-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation
p-ISSN: 2163-2405 e-ISSN: 2163-2413
2016; 6(5A): 121-125
doi:10.5923/c.jmea.201601.23

Analysis of Temperature Changes during Dry Drilling of Austenitic Stainless Steels on Twist Drills Having Different Point Angles
Jolene S. Vas1, Aster Fernandes1, Arnold D’Souza1, Ankith Rai1, Jaimon D. Quadros2
1UG Students, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahyadri College of Engineering & Management, Mangalore, India
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Offshore campus, Ras-Al-Khaimah, UAE
Correspondence to: Jolene S. Vas, UG Students, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sahyadri College of Engineering & Management, Mangalore, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In this work, effects of drilling parameters (feed rate and spindle speed) on the twist drill bit temperature in drilling of austenitic stainless steel material with and without the use of coolant is experimentally investigated. During drilling experiments, the drill bit temperature was measured by using SMART SENSOR AR360 Infrared Thermometer. The performance parameters viz. feed rate and spindle speed are varied as per L9 orthogonal array. The experiments were conducted by using High Speed Steel (HSS) drills having 82°, 100° and 118° drill point angles respectively. Analysis of temperature on the drilling parameters concluded that, the drilling temperature of the specimen increases with increase in both cutting speed and feed rate. This work thoroughly construes that 118° drill point angle produced the highest drilling temperature during the specimen drilling. Thus in order to reduce the thermal effects during machining of the specimen, the 80° drill point angle is recommended.
Keywords: Drilling, Austenitic stainless steel, Cutting speed, Feed rate, High Speed Steel
Cite this paper: Jolene S. Vas, Aster Fernandes, Arnold D’Souza, Ankith Rai, Jaimon D. Quadros, Analysis of Temperature Changes during Dry Drilling of Austenitic Stainless Steels on Twist Drills Having Different Point Angles, Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Vol. 6 No. 5A, 2016, pp. 121-125. doi: 10.5923/c.jmea.201601.23.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The cutting temperature directly influences the hole sensitivity (hole diameter, perpendicularity, and cylindricity), surface roughness, and tool wear. The experimental and numerical investigation of the temperature changes that occur on the cutting tool during the material removal processes is a traditional concern. In the aerospace industry depending on the application, hole quality is very important. Thus the quality characteristics of holes in this experimental investigation process are analyzed using spindle speed, feed rate and different drill diameter are as input parameter.During the drilling process, the most important factor affecting the cutting tool performance and work-piece properties is the cutting temperature that emerges between the drill bit and chip. The cutting temperature directly influences the hole sensitivity (hole diameter, perpendicularity, and cylindricity), surface roughness, and tool wear. The experimental and numerical investigation of the temperature changes have been recently conducted in works to calculate the cutting temperature by using FEM have also been conducted. Chen [1] has developed the 3-D finite element model to be able to compute the temperature distribution that may take place at the first cutting edge of the drilling tool and along the flank face. Fuh et al. [2] calculated the temperature distribution on the conventional drill during the cutting process by means of 3-D FEM. In this study, the effects of the cutting depth, cutting speed, web thickness, and helix angle on the temperature changes are investigated. Agapiou and Devires [3, 4] have analytically calculated the temperature distribution of twist drills on the flank face and cutting edge to explain thermal phenomena during the cutting process. They also have proposed a comparison between experimental and analytical results. On the other hand, Agapiou and Stephenson [5] have described a model for calculating transient and steady-state drill temperatures for a drill with arbitrary geometries. They have additionally compared the analytical results acquired to the experimental ones gathered by implementing welded thermocouple and thin wire thermo-junction methods. Despite that there are many experimental works on turning and grinding operations in the literature, there is little work directed toward calculating the drill temperature. Bono et al. [6, 7] developed a model for predicting the heat flow into the work-piece and investigated the influence of the heat that emerges on hole diameter and cylindricity in dry drilling. Finally, he has presented a comparison between numerical and experimental results. Baˇgcı [8] has developed a new approach for experimental measurement of the drill bit temperature in the dry drilling process. Drill temperatures were measured by inserting standard thermocouples through the coolant (oil) hole of TiAlN-coated carbide drills. In his work, the effects of sequential, continuous, and step by step dry drilling operations and drilling parameters on the drill bit temperature experimentally and numerically have been investigated. The drill bit temperature was predicted using a numerical computation with Third Wave Advant Edge FEM software based on langrangian explicit method. Finally, he has presented a comparison between experimental study and finite element analyses (FEA). Kalidas et al. [9] has measured the work-piece temperature to find out how different drill coatings affects the hole quality under dry and wet cutting conditions. For this purpose, four thermocouples were inserted onto the work-piece and the temperature values for various feed rates and spindle speeds were determined. V. N. Gaitonde et al. [10] used Taguchi L9 Methodology to design the number of experiments for drilling of AISI 316L by varying the input parameters cutting speed, point angle, lip angle and found that point able has major influence on burr height. Tsann-Rong Lin et al. [11] studied the Cutting behavior of a TiN-coated carbide drill with curved cutting edges during the high speed machining of stainless steel AISI304 and measured surface roughness and burr height. Based on the literature cited above, the current research endeavour is one such attempt to determine the temperature for drill bits of drill point angles 82°, 100° and 118°.
2. Materials
- The material used for drilling in the present study is Austenitic Stainless Steel. These are alloys containing chromium and nickel, and sometimes molybdenum and nitrogen, structured around composition of iron, 18% chromium, and 8% nickel. Austenitic stainless steels replace the majority of their nickel content with manganese to reduce cost. Austenitic steels are not hardenable by heat treatment. This alloy exhibits superior resistance to stress-corrosion cracking in boiling 20-40% sulphuric acid. It has excellent mechanical properties and the presence of Niobium in the alloy minimizes the precipitation of carbides during welding.
3. Plan of Experiments
- Taguchi method uses a special design of orthogonal arrays to study the entire parameter space with only a small number of experiments. Taguchi is the developer of the Taguchi method [12]. Taguchi methods(orthogonal array) has been widely utilized in engineering analysis and consists of a plan of experiments with the objective of acquiring data in a controlled way, in order to obtain information about the behavior of a given process. Taguchi methods, which combine the experiment design theory and the quality loss function concept, have been used in developing robust designs of products and processes and in solving some confusing problems of manufacturing [13]. The orthogonal array selected was the L9 (24) which has nine rows corresponding to the number of tests(eight degrees of freedom) with two columns at three levels, as shown in Table 1.
|
4. Machining Set-up and Drilling Procedure
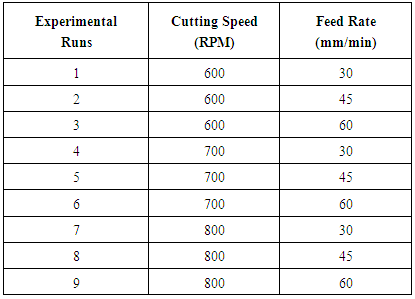
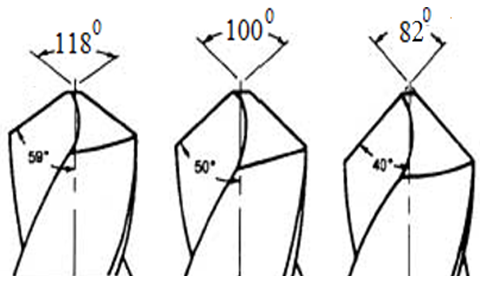
- Drilling was performed on a BATLIBOI make radial drilling machine by using HSS twist drill of 12 mm diameter with 82°, 100° and 118° point angles shown in Figure 1. The temperature was recorded for different cutting conditions by using SMART SENSOR AR360 Infrared Thermometer which is a non- contact digital thermometer providing temperature readings ranging from -50ºC to 320ºC with an accuracy of ±2%. Drilling operations were carried out on the austenitic steel plates with the cutting conditions that are already listed. The experimental set up is shown in Figure 2. The coolant ECOCUT SSN 322 neat oil with 40.2 cSi at 40ºC from FUCHS was used as MQL oil for thin pulsed jet system.
 | Figure 1. Drill point angles of different drill point geometries used in the present study |
 | Figure 2. Experimental Set up |
5. Results and Discussions
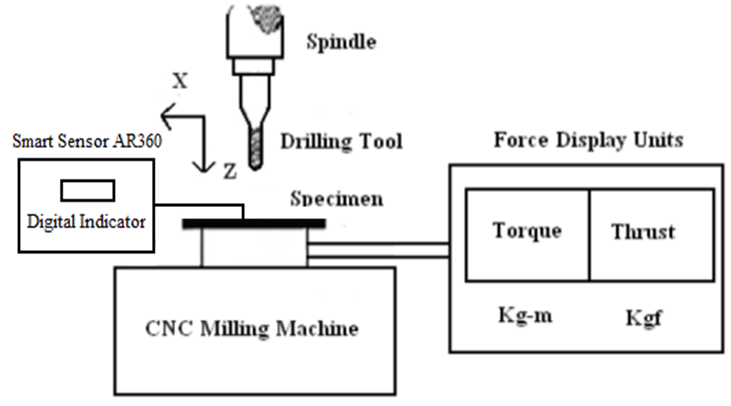
- The Figures below shows the detailed drilling temperature response values obtained with respect to feed rate and cutting speed respectively with and without the use of coolant. It is observed from Figure 3 (a, b) that, drilling temperature is found to increase considerably with the increase in feed rate for drill point angles of 82° and 100°. However for drill point angle of 118°, temperature tends to marginally decrease with increasing feed rate. Thus it can be thoroughly construed that, temperature changes produced by drill point angle of 118° have a comparatively lesser effect in drilling austenitic stainless steels when compared to 82° and 100° drill point angles. From previous studies [13, 14] it has already been concluded that thrust force and torque generally increase with increase in feed rate. This was mainly due to the increase in the cross-sectional area of the un-deformed chip. This increases the hardness and the cutting resistance of the material resulting in wears the cutting edges of the drill through drilling one hole. Thus during penetration of the drill bit into the material, the un-deformed chip tends to melt due to increased friction at the tool-chip interface likewise increasing the temperature. It is observed from Figures 4 (a, b) that, drilling temperature is found to increase considerably with the increase in cutting speed for all drill point angles of 82°, 100° and 118° respectively. Unlike drilling with respect to feed rate; the drilling temperature for increase in cutting speed showed sizable deviation for all the drill point angles employed in the present study. During drilling of austenitic steel specimens, drilling torque increases with the increase in RPM of the spindle and this torque increases with the increase in depth of cut. This developing torque enhances the plastic deformation over the sides of the drill bit resulting in rigorous chip formation and larger burr formation. The temperature changes observed during the use of coolant were much lesser when compared to drilling without its use.
 | Figure 3. Variation of drilling Temperature (°C) with respect to Feed (mm/min) for drill point angles of 82°, 100° and 118° respectively. (a) With coolant; (b) Without coolant |
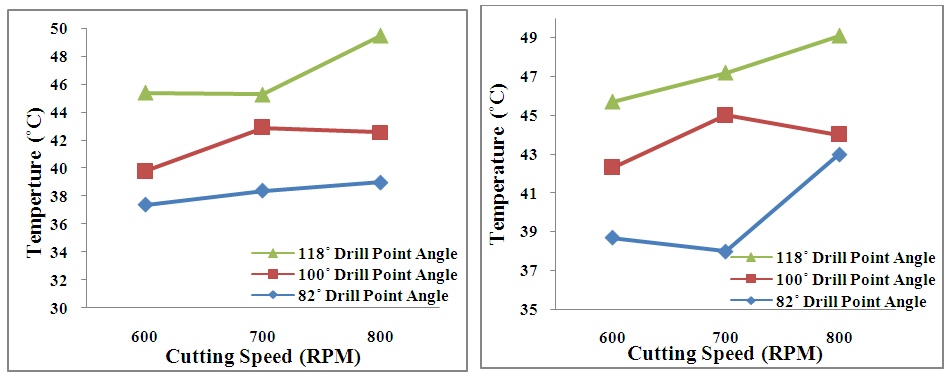 | Figure 4. Variation of drilling Temperature (°C) with respect to Cutting Speed (RPM) for drill point angles of 82°, 100° and 118° respectively. (a) With coolant; (b) Without coolant |
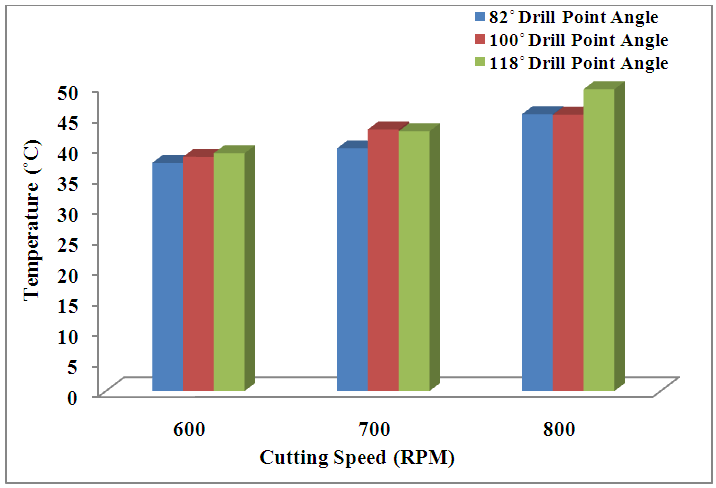 | Figure 5. Variation of drill temperature for different drill point angles |
6. Conclusions
- The present work analyses the effects of drilling parameters viz. feed rate and spindle speed on the twist drill bit temperature in the dry drilling of austenitic stainless steel material. The following conclusions have been drawn:Ÿ The drilling temperature of the specimen is found to increase with the increase in feed rate for all the drill point angles employed in the study.Ÿ The drilling temperature is found to increase considerably with the increase in cutting speed for all drill point angles.Ÿ The 80° point angle drill recorded the least drilling temperature and 118° point angle drill recorded the highest drilling temperature during drilling of austenitic steel specimens.Ÿ This work thoroughly construes that 118° drill point angle produced the highest drilling temperature during the specimen drilling. Thus in order to reduce the thermal effects during machining of the specimen, the 80° drill point angle is recommended.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML