-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Ecosystem
p-ISSN: 2165-8889 e-ISSN: 2165-8919
2015; 5(3A): 75-85
doi:10.5923/c.ije.201501.11
A Brief Review on the Scenario of Ground Water Pollution by Arsenic in West Bengal
Bikash Kumar Panda
Assistant Professor in Chemistry, Jangipur College, Jangipur, Murshidabad, West Bengal, India
Correspondence to: Bikash Kumar Panda, Assistant Professor in Chemistry, Jangipur College, Jangipur, Murshidabad, West Bengal, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Arsenic (As) is a naturally occurring element which is presents in food, water and air. Although arsenic is known to be an effective poison but some animal studies suggest that arsenic may be an essential nutrient at low concentrations. The dangers associated with long-term exposure to arsenic are now well known. Arsenic toxicity in groundwater has affected major parts of the Bengal Basin covering Bangladesh and southern West Bengal as well as other parts of the world. The metalloid arsenic has poisoned approximately 130 to 140 million people though out the world and has the highest toll in developing countries such as India. Arsenic pollution is a major and acute environmental problem affecting Bengal. The permissible limit of arsenic content in groundwater is 0.05 mg/l and it was first recorded in West Bengal in the year of 1978 that presence of arsenic in groundwater beyond this limit. The cases of arsenic poisoning were diagnosed in 1983 initially. The recommended limit of arsenic in potable water has been lowered to 0.01mg/l by the Bureau of Indian Standards. It was also reported in the literature that by the end of 2001 the problem of arsenic pollution spreads from few villages to about two thousand and sixty five villages of seventy five blocks in nine district i.e. around 9.5 million people in nine districts in southern West Bengal were affected. This is due to the over withdrawal, misuse and abuse of groundwater resource. During the past forty years, groundwater has been extensively used for irrigation and the use of phosphate fertilizers has increased enormously. Excessive withdrawal of groundwater possibly triggered mobilization of degraded organic chemicals and phosphates into the aquifer system. The arsenic-affected deltaic plains of Bengal and other such areas are free of any industrial, mining or geothermal activities and represent natural geological settings. The nature of arsenic pollution in West Bengal, diseases cause by arsenic and progress made so far is reviewed in this article completely on the basis of literature survey.
Keywords: Ground Water, Arsenic Toxicity, Mobilization of As, Arsenic Removal Technologies
Cite this paper: Bikash Kumar Panda, A Brief Review on the Scenario of Ground Water Pollution by Arsenic in West Bengal, International Journal of Ecosystem, Vol. 5 No. 3A, 2015, pp. 75-85. doi: 10.5923/c.ije.201501.11.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Water is the prime necessities of life and we can hardly live for a few days without water. The progress of human life will be tremendously hindered if good quality of pure water is not readily available to them in adequate quantity. Good quality of water means the water, which is colorless (in thin layers) or blue-green (in thick layers) having neitherodour nor taste. By far the most serious and ominous problem the world is facing today is the problem of water pollution [1-9]. In spite of adopting various measures in existence so far to check the pollution, the situation is worsening day by day due to rapid industrialization, urbanization and exponential growth in population. Moreover, reckless exploitation of water resources to meet the growing demands without paying heed towards sustainability factors has deteriorated the situation furthermore. All major rivers of our country are facing problems of water pollution as well as underground water in getting polluted and not safe to drink.
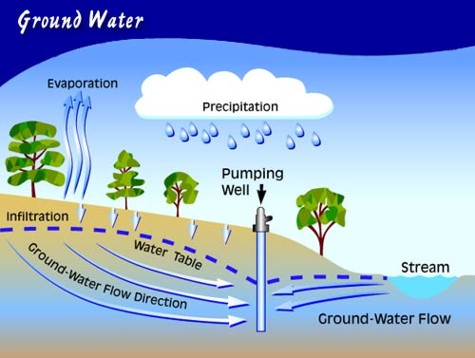 | Figure 1. Ground Water [Source: tapintoquality.com] |
 | Figure 2. Image of the metalloid arsenic [Source:http://www.isgtw.org/feature/isgtw-feature-grids-point-pollution-solutions] |
2. Occurrences of Arsenic in Groundwater
- It was revealed from the studies of the several scientist that the groundwater arsenic contamination is mostly restricted to the alluvial aquifers of the Ganges delta which is comprising sediments carried from the sulphide-rich mineralized areas of Bihar and elsewhere surrounding the basin of deposition [3, 14]. Although, recent studies furnished that the vast tract of Indo-Gangetic alluvium extending further to the west and the Brahmaputra alluvium have elevated concentrations of arsenic in wells placed in the late Quaternary and Holocene aquifers. Arsenic released during the weathering of sulphide minerals is mainly adsorbed onto the surface of iron oxy-hydroxides that precipitated under oxidizing conditions normally prevailing during the deposition of the Holocene sediments. However the redox processes in the sediments triggered the reductive dissolution of iron oxides that transferred substantial amounts of arsenic in aqueous phases through biogeochemical interactions [15, 16]. Arsenic-containing groundwater in Ganga–Brahmaputra River basin is hosted by the sediments deposited by the rivers during the late Quaternary or Holocene age (< 12 thousand years). There is a thick layer of newer alluvium containing sand, silt and clay, which spread out by numerous rivers. The rivers are originates from the Himalayas both in the north and northeast region. The environmental arsenic problems which were recognized so far are mainly the result of mobilization under natural conditions.
3. Extent of Arsenic Pollution in West Bengal
- It was reported [17-25] by several arsenic researchers that some cases of arsenical dermatitisare observed especially in the districts of North 24 Parganas, South 24 Parganas, Murshidabad and Nadia of West Bengal during the year of 1980. The problem spreads from few villages to 2065 villages of 75 blocks in nine districts of the state by the end of 2001. It was also reported that about 10% of the total population of the state is exposed to the above risk. The extent problem in West Bengal shown via a Map in the Figure 3 and the red portion of the map indicate the highly arsenic affected area. The green portion indicates the arsenic safe area and yellowish red parts are mildly arsenic contaminated area.
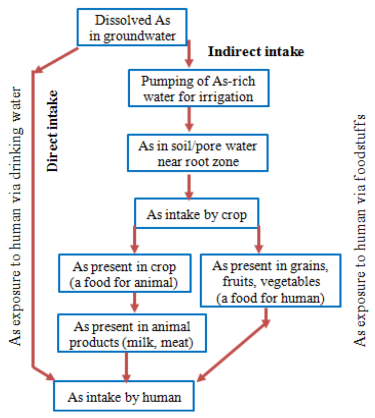 | Figure 3. Arsenic Exposure to human via drinking water and foodstuffs [Source: Internet] |
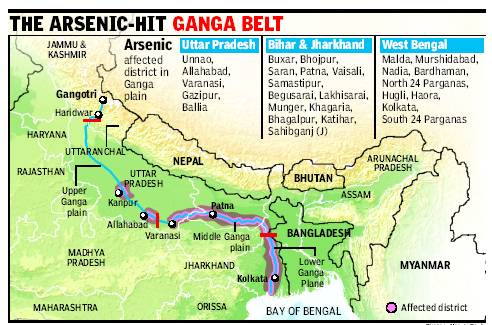 | Figure 4. Occurrence of Arsenic in the Ganga Belt [Source: lite.epaper.timesofindia.com] |
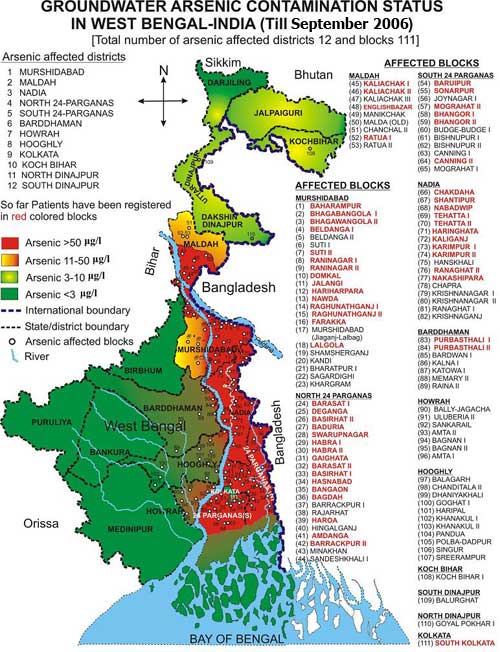 | Figure 5. Extent arsenic pollution in West Bengal [Source:-http://www.soesju.org/arsenic/wb.htm] |
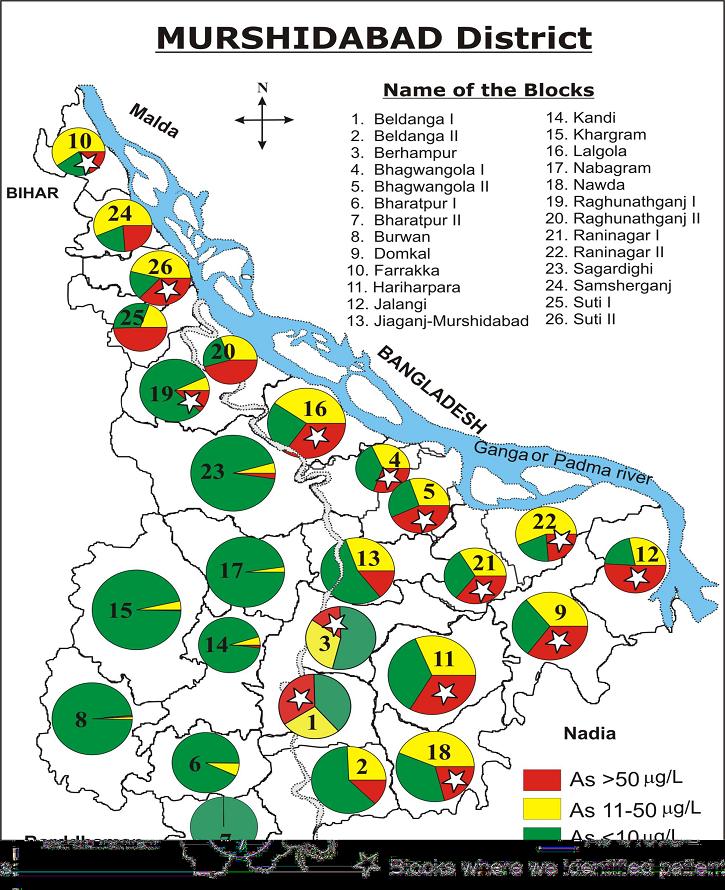 | Figure 6. Extent of Arsenic Pollution in Murshidabad District [Source:-http://www.soesju.org/arsenic/wb1.htm] |
4. Reason of High Incidence of Arsenic in Groundwater
- Several research workers believed that leaching of arsenic in groundwater seems to have been influenced by the number of interacting factors as discussed below [5, 6, 17]:i) Due to rapid growth in Agro-commercialization. ii) Cultivation of Summer Paddy (Boro). iii) The Boro cropping is almost dependent on the tube well irrigation. Immediate manifestation of that agro practice was lowering of ground water level at alarming rate.iv) The ground water occurring mainly within the shallow zone (20-60m) is characterized by high arsenic (>0.5 to 1 or above mg/l) and the principal source of arsenic is the arsenic sulphides minerals deposited along with clay, peat and with iron in the reducing environment. v) However, the cause of arsenic contamination in groundwater is still a debatable topic. Thus, it is necessary to study extensively the groundwater reservoir condition, mode of recharge-discharge relationship, groundwater movement characteristics in time and space and to determine dissolved oxygen and oxidation-reduction potential in groundwater to understand the cause of such arsenic concentration in groundwater.
5. Difference in Toxicity and Occurrence of Several Forms of Arsenic (AS)
- Arsenic (As) exists in different forms which are differ from one another in toxicity and occurrence. The metallic form of arsenic i.e. zero valent arsenic is not absorbed by the stomach and intestines and does not exert adverse effects. On the other hand, a volatile compound such as AsH3 is toxic, but is not present in water or food. Moreover, the primary organic forms (arsenobetanine and arsenocholine) found in fish and shellfish seem to have little or no toxicity. Arsenobetanine quickly passes out of the body through urine without being metabolized to other compounds. Arsenite (+3) and arsenate (+5) are the most prevalent toxic forms of inorganic arsenic that are found in drinking water. Arsenite i.e. As(+3) in reduced state in inorganic is a toxic pollutant in natural environment and is more soluble and mobile than the oxidized state of inorganic arsenic, arsenate i.e. As(+5). In summary the inorganic forms of arsenic exhibit the highest toxicity level [26], while organoarsenicals are usually less toxic than the inorganic arsenic species. Indeed, some organic arsenic compounds, such as arsenobetaine (AsBet) and arsenocholine (AsChol), are well tolerated by living organisms [27, 28].
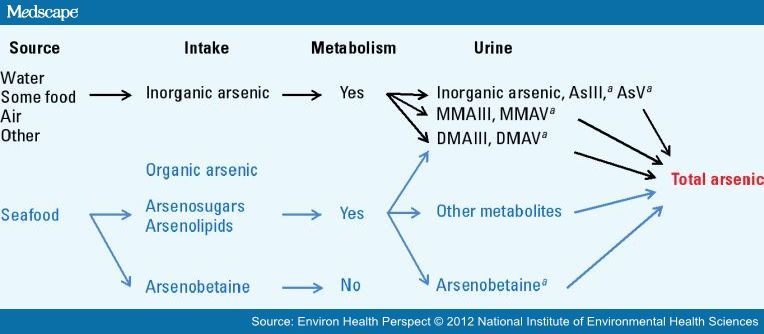 | Figure 7. Different Forms of Arsenic and its Metabolism |
6. Primary Symptoms of Arsenic Poisoning
- Clinical symptoms occurring in the early stage of human arsenic poisoning were unspecific. The clinical manifestations of arsenic poisoning are myriad, and the correct diagnosis depends largely on awareness of the problem. Among the people who were taking high-arsenic water, early symptoms included, following non-specific symptoms, which can be present in many other diseases.i) Palpitations ii) Fatigue iii) Headache, dizziness, insomnia, weakness iv) Nightmare v) Numbness in the extremities, anaemia
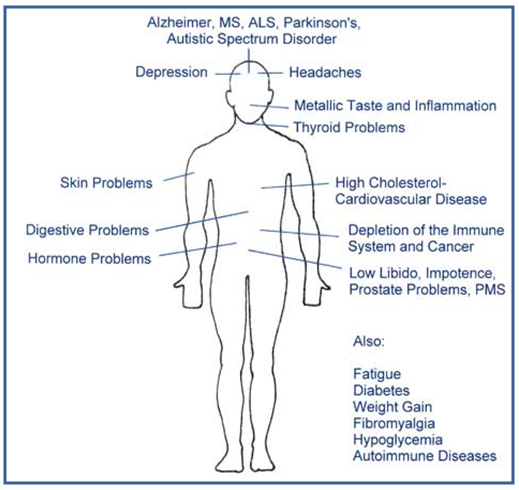 | Figure 8. Clinical Symptoms of Arsenic Poisoning [Source: Internet] |
7. Diseases Cause by Arsenic due to Long-term Exposure to Arsenic
- Long term intake of drinking water having arsenic concentration beyond the permissible limit of 0.05 mg/lit has deleterious effects on human health viz., Respiratory Effects [29, 30], Cardiovascular Effects [31-33], [Gastrointestinal Effect [34], Hematological Effects [35, 36], Hepatic Effect [37, 38], Renal Effects [39], Dermal Effects [40], Neurological Effects [41], Developmental Effects [42], Reproductive Effects [43], Genotoxicity Effects [44], Mutagenic Effects [45], Immunologic Effect [46], Carcinogenic Effect [47] and Biochemical Effects [48].
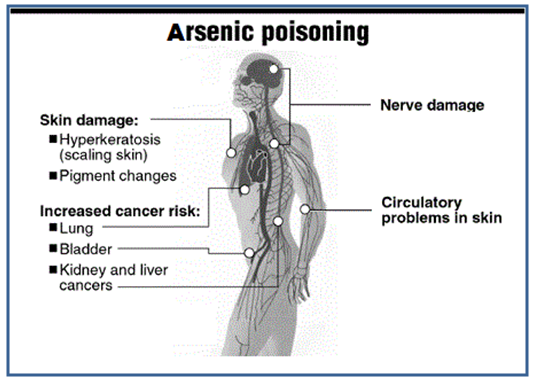 | Figure 9. Danger of Arsenic Poisoning [Source:medicalassessmentonline.com] |
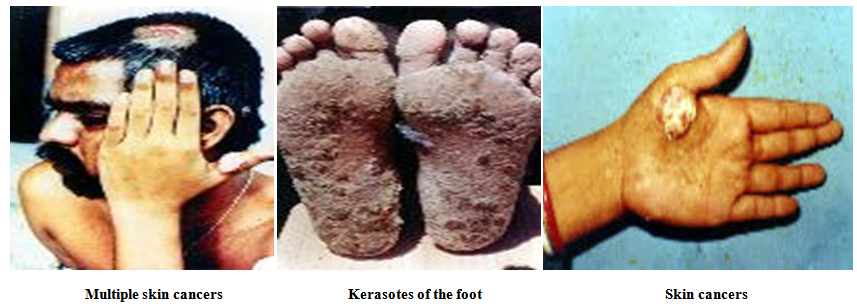 | Figure 10. Diseases causes by arsenic [Source:http://users.physics.harvard.edu/~wilson/arsenic/ remediation/arsenic_project_remediation_technology.html] |
8. Mechanism of Arsenic Poisoning
- Arsenic disrupts the cellular process that produces ATP, the molecule in charge of transporting energy throughout your body's cells so they can perform the tasks that keep you alive. Arsenic both blocks and competes with the chemicals that form ATP, leaving your body well short of what it takes to keep up even the most basic cellular processes. Messing with the ATP pathway can disturb neurological and cardiovascular systems. If the dosage in the body is high enough, arsenic poisoning can eventually cause multi-system organ failure, most likely driven by cell death. Inorganic As(V) and As(III) have different mechanisms of action. Arsenate (As(V)) behaves very much like phosphate consequently, it can substitute for phosphate in normal cell reactions, interesting with normal cell functions. In contrast, arsenite [As(III)] has a high affinity for thiol (-SH) groups in proteins, causing inactivation of a variety of enzymes [49-51]. Because arsenate is reduced in the body to arsenite, arsenate in drinking water may have a biological effect identical to arsenite.The good news is that, caught early, arsenic poisoning is treatable. Most medicines are synthetic compounds that work by absorbing the arsenic and arsenic-containing chemicals from your blood stream. Some studies have shown that garlic can treat arsenic poisoning, but various scientist and doctors suggest heading to the hospital before the pantry.
9. Remedy for Arsenicosis
- Chelation therapy is a procedure [52-55] that involves the administration of chelating agents to remove heavy metals from the human body. Chelation therapy has a long standing interest due to its use in clinical toxicology and remains in use for some very specific medical treatments; however it is administered under very careful medical supervision due to various inherent risks. Chelation therapy must be administered with care as it has a number of possible side effects, including death. Chelation therapy is used as a treatment for metal poisoning, including acute mercury, iron, arsenic, lead, uranium, plutonium and other forms of toxic metal poisoning. There are a variety of common chelating agents with differing affinities for different metals, physical characteristics, and biological mechanism of action.
 In cases of chronic arsenic poisoning one should consider BAL (British antilewisite) as a chelator the signs of arsenicosis are severe or the patient is in complications. Treatment by BAL is superior to penicillamine. During the clinical phase, when symptoms like melanosis and keratosis appear on the skin, chelating agents like BAL, Penicillamine, DMSA/DMPS help in clearing melanosis. Mechanical scraping of soles of feet can be done to relieve keratosis. Urea and salicylate ointments can also be used. Prolonged used of chelating agent BAL with mechanical scraping of water soaked keratotic soles and palms give encouraging results. Penicillamine, although only a monothiol agent, has been used successfully; its great advantage is thatit may be orally administered. Both agents have a high frequency of side effects, although this is less of aproblem in the presence of large amounts of body arsenic. A recently reintroduced drug that appears to be a promising agent for treating arsenic poisoning is 2,3-dimer captosuccinic acid. This is a dithiol agent that can be orally administered and has few reported side effect.
In cases of chronic arsenic poisoning one should consider BAL (British antilewisite) as a chelator the signs of arsenicosis are severe or the patient is in complications. Treatment by BAL is superior to penicillamine. During the clinical phase, when symptoms like melanosis and keratosis appear on the skin, chelating agents like BAL, Penicillamine, DMSA/DMPS help in clearing melanosis. Mechanical scraping of soles of feet can be done to relieve keratosis. Urea and salicylate ointments can also be used. Prolonged used of chelating agent BAL with mechanical scraping of water soaked keratotic soles and palms give encouraging results. Penicillamine, although only a monothiol agent, has been used successfully; its great advantage is thatit may be orally administered. Both agents have a high frequency of side effects, although this is less of aproblem in the presence of large amounts of body arsenic. A recently reintroduced drug that appears to be a promising agent for treating arsenic poisoning is 2,3-dimer captosuccinic acid. This is a dithiol agent that can be orally administered and has few reported side effect.10. Mobilization Mechanisms of As
- It was revealed from the study of the different areas that high-arsenic groundwater was not related to areas of high arsenic concentration in the source rock. The most common source of arsenic contamination in ground water is the mobilization of naturally occurring arsenic on sediments. Given the right chemical conditions in the subsurface arsenic can dissolve into ground water used for drinking water. Two key factors were identified: first, there should be very specific biogeochemical triggers to mobilize arsenic from the solid/sorbed phase to groundwater, and second, the mobilized arsenic should have sufficient time to accumulate and not be flushed away, that is, it should be retained in the aquifer. In other words, arsenic released from the source should be quick, relative to the rate of groundwater flushing. There are number of processes for mobilization of arsenic in groundwater namely, (i) mineral dissolution, (ii) The desorption of arsenic under alkaline and oxidizing conditions, (iii) The desorption and dissolution of arsenic under reducing conditions, (iv) The reduction of oxide mineral surface area, and (v) The reduction in bond strength between arsenic and holt mineral surface. Although there are number of hypotheses explaining chemical processes of groundwater arsenic contamination, however, the most commonly believed chemical processes are dissolution. Among few hypotheses proposed to explain the possible mechanism of arsenic groundwater contamination, most scientists have settled down to two hypotheses: (i) oxidation of arsenopyrite or arsenic rich pyrite in soil strata, and (ii) reductive dissolution of arsenic from soils. However, based on arsenic geochemistry, three hypotheses describing probable mechanisms of As mobilization [56-60] in groundwater specially, with reference to Holocene aquifers like in West Bengal and Bangladesh, have been suggested. These are: (i) Mobilization of arsenic due to the oxidation of As-bearing pyrite minerals: Insoluble As-bearing minerals, such as Arsenopyrite (FeAsS), are rapidly oxidized when exposed to atmosphere, realizing soluble As(III), sulfate (SO42-), and ferrous iron (Fe2+). The dissolution of these As-containing minerals is highly dependent on the availability of oxygen and the rate of oxidation of sulfide. The released As(III) is partially oxidized to As(V) by microbially mediated reactions. The chemical reaction is given by:

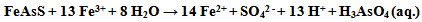 (ii) Dissolution of As-rich iron oxyhydroxides (FeOOH) due to onset of reducing conditions in the subsurface: Under oxidizing conditions, and in the presence of Fe, inorganic species of As are predominantly retained in the solid phase through interaction with FeOOH coatings on soil particles. The onset of reducing conditions in such environments can lead to the dissolution of FeOOH coatings. Fermentation of peat in the subsurface releases organic molecules (e.g., acetate) to drive reducing dissolution of FeOOH, resulting in release of Fe2+, As+3, and As+5 present on such coatings. The chemical reaction is given by:
(ii) Dissolution of As-rich iron oxyhydroxides (FeOOH) due to onset of reducing conditions in the subsurface: Under oxidizing conditions, and in the presence of Fe, inorganic species of As are predominantly retained in the solid phase through interaction with FeOOH coatings on soil particles. The onset of reducing conditions in such environments can lead to the dissolution of FeOOH coatings. Fermentation of peat in the subsurface releases organic molecules (e.g., acetate) to drive reducing dissolution of FeOOH, resulting in release of Fe2+, As+3, and As+5 present on such coatings. The chemical reaction is given by: 
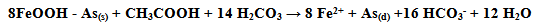 where As(s) is sorbed As, and As(d) is dissolved As.
where As(s) is sorbed As, and As(d) is dissolved As. 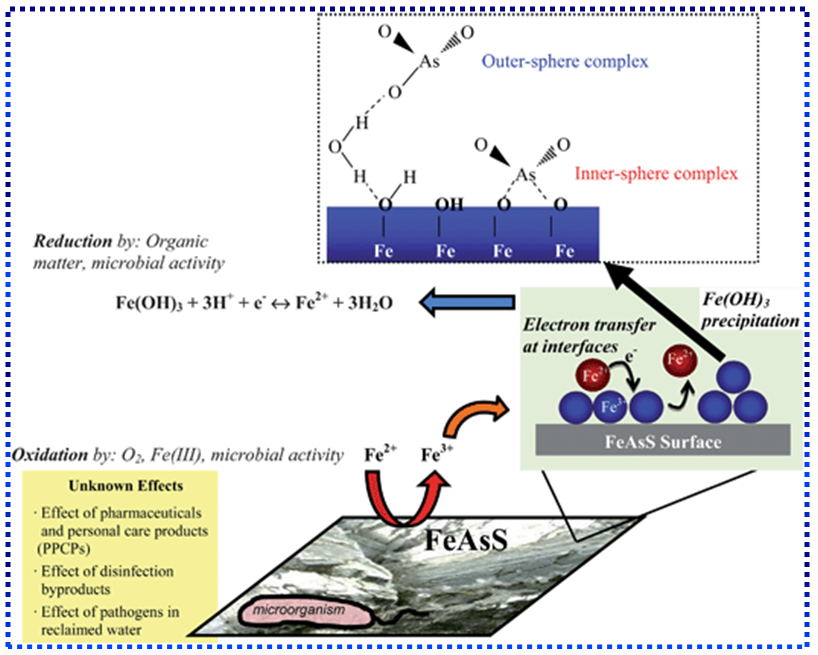 | Figure 11. Mobilization of Arsenic [Source:http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2012/em/c2em30323j#!divAbstract] |
11. Conventional Arsenic Removal Technologies and Remedial Options
- A numerous number of technologies [61, 62] have been developed for the removal of high concentrations of arsenic from drinking water. The most common arsenic removal technologies use oxidation, coagulation, precipitation adsorption, and ion exchange and membrane techniques. Other potential approaches would include phytoremediation or the use of bacteria, which can play an important role in catalysing biological arsenic removal processes. All the arsenic treatment technologies ultimately concentrate arsenic in the sorption media, the residual sludge or in a liquid media. To avoid indiscriminate disposal and environmental pollution, these wastes need to be treated or disposed of properly.Coagulation/filtration (also known as flocculation) removes arsenic by coprecipitation and adsorption using iron coagulants. Coagulation/filtration using alum is already used by some utilities to remove suspended solids and may be adjusted to remove arsenic. But the problem of this type of filtration system is that it gets clogged very easily, mostly within two to three months. The toxic arsenic sludge are disposed of by concrete stabilization, but there is no guarantee that they won't leach out in future.Iron oxide adsorption filters the water through a granular medium containing ferric oxide. Ferric oxide has a high affinity for adsorbing dissolved metals such as arsenic. The iron oxide medium eventually becomes saturated, and must be replaced. The sludge disposal is a problem here too.Activated alumina is an adsorbent that effectively removes arsenic. Activated alumina columns connected to shallow tube wells in India and Bangladesh have removed both As(III) and As(V) from groundwater for decades. Long-term column performance has been possible through the efforts of community-elected water committees that collect a local water tax for funding operations and maintenance. It has also been used to remove undesirably high concentrations of fluoride.Ion Exchange has long been used as a water-softening process, although usually on a single-home basis. Traditional anion exchange resins are effective in removing As(V), but not As(III), or arsenic trioxide, which doesn't have a net charge. Effective long-term ion exchange removal of arsenic requires a trained operator to maintain the column.Both Reverse osmosis and electrodialysis (also called electrodialysis reversal) can remove arsenic with a net ionic charge. (Note that arsenic oxide, As2O3, is a common form of arsenic in groundwater that is soluble, but has no net charge.) Some utilities presently use one of these methods to reduce total dissolved solids and therefore improve taste. A problem with both methods is the production of high-salinity waste water, called brine, or concentrate, which then must be disposed of.In some places, all the water supplied to residences by utilities must meet primary (health-based) drinking water standards. Regulations may necessitate large-scale treatment systems to remove arsenic from the water supply. The effectiveness of any method depends on the chemical makeup of a particular water supply. The aqueous chemistry of arsenic is complex, and may affect the removal rate that can be achieved by a particular process.Some utilities with multiple water supply wells could shut down those wells with high arsenic concentrations, and produce only from wells or surface water sources that meet the arsenic standard. Other utilities, however, especially small utilities with only a few wells, may have no available water supply that meets the arsenic standard. Thus the remedial options are as follows:(i) Uses of surface water sources, (ii) Exploring and harnessing alternate arsenic free aquifer, (iii) Removal of arsenic from groundwater using arsenic treatment plants/filters, (iv) Adopting rainwater harvesting/ watershed management practices.
 | Figure 12. Arsenic Removal Plant [Source: dir.indiamart.com] |
12. Concluding Remark
- It is obvious that high-arsenic drinking water may be a factor in arsenic toxicosis in human beings. It seems to be important in the control of the disease to consider how to prevent arsenic intake from drinking water. The symptoms and signs of arsenic poisoning may be reduce if the quality of drinking water improved. In some cases, the symptoms and signs of arsenic poisoning were reduced three years after the quality of drinking water improved. The morbidity rate also declined. Numerous studies suggested that improvement of water quality, the rate of improvement in the symptoms and signs of arsenic poisoning in human beings may increase with a decrease in arsenic level in the drinking water source.We should use more surface water after appropriate purification. Reduce anthropogenic pollution of the surface water bodies. Stop or reduce drastically the uncontrolled extraction of ground water and allow the aquifer and water tables to regenerate sufficiently. Carefully use modern technologies for removal of toxic substances like arsenic and fluoride salts from the water. Finally, rain water harvesting and preservation should be widely used in urban and rural areas to have pollution free water round the year.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML