-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Ecosystem
p-ISSN: 2165-8889 e-ISSN: 2165-8919
2015; 5(3A): 13-17
doi:10.5923/c.ije.201501.03
Ever-Growing Concerns about the Fatal Consequences of Groundwater Plunder
Ashim Chakravorty1, Indranil Saha2, Nirmalya Pahari3, Debasis Jana1
1Department of Botany, Sripat Singh College, Jiaganj, Murshidabad, West Bengal
2Department of Chemistry, Sripat Singh College, Jiaganj
3Department of Physics, Sripat Singh College, Jiaganj
Correspondence to: Ashim Chakravorty, Department of Botany, Sripat Singh College, Jiaganj, Murshidabad, West Bengal.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The present communication is about the source of toxic metals and arsenic contamination in groundwater, accumulation of the toxin in soils and crops in the affected belt of West Bengal irrigated with contaminated groundwater, and in animal tissues and products, and demonstrates the pathways, other than drinking water, through which toxicity may have access to human, animal and crop systems. There are several monitoring methods on the environmental quality, specially biological method. Biological methods assess the presence of several species such as plants insects, fish, bacteria and viruses as environmental indicator. Some plants species have been used as an indicator in monitoring the environmental quality, e.g., Eichhornia crassipes, Hydrilla verticillata Casp, Trichosanthes dioica, rice, elephant-foot yam, green gram, Agrostis castellana and A. delicatula, along with some cryptogams like Chlorella ovalis, Phaepdactuylum tricornutum and Candida humicola. Also, this paper shows the knowledge gap and area of action with remedial measures which are to be removed for further study.
Keywords: Arsenic pollution, Heavy metal pollution, Different effects, Precautionary means, Bioremediation
Cite this paper: Ashim Chakravorty, Indranil Saha, Nirmalya Pahari, Debasis Jana, Ever-Growing Concerns about the Fatal Consequences of Groundwater Plunder, International Journal of Ecosystem, Vol. 5 No. 3A, 2015, pp. 13-17. doi: 10.5923/c.ije.201501.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
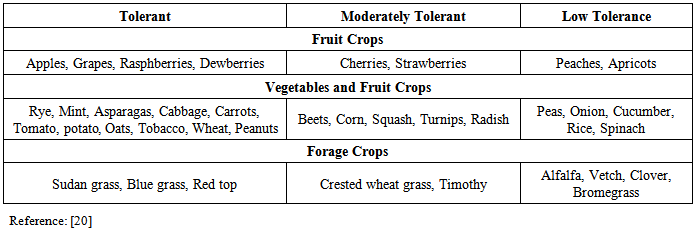
- Exposure to inorganic arsenic in groundwater has wreaked havoc on the Gangetic plains of India and the adjoining areas of Bangladesh. Inorganic arsenic, a carcinogen for human, (not yet proved for animals), breeds various cardiovascular and vascular diseases to human. Arsenic poisoning of drinking water tells upon about 137 million people in more than 70 countries. So, a taking measure to reduce the arsenic concentration in groundwater on a large scale is a great imperative. Arsenic groundwater contamination has wide spread effects including its absorption through food chain which are in the form of various social disorders, health hazards and socio-economic dissolution besides its sprawling with movement and exploitation of groundwater. Also, the hazards of soil pollution are going up at alarming rates not only in developed countries but in developing countries including India as well. Arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Gangetic alluvial zones of West Bengal has resulted into a huge proportion of drinking water-related disaster in recent years with reports of arsenic related health hazards for millions of people. As many as 75 blocks in 9 districts covering an area of 38865 km2 are reported to be severely affected [1]. Arsenic uptake by crop plants grown in soils contaminated with high concentrations of arsenic, and irrigated with arsenic-contaminated groundwater has also been reported [2, 3].The recommendation by the World Health Organisation (WHO) for the provisional guideline value of total As concentration in drinking water is 0.01 mg As/L since 1993 [4] mainly because lower levels preferred for protection of human health are not reliably measurable on a large scale. However, the National Standard for maximum acceptable concentration (MAC) of arsenic in drinking water is 0.05 mg As/L in several countries including India and Bangladesh based on an earlier WHO [5] advice.The proposed new standard value of 0.005 mg As/L is under consideration [6]. This is due mainly to the fact that inorganic As compounds are classified in Group 1 (carcinogenic to humans) on the basis of adequate evidence for carcinogenicity in humans and limited evidence for carcinogenicity in animals [7]. Adequate data on the carcinogenicity of organic arsenic have not been generated. The joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) set a provisional maximum tolerable daily intake (PMTDI) of inorganic arsenic as 0.002 mg/kg of body weight for humans in 1983 and confirmed a provisional tolerable weekly intake (PTWI) as 0.015 mg/kg of body weight in 1988 [8].It is an alarming signal for the health of humans, animals and plants for rise in As concentration in ground water [9]. As were found in higher levels in various resources of ground water than in the surface water. Irrigation of crop using contaminated ground water lead to the soil pollution in Agricultural system. Description of As from Fe oxides along with weathering of primary silicate minerals causes presence of high As concentration in the aquifer.Various methods like immobilization, soil washing, precipitation, vitrification, adsorption, ion exchange and thermal process may be undertaken to get rid of As from water and soil contamination. Most of these methods are very costly [10]. But, among these, the most cost effective method may be suggested as phytoremediation for the minimization and control of heavy metal contamination in water also well in soil [11]. Very first proposal of phytoremediation was over 20 years ago and the process has more advantages than the chemical process of stabilization for its less impact on health hazards which develop due to the contamination of toxic metals [12]. Several terms like botanoremediation, green remediation and agro remediation has been used in place of phytoremediation. This is a process of growing plants naturally for remediation of toxic metals from water and soil where landscape remains unaffected from any alterations.This remediation system is plant based which can be taken into account as solar-driven, biological, pump- and – treat systems extensive root system of uptake which develop underground ecosystem and the productive use of the matters [13, 14]. Plants belongs to phenotypes and tolerant types like, Rye, Asparagas, Cabbage, Carrots, Tomato, onion etc. (Table 1) have that adaptive mechanism to face the elevation of metal concentration in ground water [10, 15]. Absorption and accumulation of metals in plants occur in higher rate than the amount they require for their metabolism and accumulation takes place in the areal tissues of the plant body [16].This paper therefore highlighted the state of affairs of overusing the groundwater arsenic contamination in India specially the North East side along with explanation of various ill effects with their precautionary means taken so far and different views and techniques which may be taken up to a chronic success and failure if, can be experienced.
2. Role of Phytoremediation and Role of Plants in the Process of Arsenic Removal
2.1. Phytoremediation
- Phytoremediation include several steps and techniques to dispose of the pollutant from the site of pollution of heavy metals [13, 14]. Phytotoxication, Phytodegradation, Rhizofiltration, phytostabilization and phytovolatilization are the possible means of getting rid of As from soil and plants where it gets accumulated. Adequate nutrients in all respects are required for the growth and development of a plant [17] even they include As for maintaining normal metabolic reactions in its different physiological pathways. It is recommended 41mg Kg-1for As for soil by USEPA, whereas, WHO recommended standards for drinking water and effluents released by standarders for drinking water and effluents released by industries are 1, 0.01 and < 0.01mgL-1. In last decade, the global input of As to soils by humans was estimated between 52000 and 11, 21, 000t year-1 [10]. Thus, physical and chemical techniques are utilized for As remediation process but they lead to the destruction of biological activities shared by microbes to the plants along with the rendering of land futile for further use. Also, determination of ecosystem with a loss of biodiversity with adverse soil condition needs the generation of the process of plantation of those plants which can adapt to this hostile metal contaminated system. A plant species must possess an appropriate variance [18] to thrive and survive in the As contaminated soil and that species can be imposed for selection for cultivation in that area. Some examples of plants which possess tolerance to show some preadaptation to these harsh conditions are Tamarix parviflora, Eukalyptus, Camaldulensis and P. Vitatta [18, 19]. Metal uptake system in plant develops the tolerance activity in plant which is depended on the amount of metal concentrations in the soil (Table 1). There may have toxic effect on plants and the animals feeding on the same by soil contamination by arsenic. It is not mandatory that As will be translocated from root to shoot. Different crop plants show different tendencies to accumulate and tolerate As (Table 1). In the flooded rice field and soils of lowland areas, there is a tendency in plants which show the susceptibility of the plants to As toxicity.
|
2.2. Detoxification in Plants
- Plants have several detoxification mechanisms (both intra and extra cellular) for removal of heavy metals from soils [10, 31] which include chelation, compartmentalization, biotransformation and cellular repair [32]. Among the intracellular mechanism, detoxification takes place by alteration in the cell membrane or other protein’s structure for lowering the effects of metal toxicity and transport of metal to the vacuole where it gets detoxified. The mechanisms included in extracellular process are exudations which change the pH of rhizosphere, metal speciation and binding of metals to the cellwall.
3. Bioindicator
3.1. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater
- Not only in India but also in other countries, arsenic contamination in groundwater has been reported several times [33]. The first detection of As in groundwater in West Bengal exceeding MAC was in 1978, the credit goes to the School of Tropical Medicine in Calcutta in 1983 where the first case of As poisoning in humans was diagnosed [34]. In groundwater, besides its organic form, Arsenic is found as arsenites (AsIIIO3 -3; Hn AsIIIO3(3-n)-, with n = 1,2) or arsenate (AsVO43-, HnAsVO4(3-n)-, with n = 1,2), or both. The toxicity of As compounds in groundwater/soil environment depends largely on its oxidation state, and hence on redox status and pH, as well as whether As is present in organic combinations. The toxicity follows the order: arsine (valence state of As: -3) > organo-arsine compounds >arsenites (+3) and oxides (+3)> arsenates (+5)> arsonium metals (+1)> native arsenic (0). The arsenites are much more soluble, mobile, and toxic than arsenates in aquatic and soil environments. At pH 6-8, in most aquatic systems, both H2AsVO4- and HAsVO42- ions occur in considerable proportions in an oxidized environment (Eh = 0.2-0.5V), while H3AsIIIO3 is the predominant species under reduced conditions (Eh = 0-0.1V) [35]. Reduction of As (V) to As (III) would be accompanied by mobilization of As in aquatic system.
3.2. Studies from Various Aspects of Literature Reveal that a Number of Plant/Microbial Species, Known for Arsenic Accumulation/Bioindicator, can Effectively Remove Arsenic (and Other Heavy Metals) from the Aquatic System
- When Eichhornia crassipes is grown in a pond containing 10 mg As/dm3 [36], it absorbs As 170 and 340 μg As/g dry weight of water hyacinth in its stem and leaves, respectively, though leaching out of accumulated As in the water body has been found more profoundly with decaying the matters. So, appropriate precautionary measurements are taken into account while elaborating the As status of aquatic environment [37]. Hydrilla (Hydrilla verticillata Casp.), [38] and Pointed gourd, (Trichosanthes dioica), have also been found to accumulate arsenic when cultivated in the contaminated soils of West Bengal [39]. Several crop plant species (rice, elephant-foot yam, green gram, etc.) are also reported to accumulate As in substantial quantities [2]. Accumulation of As, and transformation of As species in rice plant have also been reported [3]. However, information on the transformation of As within plants is limited. The toxicity of As species in plant body is reported to follow the order AsH3>As(III)>As(V)>MMA (monomethylarsonic acid)> DMMA (dimethylarsinic acid) [40]. Arsenate tolerance by the grassy weeds, namely Agrostis castellana and A. delicatula, has been discussed in terms of the comparison of the corresponding reduction of maximum root growth (MRG) with that in the sensitive populations upon exposure to arsenic [41]. The fungus, namely Candida humicola and the freshwater algae, viz., Chlorella ovalis, Phaepdactuylum tricornutum and Oscillatoria rubescens have been found to accumulate As in their areal part. Also, few alga like Chroococcus paris (uptake Zn, and Cd), Scenedesmus sp. (accumulate Ni-63), Chladophora glomerata (accumulate Pb), Green algae(accumulate Zn) which have been used profusely as metal removers.
4. Pond System
- The study of observation on some low land rice revealed that application of Zn may be helpful in drastic reduction of As accumulation and build up in the plant body. Also, it has been found that grain yield does not vary much between the ponding and intermittent ponding [42] though the intermittent ponding may bring less toxin to soil leading to save the irrigation water also.The study also suggests to store and use the pond water for irrigation purpose which aid in less toxification of soil involving people of rural area [43, 44].Also, soil monitoring by application and use of microorganisms (namely, Anabaena sp. and Nostoc sp.) found in the contaminated soil may give a good result in detoxification process.
5. Conclusions
- The countries yet to be financially developed and wanting the capacity of technologically sound solutions for over population, can adapt this sustained option of phytoremediation of toxic metal and metalloid from the soil. Many aquatic and wetland plants have been found to be promising for their citing uptake and accumulation of heavy metals from contaminated environments. Free metals are converted to metal chelates by reduction process by plants. Thus, possible tolerance mechanism which is prevalent in plants against As concentration is the bioaccumulation in shoots (specially in leaves and stems); also its phytovolatiliaztion in plant system can find out the possible way to solve the over use of ground water in our present day’s need. Also various effective remedial measurements like optimum conjunctive use of ground and surface water (e.g., use of harvested rain water during the lean period), development and identification of suitable low arsenic accumulating high yielding crops/ varieties suitable for As contaminated areas, irrigation with ponds stored ground water –decontamination being facilitated by rainfall and sedimentation, recharge of groundwater resource with harvesting rain water, free of As, increasing the use of water efficiency (through optical water management) for ground water irrigation specially for summer (Boro rice), preferring low-water requiring, Farmer-attractive cropping sequences, increased use of FYM and other manures plus green manure crops, inclusion of pulses/other legumes in the cropping sequences, as well as application of appropriate amendments may be adapted.The sustained research in support of As mitigation needed urgently includes specification of As in various substrates for determining its net toxicity, release mechanism, special resolution, chemical transformations, hence its toxicity, bioavailability and impact on human health, evaluation of mechanism for microbial transformations of As on soil components, transformation of toxic species to less toxic forms or production of volatile species of the toxins, effective remediation and waste management strategies and advance knowledge generation regarding speciation of As within the plant biomass and possible relation to rhizosphere speciation and biochemistry and the chemical structure of metal binding protein.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML