-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation
p-ISSN: 2163-2405 e-ISSN: 2163-2413
2016; 6(5A): 142-146
doi:10.5923/c.jmea.201601.27

Static Characteristics of Journal Bearings Operating on TiO2 Nanolubricants at Low Shear Condition
K. G. Binu1, K. Yathish1, D. S. Rao2, R. Pai2, B. S. Shenoy3
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, St Joseph Engineering College, Vamanjoor, Mangalore, Karnataka, India
2Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal, Karnataka, India
3Department of Aeronautical and Automobile Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Correspondence to: K. Yathish, Department of Mechanical Engineering, St Joseph Engineering College, Vamanjoor, Mangalore, Karnataka, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The use of TiO2 nanoparticles as lubricant additives is reported to improve the static performance characteristics of journal bearings. A variable viscosity analysis using Krieger-Dougherty viscosity model and couple stress model reported an increase in load carrying capacity of fluid film bearings operating on TiO2 nanolubricants at high shear condition. The shear condition was modelled using the maximum particle packing fraction of TiO2 nanoparticle aggregates. The current study simulates the static characteristics of journal bearings for low shear conditions and compares it with the published results for high shear. Results reveal an increase in load carrying capacity for journal bearings operating at low shear conditions in comparison to high shear for nanolubricants. Results point to an increase in operational region of the journal bearing at low speed conditions due to the presence of TiO2 nanoparticle additives.
Keywords: Hydrodynamic journal bearings, TiO2 nanoparticle, High shear and Low shear conditions
Cite this paper: K. G. Binu, K. Yathish, D. S. Rao, R. Pai, B. S. Shenoy, Static Characteristics of Journal Bearings Operating on TiO2 Nanolubricants at Low Shear Condition, Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Vol. 6 No. 5A, 2016, pp. 142-146. doi: 10.5923/c.jmea.201601.27.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The use of nanoparticles as additives in carrier fluids for enhanced physiochemical properties has gained significant research interest over the past two decades. The resulting dispersion of nanoparticles in base fluids is termed as nanofluids. Owing to the increase in thermal conductivity of nanofluids in comparison to base fluids, nanofluids have found increased use in heat transfer applications [1, 2]. Coolants [3-5], refrigerants [6-8], cutting fluids [9-11], and lubrication [12-15] are few other applications using nanoparticle additives. Addition of nanoparticles is reported to improve the tribological properties of base oils under conditions of boundary lubrication [16, 17]. Wu et al. [18] has compared the performance of CuO, TiO2, and nano-diamond nanoparticles as additives in base oils. The paper also reports an increase in viscosity of base oil due to the addition of nanoparticle additives. TiO2 nanoparticles were reported to provide comparatively higher viscosity increase and also displayed enhanced tribological behaviour. The viscosity values of nanolubricants provided by Wu et al. [18] were used subsequently by Nair et al. [19] and Shenoy et al. [20] to perform a variable viscosity analysis of journal bearings operating on nanolubricants. These studies reported an increase in load carrying capacity of journal bearings operating on nanolubricants. A more generalized study was performed by Binu et al. [21, 24] by obtaining a viscosity model for TiO2 nanolubricants and performing a variable viscosity analysis in conjunction with couple stress model to obtain journal bearing performance characteristics under the influence of particle concentration and particle size. The current paper extends the results published in Binu et al. [24] by considering the viscosity variations of TiO2 nanolubricants at low shear conditions. The results of this paper compares the static journal bearing characteristics published by Binu et al. [24] at high shear with the results obtained for low shear. The maximum particle packing fraction ϕm is used as the control variable.
2. Viscosity Model
- A modified Krieger-Dougherty model is reported to simulate viscosities of TiO2 nanoparticle dispersions in engine oil for increasing TiO2 nanoparticle concentrations that are in good agreement with experimental results [21, 24]. The modified Krieger-Dougherty (K-D) model is expressed as equations 1 and 2 shown below.
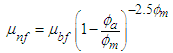 | (1) |
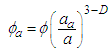 | (2) |
2.1. Maximum Particle Packing Fraction
- In the modified Krieger-Dougherty model presented in equation 1, ϕm is the maximum particle packing fraction in the suspension, which is dependent on the extent of shear. For high-shear applications, 0.605 is the prescribed value and for low shear applications ϕm is taken as 0.5 [22]. The fractal index D is generally taken as 1.8 for nanofluids [22]. The modified Krieger-Dougherty model therefore reduces to equation 3, presented below.
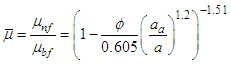 | (3) |
3. Theoretical
- The governing equation for this analysis is the modified Reynolds equation; integrated with the modified Krieger-Dougherty viscosity model to simulate the influence of TiO2 nanoparticle concentration and the couple stress model to simulate the influence of TiO2 nanoparticle size on the journal bearing performance characteristics. The governing equation is presented in equation 4. Further details on the numerical formulation and validation of the theoretical framework is presented in Binu et al. [21, 24].
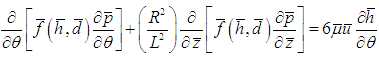 | (4) |
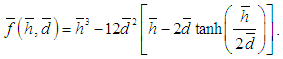 In solving the Reynolds equation, the effective viscosity term,
In solving the Reynolds equation, the effective viscosity term, 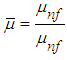 in the RHS, is simulated for varying TiO2 nanoparticle concentration, using the modified Krieger-Dougherty viscosity model, expressed as equation 1. The modified Reynolds equation is thus equipped to include the effective viscosity of nanolubricants and particle size of TiO2 aggregates in modeling the hydrodynamic pressure distribution. Equation 4 is solved numerically using finite difference scheme to obtain the pressure distributions at both high shear and low shear conditions. The pressure distributions are then used to compute the load carrying capacity and friction force at low shear and high shear conditions.
in the RHS, is simulated for varying TiO2 nanoparticle concentration, using the modified Krieger-Dougherty viscosity model, expressed as equation 1. The modified Reynolds equation is thus equipped to include the effective viscosity of nanolubricants and particle size of TiO2 aggregates in modeling the hydrodynamic pressure distribution. Equation 4 is solved numerically using finite difference scheme to obtain the pressure distributions at both high shear and low shear conditions. The pressure distributions are then used to compute the load carrying capacity and friction force at low shear and high shear conditions.3.1. Load Carrying Capacity
- Load carrying capacity of the bearing is obtained by integrating nodal hydrodynamic pressures across the bearing surface. The two components of generated oil film force, along the line of center and perpendicular to the line of center, are computed using the pressure integration equations given below.
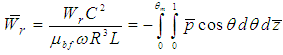 | (5) |
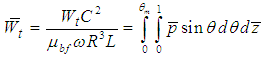 | (6) |
3.2. Friction Force
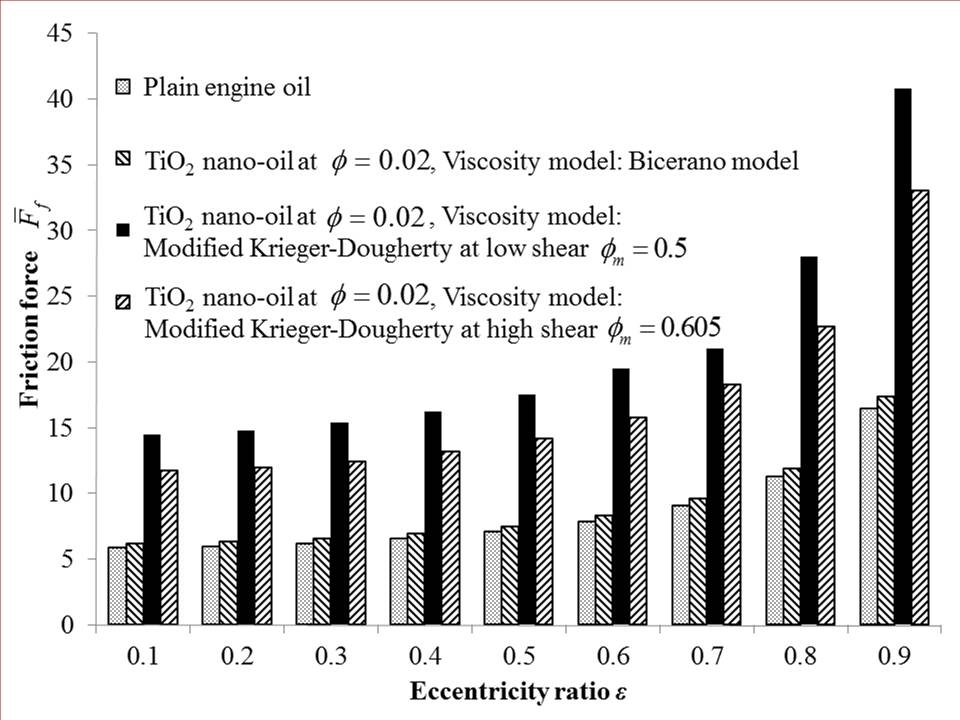
- The friction force generated within the oil film thickness, due to its continuous shearing by the surface motion of journal, is computed by integrating the shear stresses induced around the journal surface. The effective viscosity of TiO2 nanolubricants with considerations to both volume fraction and aggregate particle size influences the friction force. The shear stress developed at the journal surface is given by the equation stated below [24].
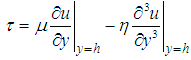 | (7) |
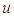 using equation 7, the shear stress is obtained as:
using equation 7, the shear stress is obtained as: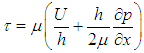 | (8) |
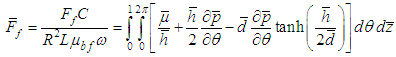 | (9) |
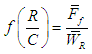 | (10) |
4. Results and Discussions
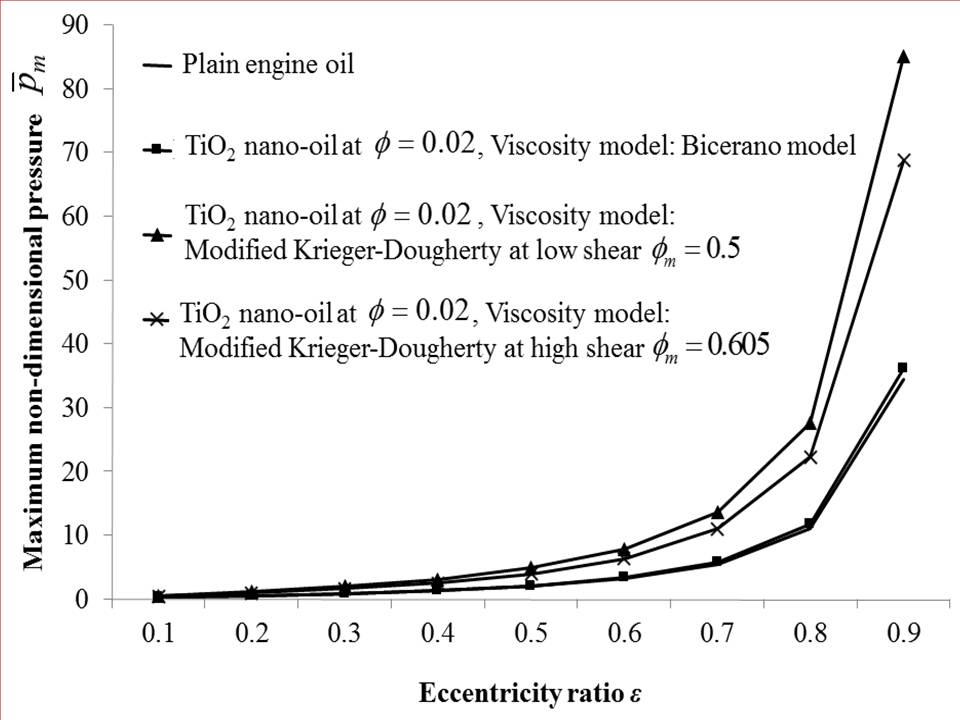
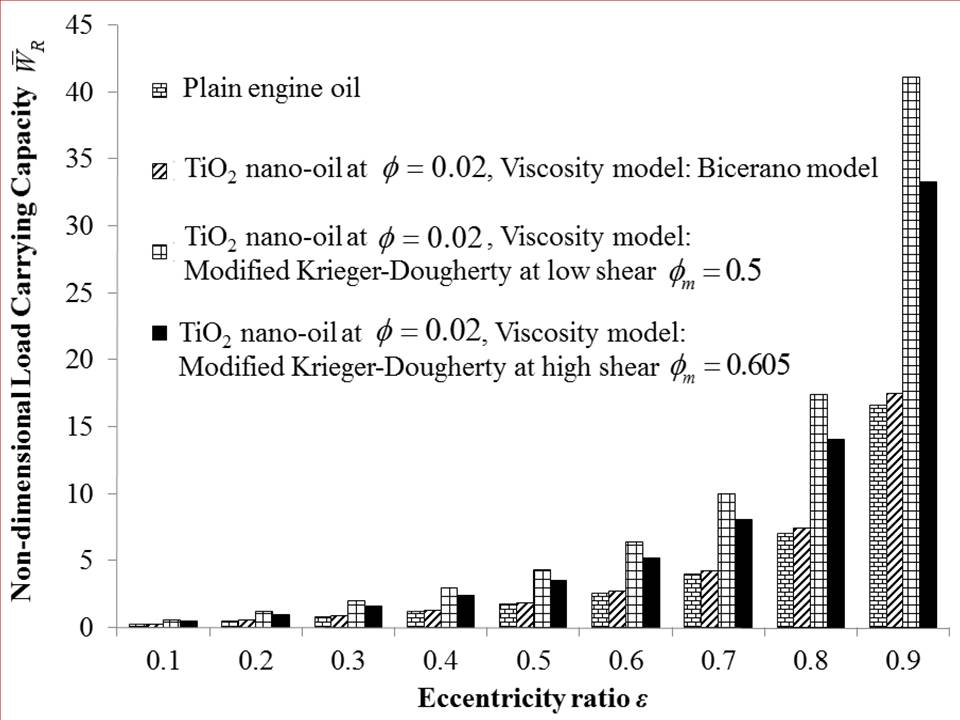
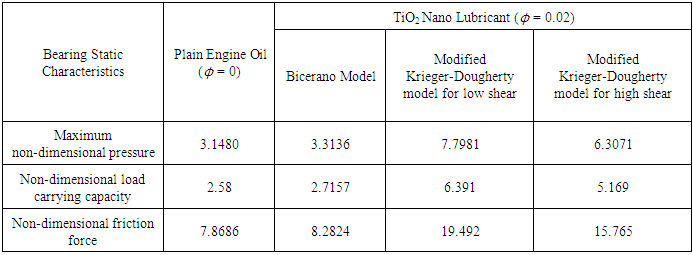
- The comparison of static characteristics for low shear and high shear is performed at a volume fraction of ϕ = 0.02. Comparisons are made of maximum non-dimensional pressures for plain engine oil and nanolubricants at high and low shear conditions. A comparison of static characteristics of journal bearings is also provided between values obtained between the aforementioned modified Krieger-Dougherty model and the Bicerano model [25]. The Bicerano model provides effective viscosities of suspensions and is expressed as:
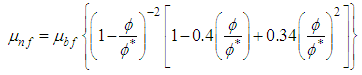 | (11) |
|
5. Conclusions
- The study simulates the journal bearing performance characteristics, viz. maximum pressures, load carrying capacity and friction force for TiO2 nanolubricants under low shear conditions. The obtained characteristics are then compared with the published results for high shear conditions [24]. Results reveal increased pressures and corresponding load carrying capacity of journal bearing operating with TiO2 nanolubricants at low shear condition in comparison to high shear. This result reveals the potential of using nanoparticle additives to improve hydrodynamic performance at low shear conditions characterised by low speed of journal rotation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The first, second and third authors would like to acknowledge The Management, St Joseph Engineering College, Mangalore for supporting their research.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML