-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Journal of Civil Engineering Research
p-ISSN: 2163-2316 e-ISSN: 2163-2340
2014; 4(3A): 208-213
doi:10.5923/c.jce.201402.35
Acceleration Time Analysis of Project Work on Optimum Structure with Additional Cost
Syahrizal
Department of Civil Engineering, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Syahrizal, Department of Civil Engineering, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
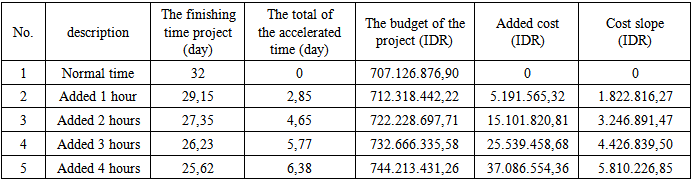
The construction project is a series of activities carried out only once and generally short-term. Project management is how to ensure that their resources are involved in a construction project can be applied to the construction manager as appropriate. The main purpose of the study was to determine the amount of time that can be accelerated and how much will it cost. The steps that need to be done such as preparing a network with methods of Critical Path Method (CPM), to identify the critical path and non-critical path analysis and calculation of the acceleration of time and project costs. The result of the calculation has shown the implementation of the normal work time for the first floor is 32 day and the normal cost is IDR 707,126,876.90. With the addition of 1 hour of working time, the finishing time is 29.15 days with an increase in cost of IDR 5,191,565.32, and cost slope value is IDR 1,822,816.27 per day. With the addition of 2 hours of working hour, the finishing time is 27.35 days with an increase in cost of IDR 15,101,820.81, and cost slope value is IDR 3,246,891.47 per day. With the addition of 3 hours of working time, the finishing time is 26.23 days with an increase in cost of IDR 25,539,458.68, and cost slope value is IDR 4,426,839.50 per day. With the addition of 4 hours of working time, the finishing time is 25.62 days with an increase in cost of IDR 37,086,554.36 and cost slope value is IDR 3,246,891.47 per day. The addition of working time should be used in critical work (the work that has to be done as soon as possible). If the addition of time is used in all works including non-critical work, it will only increase the cost while the accelerated time is constant.
Keywords: Acceleration of the Project, Critical Path Method, the Optimum Cost
Cite this paper: Syahrizal, Acceleration Time Analysis of Project Work on Optimum Structure with Additional Cost, Journal of Civil Engineering Research, Vol. 4 No. 3A, 2014, pp. 208-213. doi: 10.5923/c.jce.201402.35.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- A good teamwork between owner, consultant and contractor is required in a construction project. In this case, the owner of a project will ensure that the project would follow the scheduled timing. Therefore, a contractor must be able to manage construction project systematically in order to complete the project within the given time and the given budget effectively.In fact, there will always be discrepancy between the real project timing and the scheduled timing. There are several things that can delay the project implementation; such as, unfavorable weather - rain that forces the workers to stop their work, errors or changes of plan because of delayed material, the lack of supervision that results to errors, or the presence of government regulations especially about traffic that slow down the work, and the influence of the surrounding environment.The delay of project timing is the responsibility of a contractor as the project manager. If the project timing is dragged for a longer period of time, then the owner of the project will penalize the contractor. For instance, The School Building project, Yayasan Pelita Bangsa, which is located on Jl. Iskandar Muda Medan, Sumatera Utara. It was planned to begin on April 18, 2011 and to be completed by December 12, 2011. In the ninth weeks, dated June 13, 2011, It began to show a delay in the project timing. The project that was supposed to be finished by 15.54%, was only 12.98% complete. It also showed a delay on the following weeks. One of the ways to solve this issue is to add the working time of the workers. The Addition of working hours can be done by adding in 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours and 4 hours. With this analysis, accelerated time can be known and the cost for the acceleration of the project can be calculated.
2. Literature
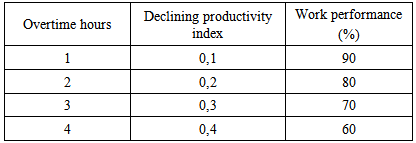
- CPM method (Critical Path Method)CPM is a method that uses AON (Activity on Node) diagram to determine the critical path of a project. CPM is using estimated duration of a particular activity (deterministic), There are some elements that are used in CPM. They are EET (Earliest Even Time), LET (Last Even Time), total float, free float, and interfering float. EET is the earliest starting point of a project while LET is the latest finishing point of a project.In CPM method, critical method is used to determine the activity that cannot be delayed, as the delay in the critical activity will cause the delay in the entire project.Worker ProductivityProductivity is defined as the ratio of output and input, or the ratio of total production and total resource. In a project, productivity ratio is the value that is measured during the construction. It can be categorized as direct labor, direct material, cost, method and tools. The success rate of a project is determined by the effectiveness of resource management. Labor is one of the resources that is not easy to be managed. The cost of each labor varies, depends on each worker’s skills; as, different worker has different skills.Accelerate the Project Time (Crashing Project)On way to crash a project is to adding the working time of workers. Adding working time is the most often method that is used in project management. It can empower the existing resources in the working environment and would not burst the budget by too much. The normal working hour is 7 hours (starting from 8am to 4pm, with 1 hour break). Overtime is calculated once worker exceed the normal working hour. The addition of working hours can be perform by the addition of 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours and 4 hours in accordance to the desired additions.The decreasing of the labor productivity towards the increasing of working hours can be seen in the picture that shown below:From the description above can be written as follows :
 Where:
Where:
|
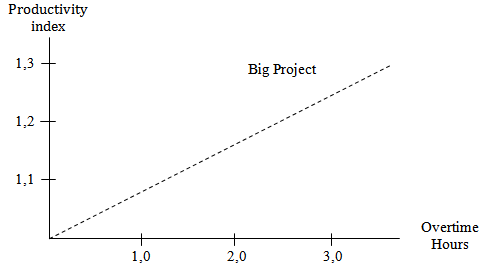 | Picture 1. Indicate decreased productivity due to the addition of working hours (sourc: Soeharto, 1997) |
 | Picture 2. Relationship between time-normal cost and be shorten for one activites (sourc: Soeharto, 1997) |
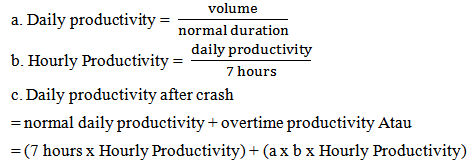
 = 1.5 x normal hourly wages for the first hour + 2 x n x normal hourly wages for the next hour Where: n = the number of extra working hour4. Crash cost daily workers = (7 hours x normal workers cost) + (n x overtime payment hourly)
= 1.5 x normal hourly wages for the first hour + 2 x n x normal hourly wages for the next hour Where: n = the number of extra working hour4. Crash cost daily workers = (7 hours x normal workers cost) + (n x overtime payment hourly) Relationship between cost and timeThe total cost of a project is equal to direct cost plus indirect cost. Total cost moves in the same direction as the project timing. The longer the project, the higher will the cost be. The relationship between cost and time is shown on picture 2. Point A shows a normal point; Point B is shorten point. The line that joins point A and B is called time-cost curve.Network arrangementThe initial step is to collect data that is required in the project as a research venue, in this case is the S curve and budget. Based on the data we obtained from the S curve. The activity components arrangement is done based on logic dependent order. Next is to reschedule the project by using CPM to determine the activities in the critical path and non-critical path. Then, the project network is made by using the desired method.The calculation of acceleration time and cost of the projectAfter the critical work has been obtained, we can gain the normal cost project based on the budget data that has been planned by a contractor. The data can also be used to calculate acceleration of the project by adding work time of 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours and 4 hours. After we obtained the acceleration cost of the project, we can then calculate the cost of acceleration and worker time based on the Decision Minister of Manpower and Transmigration of the Republic of Indonesia No. KEP. 102 / MEN / VI / 2004 that the wage increase varied, for the addition of the first hour of work time, workers get extra payment hourly 1.5 times of the normal time, and for the addition of the next hour, the workers get extra payment hourly 2 times of the normal time.
Relationship between cost and timeThe total cost of a project is equal to direct cost plus indirect cost. Total cost moves in the same direction as the project timing. The longer the project, the higher will the cost be. The relationship between cost and time is shown on picture 2. Point A shows a normal point; Point B is shorten point. The line that joins point A and B is called time-cost curve.Network arrangementThe initial step is to collect data that is required in the project as a research venue, in this case is the S curve and budget. Based on the data we obtained from the S curve. The activity components arrangement is done based on logic dependent order. Next is to reschedule the project by using CPM to determine the activities in the critical path and non-critical path. Then, the project network is made by using the desired method.The calculation of acceleration time and cost of the projectAfter the critical work has been obtained, we can gain the normal cost project based on the budget data that has been planned by a contractor. The data can also be used to calculate acceleration of the project by adding work time of 1 hour, 2 hours, 3 hours and 4 hours. After we obtained the acceleration cost of the project, we can then calculate the cost of acceleration and worker time based on the Decision Minister of Manpower and Transmigration of the Republic of Indonesia No. KEP. 102 / MEN / VI / 2004 that the wage increase varied, for the addition of the first hour of work time, workers get extra payment hourly 1.5 times of the normal time, and for the addition of the next hour, the workers get extra payment hourly 2 times of the normal time.3. The Results of the Discussion
- We can calculate it manually by using Microsoft Excel, which can expedite the calculation. To calculate the used time to finish the project and budget, Critical Path Method (CPM) is used. CPM is a method that use AON (Activity on Node) diagram to determine critical path. AON diagram is an arrow diagram that connects activities in a project together. Critical path connect the beginning and ending activities of a project. As a result, critical path is important to a project flow as a delay in an activity in the critical path means a delay in the entire project.
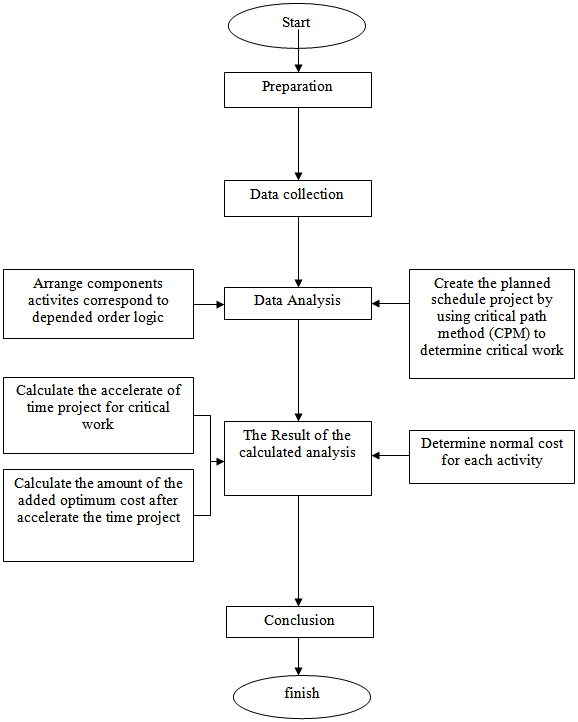 | Picture 3. The writing flow chart |
|
|
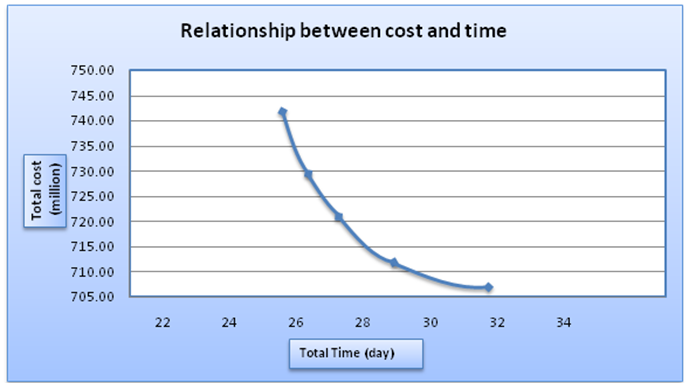 | Picture 4. Relationship between time, normal cost and the budget after accelerated for the first floor work |
4. Conclusions
- Based on the analysis of work acceleration at school building Yayasan Pelita Bangsa on jln. Iskandar Muda Medan, Sumatera Utara, we can conclude that:The result of the calculation has shown the implementation of the normal work time for the first floor is 32 day and the normal cost is IDR 707,126,876.90. With the addition of 1 hour of working time, the finishing time is 29.15 days with an increase in cost of IDR 5,191,565.32, and cost slope value is IDR 1,822,816.27 per day. With the addition of 2 hours of working hour, the finishing time is 27.35 days with an increase in cost of IDR 15,101,820.81, and cost slope value is IDR 3,246,891.47 per day. With the addition of 3 hours of working time, the finishing time is 26.23 days with an increase in cost of IDR 25,539,458.68, and cost slope value is IDR 4,426,839.50 per day. With the addition of 4 hours of working time, the finishing time is 25.62 days with an increase in cost of IDR 37,086,554.36 and cost slope value is IDR 3,246,891.47 per day.
5. Suggestion
- The addition of working time should be used in critical work (the work that has to be done as soon as possible). If the addition of time is used in all works including non-critical work, it will only increase the cost while the accelerated time is constant.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML