Ayan Das Gupta
W.B.E.S, Assistant Professor, Postgraduate Department of Geography, Krishnagar Govt. College, Krishnagar, Nadia, West Bengal, India
Correspondence to: Ayan Das Gupta, W.B.E.S, Assistant Professor, Postgraduate Department of Geography, Krishnagar Govt. College, Krishnagar, Nadia, West Bengal, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
For the holistic development of urban panorama within the jurisdiction limit of any local self Government, different planning strategies are required to be adopted on an urgent basis. Urban planning here plays a pivotal role in implementing manifold technical as well as political processes coherent to the utilization of land and design of the urban environs including its infrastructure and amenities passing in and out of the urban arena such as transportation and distribution network and so on and so forth. The current paper will through focus on urban infrastructure and amenities in Gayeshpur Municipality that is included within the District of Nadia. In the entire discussion, water supply, drainage and road network, health and educational facilities etc of Gayeshpur will be highlighted under a totalistic coverage and some selected case-studies will also be present there. Gayeshpur was declared to be a Notified Area in 1979 and thereafter it was elevated to the Municipality Status in the year of 1995. As per the 2011 census, this study unit encompasses total eighteen wards the total area of which is near about 30 Square Kilometers. From the Draft Development Plan published recently from the end of Gayeshpur (M), all the secondary datasets have been procured by the researcher whereas the vivid questionnaire survey has enlightened him a lot with all the required primary databases. In Gayeshpur, there is only one stand pump prevailing still now for the facilitation of water supply in all of its internal wards and the break-down of this pump leads to a complete disruption in water supply in the entire Municipality. Therefore the installation of an alternative pump is urgently required over there. In Gayeshpur, most of the wards are endowed with well-developed network of drains to maintain proper waste water and sullage disposal but in some specific areas, the drainage outlets have been almost choked due to excessive accumulation of garbage, plastic bags etc disposed by the inhabitants of Gayeshpur. In some particular wards of Gayeshpur, the metalled roads are broken due to frequent movement of heavy luggage-vans and lorries and that’s why prompt attention should be paid in these premises. For obtaining higher education, still today, most of the students travel from Gayeshpur to nearby municipal belts and it’s also a burning problem in the whole Municipality. Though different Health Improvement Programmes have been launched recently by the Government but not all the target group have received their blessings yet. Four market places, five banks, one stadium and one children’s park are forming the integral whole of urban amenities in entire Gayeshpur and thus much more improvement in this domain is another prime requisite here. In order to promote the social upward mobility of the urban paupers of Gayeshpur, though some NGOs have initiated contributing financial aids very recently but for ushering a totalistic development in this urban sector and to uplift its socio-economic conditions to their fullest fruition, the municipality itself will have to struggle a lot in coming days.
Keywords:
Infrastructure, Amenities, Urban Local Bodies, Local Self-Government
Cite this paper: Ayan Das Gupta, Current Layout of Urban Infrastructure and Amenities in Gayeshpur Municipality of District Nadia - A Baseline Assessment, International Journal of Ecosystem, Vol. 5 No. 3A, 2015, pp. 29-42. doi: 10.5923/c.ije.201501.05.
1. Introduction
Gayeshpur was declared to be a notified area on 1st September of 1979. Prior to this, the area was practically under no administrative jurisdiction or coverage and was associated with Saguna Gram Panchayat, which had a questionable persistence itself. After India got independent, a colony was set up in this forestland under the financial assistance of the Refugee Rehabilitation Department of the Govt. of West Bengal. Gayeshpur Notified Area has been elevated to a Municipality-Status in the year of 1995. According to 2011 Census of India, Gayeshpur Municipality has a spatial extent of near about 30 sq. km. with a population-strength of 58,998. Gayeshpur municipality is bounded in its north-west by Kalyani Municipality and in its southern part is protected by Mathura Beel. Saguna Gram Panchayat area initiates at its northern boundary whereas its southwestern boundary is delimited partially by the river Hooghly and the rest by the Kanchrapara Municipal Administrative Boundary.Gayeshpur Municipality is located in the northern fringe of the Kolkata Metropolitan District and is at about 72 kilometers north of Kolkata city. It is accessed by two State highways. The eastern side is accessed through National Highways 34 (Kolkata-Siliguri Road), and the western side through Delhi Road. Further, Gayeshpur is linked through suburban railways having two Railway stations in its vicinity. Kalyani Railway Station lies at its periphery in the north-west, and Kanchrapara railway station in the west. The spherical coordinates of Gayeshpur Municipality are as follows. This Municipality is extending latitudinally from 22°56′N to 22°58′30″N whereas longitude-wise, its extension is from 88°27′E to 88°31′E. Right now, Gayeshpur Municipality is encompassing total 18 micro-urban units and amongst those spatial entities, there is a considerable number of slums and shanties.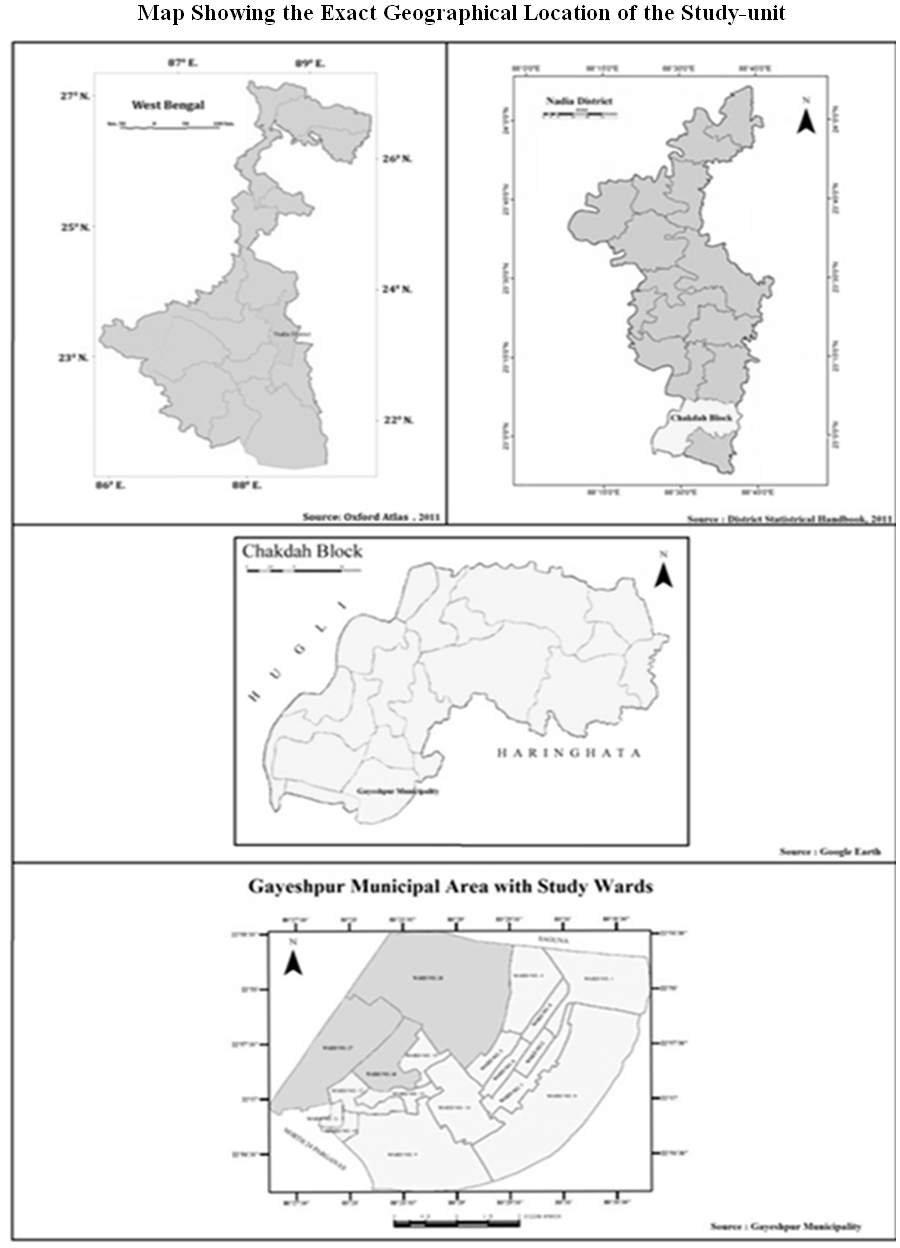 | Map 1.1. |
Objectives:-In the present paper, an attempt has been made to enunciate the condition of urban Infrastructure and Amenities as well within the jurisdiction limit of Gayeshpur Municipality in Nadia. Actually, Gayeshpur Municipality is a newly built-up urban block in the entire Nadia and therefore, the analyses of its manifold infrastructural components in terms of water supply, road network, electrification, sanitation and sewerage related facilities along with solid waste management system will throw focus on its current urban-status and through this discussion, the problems and prospects of Gayeshpur will be manifested hopefully in a clear manner. Not only, the infrastructure, but also at the same time, miscellaneous urban amenities of Gayeshpur encompassing its market places, parks, amusement outlets, shopping plaza etc. have also come under consideration in this study. The focal objectives behind the study are enlisted below in a systematic fashion: • To identify the typology of infrastructural facilities available at this municipal arena.• To depict the distribution of infrastructural facilities in different micro units of the entire Urban Local Body.• To portray the current phases of infrastructural development and improvement in amenities as well in Gayeshpur.• To find out the major problems and prospects of several municipal services associated with infrastructure and amenities in Gayeshpur as a whole.
2. Methods and Materials
Methodology and Database:-In order to accomplish the entire research on the Urban Infrastructure and amenities of Gayeshpur Municipality in Nadia District, some definite methodologies have been followed like collection of recent Census data from the Census office, acquiring the Draft Development Plan as well as City Development Report from the Official end of Gayeshpur Municipality, organizing perception survey in the selected localities by preparing a definite Questionnaire-format and so on and so forth. These methodologies adopted during the study can be divided under three broad sub-heads which are explained afterwards. In the pre-field phase, the researcher has gone through different books, journals, gazetteers, Govt. records and reports and so on and so forth related to the problem. Thereafter, he has visited different official wings of the Municipality for getting relevant secondary databases. The researcher has met the Executive Officer, Section Engineer and Chairman as well to procure all the information on urban infrastructure and amenities in details on this very municipally. Municipality-website has also been accessed thoroughly for acquiring more conspicuous database on the research-problem. During the main field-phase, the researcher has prepared a detailed oriented questionnaire-schedule where all his primary queries associated with the research-topic have been penned down. For the perception survey, the purposive stratified sampling technique has been adopted and total hundred households have been surveyed in some selected premises from different wards and only in the case of query regarding sanitation-facilities, three specific wards namely 16, 17 and 18 have been taken into consideration and the sample size remained the same. Based on family-wise total monthly income, three definite income groups have been framed and datasets have been collected in almost equal proportion from all those three income-strata. These income categories are i) below 10,000/- income per month, ii) 10,000/- to 20,000/- income per month and iii) more than 20,000/- income per month. This perception study has immensely helped the surveyor to draw a correct inference regarding infrastructural improvement in the study-unit.In the post-field phase, the researcher has analyzed all the datasets obtained from primary survey and thereafter a comparison has been done between the primary and the secondary information. Ultimately some Thematic Maps and diagrams have been prepared on the basis of some statistical analyses. Here some specific geographical software namely TNT-Mips, Geomatica, Map Info Professional etc have become quite helpful for the researcher.
3. Analyses and Inferences
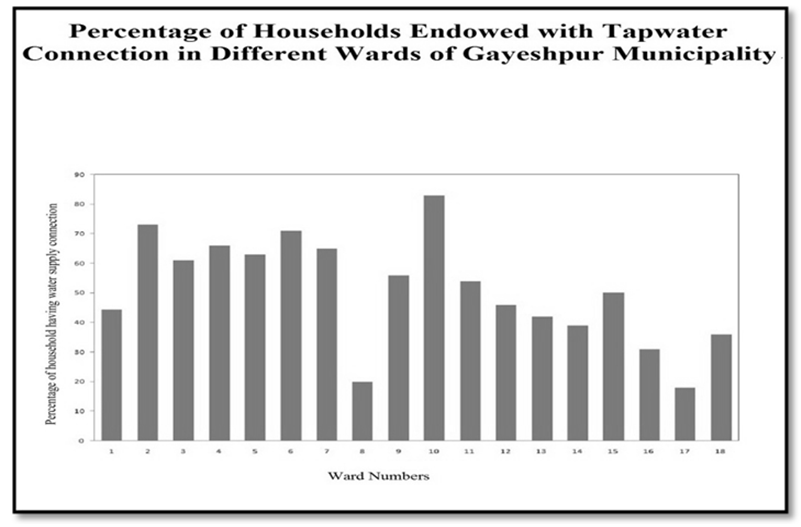
In the present discussion, a methodical attempt has been made to assess the infrastructural profile as well as the spectrum of urban amenities in Gayeshpur Municipality within the District of Nadia. With the help of schematic maps and representative lay-outs, the overall panorama of infrastructure and amenities of Gayeshpur, has been portrayed. Now, spotlight is getting focused on specific sectors of urban infrastructure and amenities below.Water supply:- The principal source of existing water supply in Gayeshpur is ground water that is withdrawn from 16 big pumping stations distributed throughout the municipal area. There is only one gigantic stands by pump is found in the entire Municipality. Any major break down of this one may lead to the complete disruption in water supply in the study-area. There are only two overhead reservoirs and their structural conditions are also very much under threat. AC pipes constitute here the main pipe network of water supply. All these AC pipes need to be replaced because these are not allowable for water supply from the perspective of health and hygiene. Leakage in pipelines is a matter of serious concern and the municipality bears the brunt of recurring cost of repair and maintenance. It can be stated that the water supply system in Gayeshpur municipal area should be planned fresh to meet the existing lacunae, future demand and the objectives set by the municipality. Presently the domestic water supply connection through Municipal pipe lines is fulfilling the demand of 83% dwellers of this urban local body. Ward-wise quantity of water supply per Capita per day is 135 liter. In the Gayeshpur Municipal area, ward numbers 10, 2, 6 and 4 are highly benefitted by the persisting water supply system connected with the main municipal reservoirs and Ward number 3,5,7 and 9 have moderate advantage of getting connected with municipal water supply system and this is characterized by the poorly-designed pipeline-network. The ward numbers 17, 16 and 18 are having considerably low number of households receiving water supply facilities from the local self Government.Drainage and Sullage:-The municipal areas of Gayeshpur are connected telescopically with drains of higher capacity and coherent to the nearest points of the Nayanjuli Canal and Beel system. In Gayeshpur Municipal area, every ward is having been covered with intensive drainage network in order to maintain waste water and sullage Disposal. The percentage of area covered in this premise, on an average, is 36.88. Maximum coverage is coming to be 45% that is identified in ward number 18, 7 and 8 basically. The drainage condition of Gayeshpur Municipality area are of four types- a) kutcha without cover, b) kutcha with cover, c) pucca without cover and d) pucca with cover. Most of the drains in the Urban Local Body of Gayeshpur are falling within the category of pucca without cover. As a whole in Gayeshpur, 32.84 percent drains are pucca with cover. Only 10.38 percent drains are totally kutcha.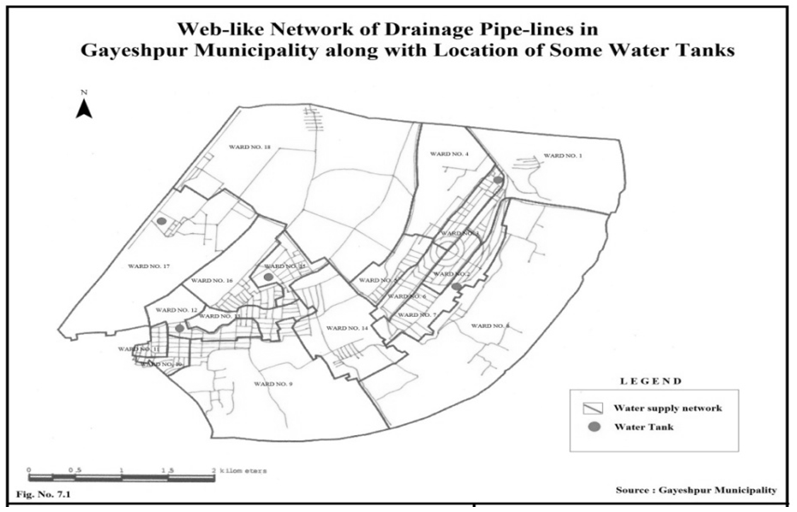 | Map 3.1. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Figure 3.1. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
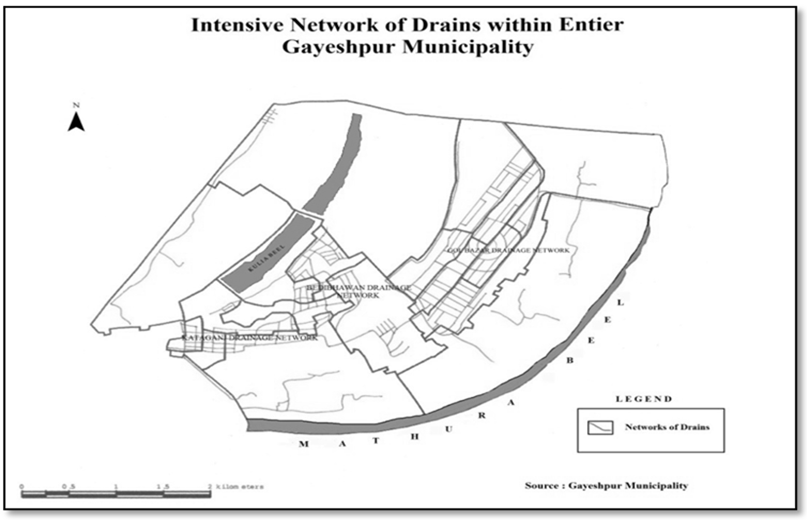 | Map 3.2. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
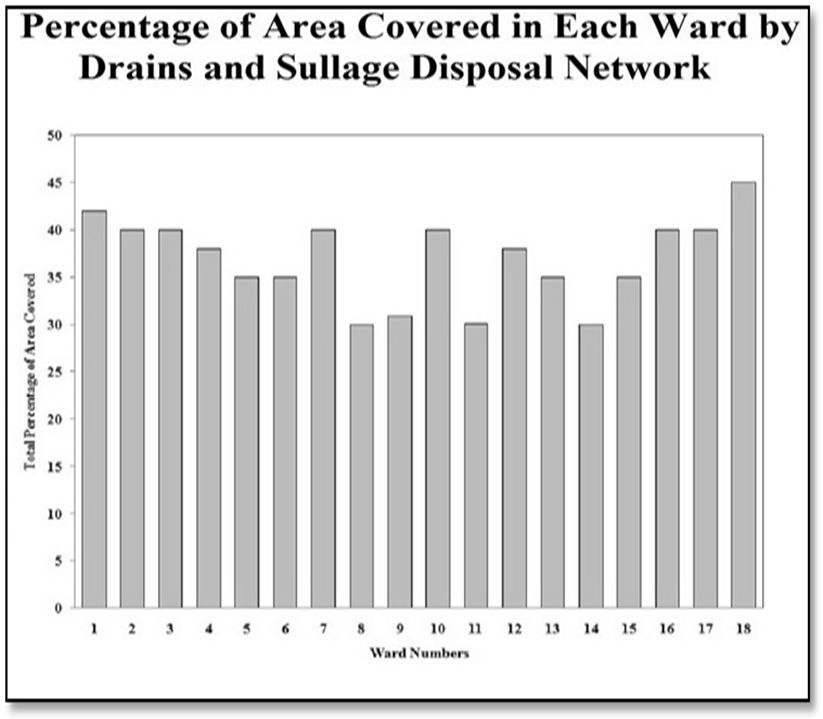 | Figure 3.2. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
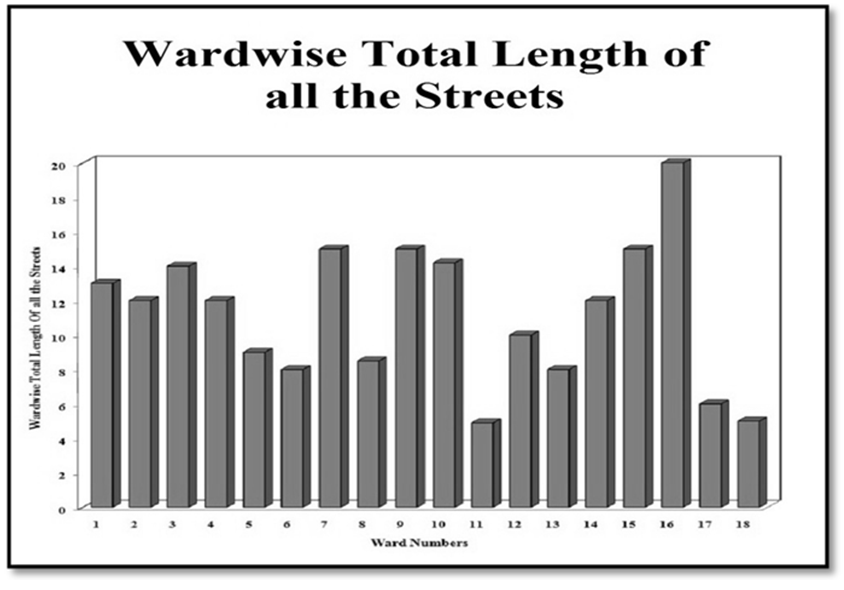
Road Infrastructure:-The Kalyani-Barrackpore Expressway runs very akin to the South-western boundary of Gayeshpur Municipality. Mooraganchha Road passes along the Northern boundary of the Municipality and provides a linkage between rail and road. These two roads are of high order and provide the municipal area better accessibility to and from different origins and destinations. They act as catalysts behind the accelerated development within Gayeshpur. Netaji Subhash Road, the spine and some of its arterial road run across the municipal area connecting the major inhabited locations. The Gayeshpur Municipality has a wide coverage of road the total length of which is 201.6 km. Ward number 16, 15 and 9 have better road network than the remaining all other wards. The typology and length of the roads are shown in the accompanying works. It is found that the existing scenario of road-network is just sufficient to cater to the present needs of Gayeshpur Municipality but some more improvisation measures from the end of the Municipality is always most welcome. 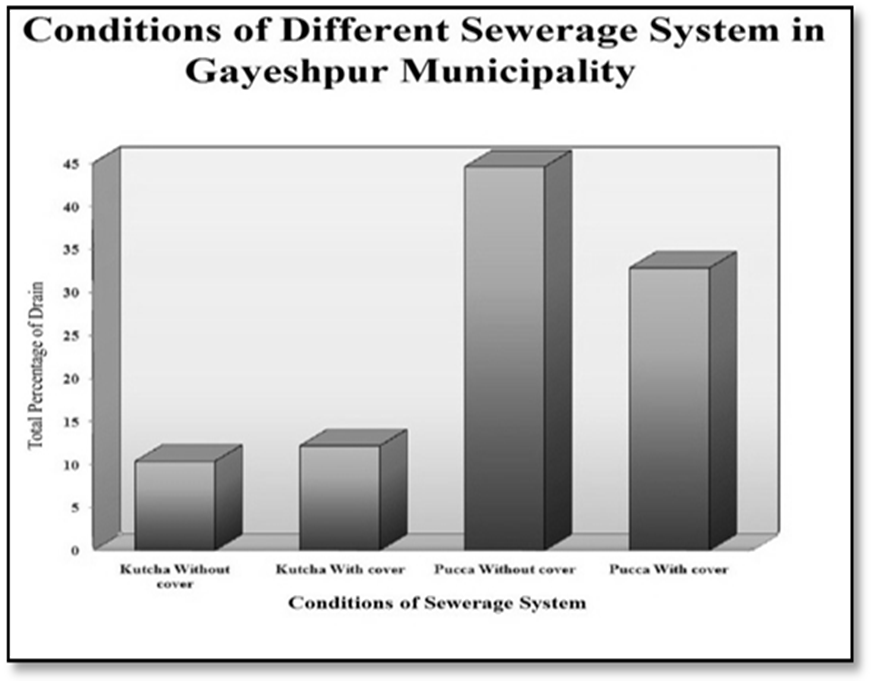 | Figure 3.3. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
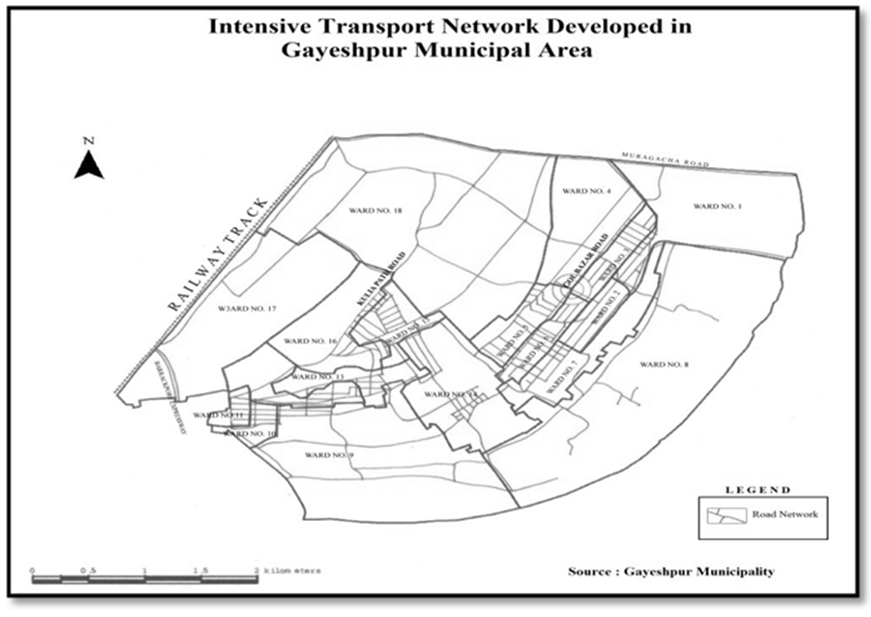 | Map 3.3. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Figure 3.4. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Figure 3.5. Data Source-Gayeshpur (M) |
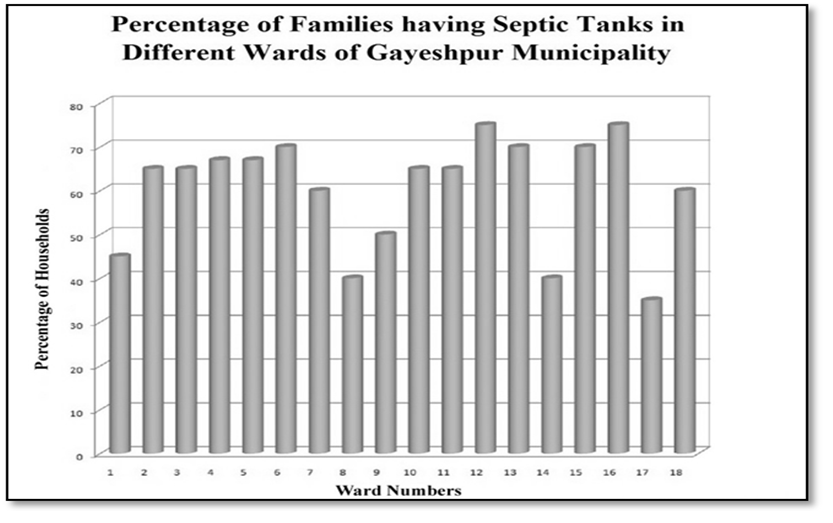
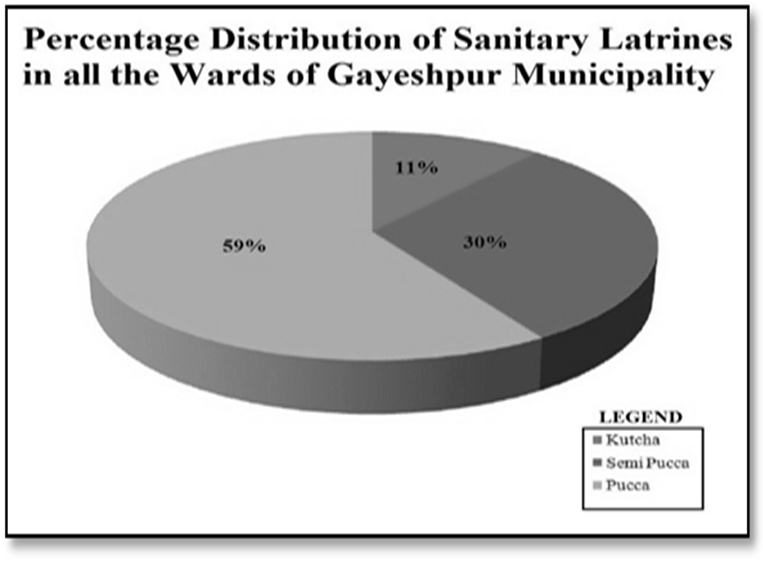
Sewerage and Sanitation:-Collection and disposal of sewage from inhabited areas and urban waste from manufacturing outlets are essential to maintain healthy living conditions in urban ambience. But there is no modern as well improvised sewerage network present in Gayeshpur Municipal area. In Gayeshpur Municipality, there is no planned sewerage system, so sanitary system entirely based on septic tanks for all the person across its different wards of Gayeshpur is the need of hour over here. The total wards of the Gayeshpur municipality encompass 60.27 percent of households only covered with septic tanks on an average. The maximum 75 percent households in this particular premise, are falling under ward numbers 12 and 16 whereas 35 percent households are benefitted by septic tanks in ward number 17. The figures are really microscopically minor with reference to the entire Municipality. The types of the sanitary latrines of the municipality are mainly pucca and its percentage of coverage is 59% on an average. 30 percent latrines are semi-pucca and 11 percent latrines are totally kutcha by type. The maximum latrines are of ownership types across the total wards of Gayeshpur. None of the inhabitants is accustomed with open-air defecation.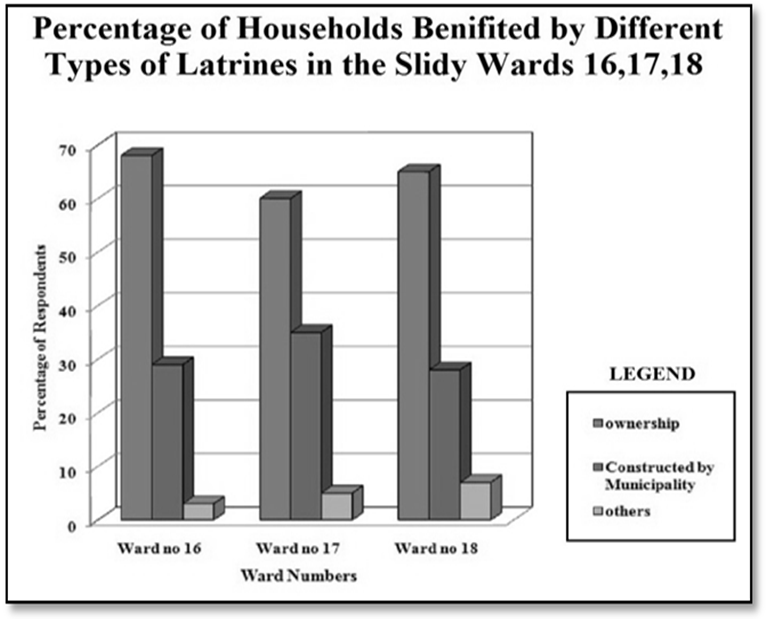 | Figure 3.6. Data Source: - Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Figure 3.7. Data Source - Gayeshpur (M) |
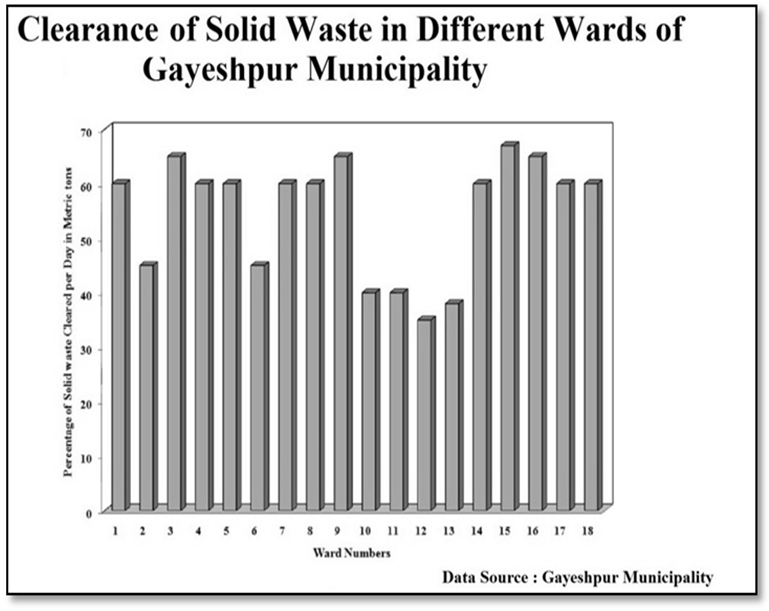
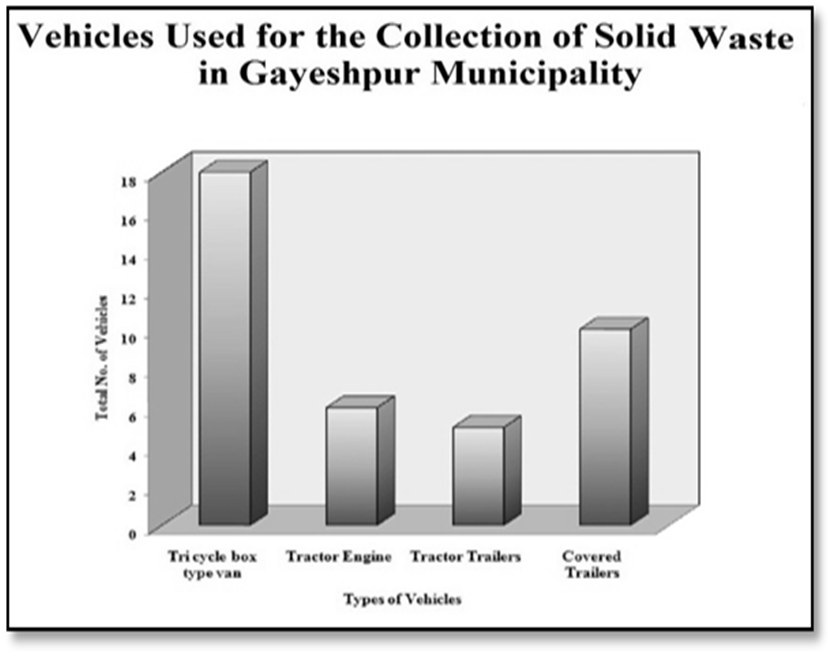
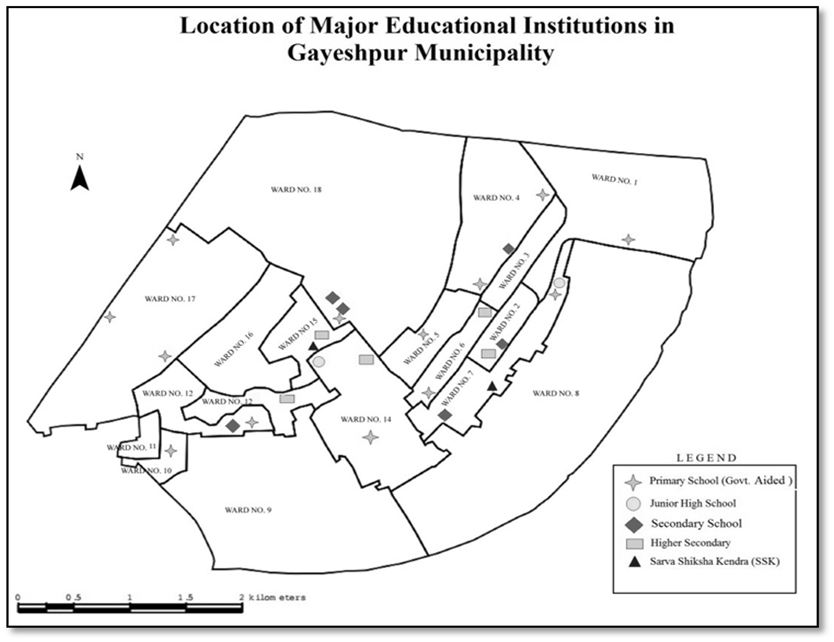
Solid Waste Management:-The recent method of solid waste management system with two bin- handcarts Dumper is prevalent here. Solid Waste treatment Plant is endowed with the facilities of segregation of organic and inorganic wastes at source and here a techno-economically feasible system should be materialized or installed on an urgent basis to provide the citizen of Gayeshpur Municipality a pollution-free modern environ. From data of Draft development plan (DDP) of Gayeshpur Municipality for the five-year plan period, 2007-2012, it has been clarified that the total solid waste generation per day is 29.309 gm and ward-wise average solid waste generation is 1.628 gm per day. Ward Number 16 and 17 generate most of the solid waste in whole Gayeshpur. Gayeshpur municipality extends 60% of solid waste collection system in every ward on an average. For collection of solid waste, the municipal workers generally use tri-cycle box-type vans and tractor-trailers. Tri-cycle box-type vans are most usable for solid waste collection in every ward. But the existing Solid waste Disposal system is little bit irregular and not at all commensurate to the strength of total population of the entire urban local body. A consistent as well as macro-scale Solid waste disposal system should be introduced here by installing a solid waste disposal Treatment plant with Vermi-culture. There is also a growing demand for establishing fully functional network for collection and disposal of solid waste from households and other municipal areas.Educational Infrastructure:-The Primary schools of the Gayeshpur Municipality area has been encompassed with a primary survey conducted by the Gayeshpur Municipality to ascertain standards of physical infrastructure and the basic needs. Gayeshpur Municipality possesses 25 Govt. Aided Free Primary schools located at different wards, 2 junior High Schools, 7 Madhyamik Schools, 6 Higher Secondary Schools and 5 nos. of Sarva Shiksha Kendras. Primary Survey has been conducted in the Schools by the municipality for the purpose of identification of the gap in the education sector and to ascertain the demand for pre-primary schools within the municipality.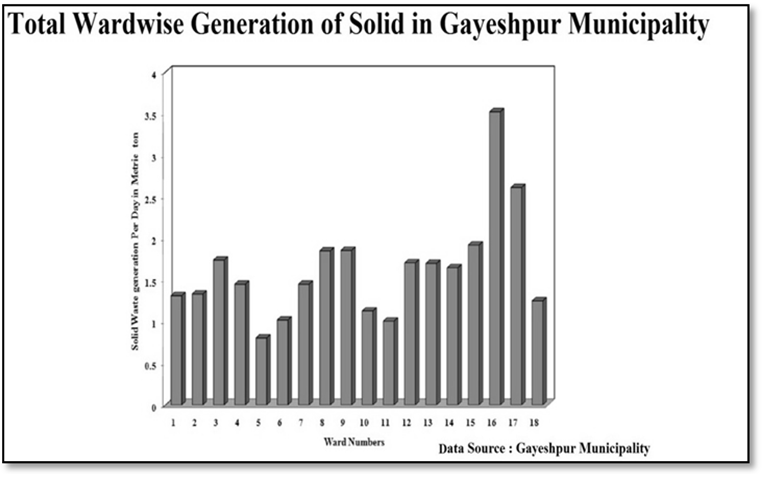 | Figure 3.8. |
 | Figure 3.9. |
 | Figure 3.10. Data Source - Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Map 3.4. Data Source - Gayeshpur (M) |
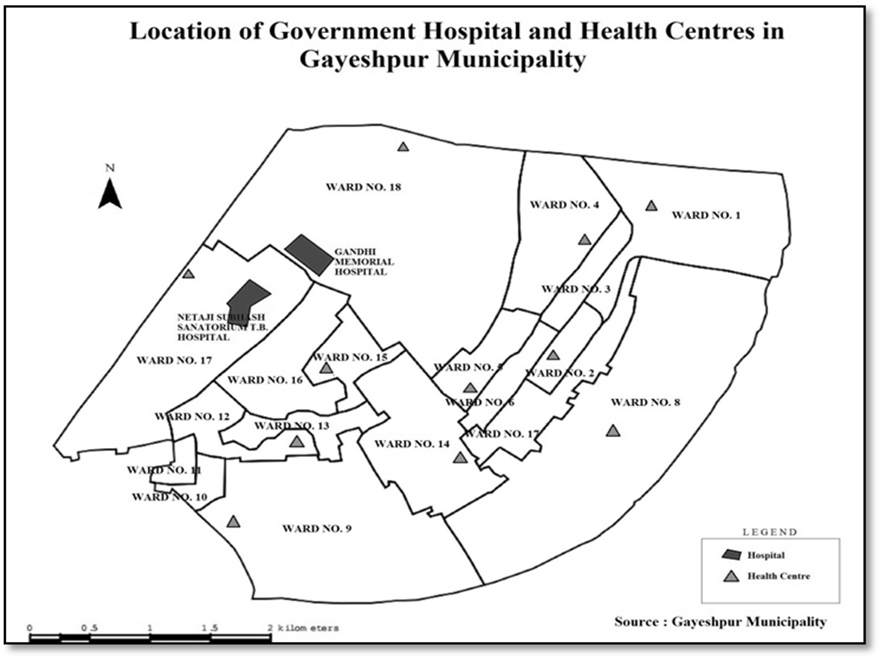
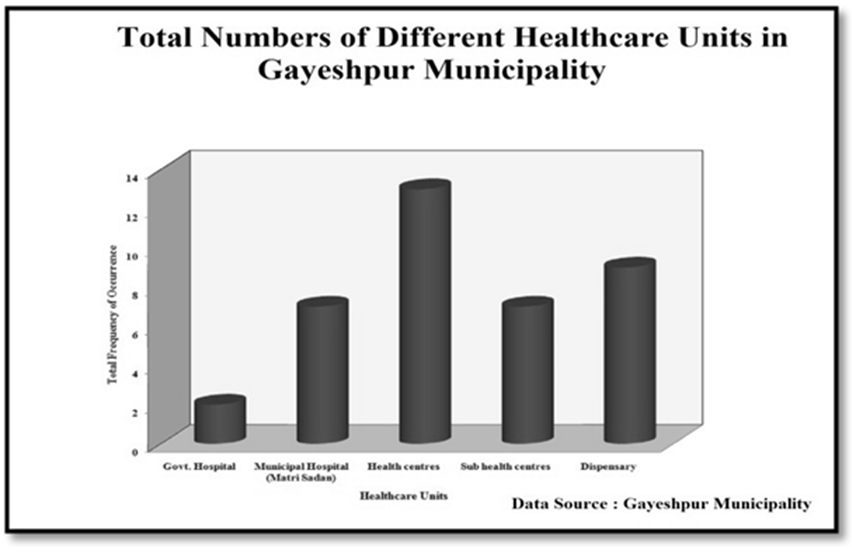
Health Infrastructure:-This ULB (Urban Local Body) has a hierarchy of healthcare services in which the apex position is occupied by the municipal hospital (Matri Sadan), Gandhi Memorial hospital and Netaji Subhas T.B. Sanatorium. Gayeshpur Municipality carries out the national health-care programmes under UHIP (Universal Health Improvement Project) and receives adequate monetary assistance and aids from Govt. of India. Apart from the municipal hospitals at the apex, there are thirteen (13) health centres more in the whole Municipality and these are distributed in manifold locations within different wards of Gayeshpur. There are 5 Sub-health centres and 9 dispensaries envisaged within the jurisdiction limit of Gayeshpur.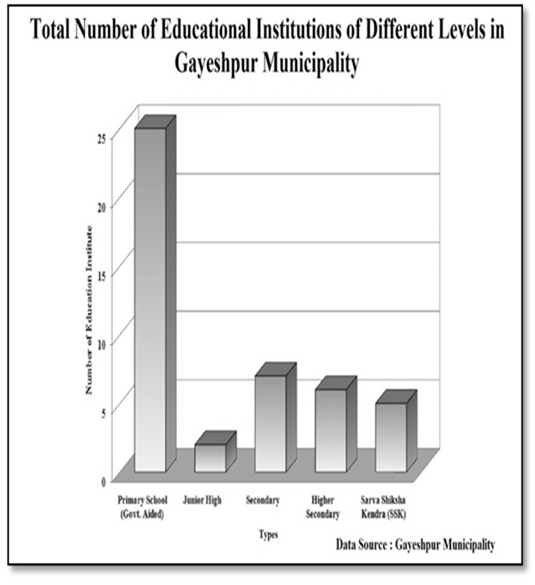 | Figure 3.11. |
 | Plate 3.1. One Girls’ School in the Locality |
 | Plate 3.2. One Higher Secondary School in the Locality |
 | Map 3.5. Data Source - Gayeshpur (M) |
 | Figure 3.12. |
 | Figure 3.13. |
Urban Amenities in Gayeshpur Municipality:-In this Municipality unit, there are 5 market-places but they are more or less concentrated in the central part of the municipality. These markets should be equitably distributed all over the wards of the municipal arena considering their population density and urban-connectivity as well. There are two banks noticed during the perception survey in ward number 6 and ward number 16. In the ward number 6 (at the Golbazar), there is a branch of State Bank of India and the other one is the united bank of India situated at Gokulpur in ward number 16. One football cum cricket stadium is under construction in ward number 14. There is only one crematorium in entire Gayeshpur and it needs immediate repairing and renovation as well. There is no fire station in the Gayeshpur Municipality area and this is really a matter of serious concern, so far the issue of safety and security of the whole municipality is concerned. Almost all the wards in Gayeshpur Municipality have reported regarding insufficient green areas in their localities. Jubilee Park and a small Children’s Park are representing the whole of recreation as well as amusement panorama of total Gayeshpur.  | Plate 3.3. Government Hospital |
 | Plate 3.4. Children’s Park |
 | Plate 3.5. Jubilee Park |
4. Problems and Prospects
Problems:-After the holistic analyses on primary as well as secondary databases regarding the details of urban infrastructure and amenity of Gayeshpur Municipality in district Nadia, some problems have come in the fore front and those problems are enlisted below:• Open drainages and their irregular cleaning. • In some wards, drain-water is falling into the ponds directly and due to this malaise of outfall, the freshwater-ecosystem is getting adulterated day by day leading to the emanation of foul smell.• Municipal water supply is not regular in selected wards of Gayeshpur Municipality.• Water pollution due to leakage of pipe line and their irregular cleaning is a matter of serious concern. • In ward numbers 16, 17 and 18, major roads are fatally broken and at the same time, they possess sufficient road network with reference to their total spatial coverage• The overall maintenance of major and minor roads is not at all upto the mark.• The Municipality is completely devoid of any fire Station and the only crematorium requires immediate renovation. .• Solid wastes are dumped in road side in many places within the boundary of Gayeshpur and this is causing environmental pollution to a considerable amount. • There is no scientific Sewerage network for all in Gayeshpur.Prospects:-The relevant suggestions from the end of the researcher are now mentioned herein:- • Proper measures are needed to be taken to stop the outfall of drain water into the pond.• Regular cleaning of the garbage-disposal bins and termination of indiscriminate garbage disposal by construction of vats after a regular interval are the dire needs in Gayeshpur.• Construction of pucca drains in the deprived areas is a prime requisite.• Leakage of pipelines to be monitored carefully and should be repaired urgently.• Regular maintenance of all the reservoirs is also a demand of the local inhabitants.• Measures to be undertaken regarding the supply of unadulterated and especially arsenic-free water across the wards of Gayeshpur (M).• Facilities like see-saw, slip, swing etc have to be provided at the children’s park to make it a model-park within the locality.
5. Conclusions
In order to improvise the urban ambience of Gayeshpur and to alleviate all its infrastructural as well as amenity-related maladies, the non-governmental organizations will have to come in the fore front along with the Local Self Government and if both of them work hand in hand together, then it is quite expected that in near future, the problematic issues will be resolved and the urban environmental quality of Gayeshpur will be lifted a lot.
References
| [1] | Badami, M.G. (2005): The Sewerage and Transport Challenges In Indian Cities: Considerations, Implications and Strategies, International Development Planning Review, Vol.27, UK. |
| [2] | Govt. of West Bengal (2012): Draft Development Plan (2007-2012) of Gayeshpur, Ministry of Urban Affairs, West Bengal. |
| [3] | Jain, A.K. (2008): Planning, Design and Infrastructural Management, JBA Publishers, New Delhi. |
| [4] | Ibid (2009): Urban Infrastructural Planning and Management, APH Publishing, New Delhi. |
| [5] | Ray, N. R. (1986): Kolkata -The Profile of a City, K P Bagchi and Company, Kolkata. |
























 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML