 130 MPa, respectively. ZA27/SiCp foam shows highest energy absorption rate among all ZA alloys studied here.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This study was supported by Indian Institute of Information Technology, Design and Manufacturing-Jabalpur.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML