-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2015; 5(3A): 52-55
doi:10.5923/c.chemistry.201501.08
Evaluation of Non-Ionic and Anionic Surfactants as Additives for Water-Based Mud
Putri Yunita1, Sonny Irawan1, Dina Kania2
1Department of Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS
2Department of Chemical Engineering, Universiti Putra Malaysia
Correspondence to: Putri Yunita, Department of Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Water-based mud (WBM) is known as the cheapest drilling fluid that possess other advantages such as environmentally friendly and non-hazardous. Compared to oil-based mud (OBM) or synthetic-based mud (SBM), WBM is more largely used in oil and gas exploration. In this study, new no-ionic surfactant and anionic surfactant were evaluated as an additive in WBM. Rheological properties in WBMs containing surfactant as additive were investigated which included the plastic viscosity, the yield point, the gel strength and filtration properties. The result of the studied non-ionic and anionic surfactants showed improvement in the rheological properties and thermal stability of the mud when used as additive for WBM.
Keywords: Water-based mud, Anionic surfactant, Non-ionic surfactant, Rheological properties, Filtration properties
Cite this paper: Putri Yunita, Sonny Irawan, Dina Kania, Evaluation of Non-Ionic and Anionic Surfactants as Additives for Water-Based Mud, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 5 No. 3A, 2015, pp. 52-55. doi: 10.5923/c.chemistry.201501.08.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Drilling fluid or drilling mud is one of the important component of the rotary drilling process [1–4]. In drilling process, the selection of drilling fluid used is very important. Compatibility of drilling fluid to the formation is crucial in order to maximize its performance. Drilling fluids are circulated through a wellbore to carry cuttings toward the surface, to control the formation pressure by providing the hydrostatic presss, to cool and lubricate the drilling tools and to support the weight of the drill bit and drill pipe[1], [2]. Generally, traditional drilling mud was grouped according to the base used, which is oil, water or air. Although, water-based mud is the most common fluid used in drilling operations due to its inexpensive base fluid material and considered non-toxic to aquatic life [3].It is no secret the stability of system, the rheological characteristics and filtration properties of WBM at high temperature are relatively poor and inefficient [3], [4]. In contrast, OBM is known to provide excellent wellbore stability, lubricity and temperature resistance at difficult well conditions. However, OBM higher damage potential to the environment through pollution of nonbiodegradable material [5], [6]. Their use has been restricted by environmental concern and regulation. Thus it is a challenge to provide the performance of OBM for environmentally friendly WBM.Based on the advantages of surfactants from previous studies, it is proposed in this work to use surfactants as an additive to improve the performance of WBM. Surfactant is reported to reduce the viscosity, risk of water blockage and fluid loss [7–9]. It is also suggested to prevent the formation of insitu water/oil emulsion and could be used as a lubricant [9], [10].In this study, two types of surfactant, which are non-ionic and anionic, were used. Non-ionic surfactant was chosen for its two main advantages. Firstly, non-ionic surfactants have excellent wetting and emulsifying properties and, secondly, they are highly aerobic biodegradable [8]. Non-ionic surfactant used in this work is 2-hexadecyloxyethnol, while anionic surfactant used is alkyl benzene sulfonate.The commercial alkylbenzene sulfonate consists of an alkylate with an average number of carbon atoms around C12 that is derived from various origins, specifically propylene tetramer whose synthesis resulted in a branched "tail". The chemical structure of used additives surfactant is showed below.
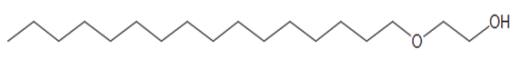 | Figure 1. Non-ionic surfactant (2-hexadexyloxyethanol) |
 | Figure 2. Anionic surfactant (alkylbenzene sulfonate) |
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Water-based Mud
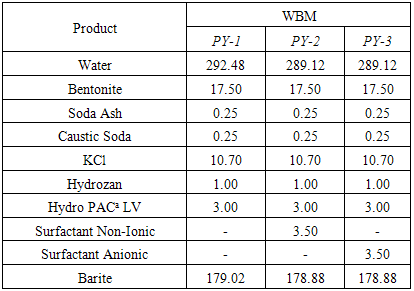
- Mud formulation was comprised basically of the following ingredients: water base fluid, surfactant, organophilic clay bentonite, xanthan gum and barite. The samples were mixed in a Hamilton mixer for 45 minutes. The formulation of each mud is listed in Table 1.
|
2.1.2. Surfactant
- The non-ionic and anionic surfactants were purchased from Samudra Energy. These type of surfactants were previously used in Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) process in some fields in South Sumatra, Indonesia. The non-ionic surfactant used in this study is 2-hexadecyloxyethanol while the anionic surfactant used is alkyl benzene sulphonat. In the previous work, the surfactant is reported to have good performance to increase the oil production. The injection of surfactant on the fields in South Sumatra has succesfully increased the oil recovery from the average rate of 90 BOPD to 230 BOPD. In this study the optimization of mud performance is focused on using those surfactants as additives.
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Rheological Properties
- The rheological properties of the mud were measured based on American Petroleum Institute (API) standard procedure [11]. The parameters such as plastic viscosity (PV) and yield point (YP) were measured by FANN VG direct-indicating viscometer equipped with a cup-heater. It determines the relationship between shear rate and share stress from a dial reading [12]. Shear rate (1), PV (2) and YP (3) are calculated by the following equations:
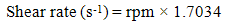 | (1) |
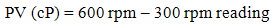 | (2) |
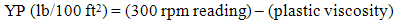 | (3) |
2.2.2. Determination of Gel Strength of the Mud
- Generally, the gel strength is a measure of the minimum shear stress needed to initiate the movement of developed gel. Two reading are generally taken: (i) immediately after agitation of the mud in the cup for 10 s, (ii) after the mud in the cup had rested for 10 min [13].
2.2.3. Filtration Loss
- The filtration characteristic of the mud was determined by measuring the volume of filter loss collected in standard static filtration tests. The tests were conducted at ambient temperature by using the API fluid loss apparatus at 30 minutes of filtrate collection time (∆P = 100 psi, no. 5 Whatman filter paper). The volume of filtrate loss was recorded from the graduated cylinder at the end of 30 minutes [13].
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties
- Rheological properties of drilling fluid depend on the type and amount of clay in the shale. The properties are controlled at such values that the mud provides optimum performances. Two of the most important properties to control are viscosity and gel strength. Viscosity and gel strength are related to removal of cuttings, holding cuttings and weight material in suspension when not circulating, releasing cuttings at the surface, reducing to a minimum any adverse effect upon the well bore, and providing information about formation penetrated [14].
3.1.1. Plastic Viscosity (PV)
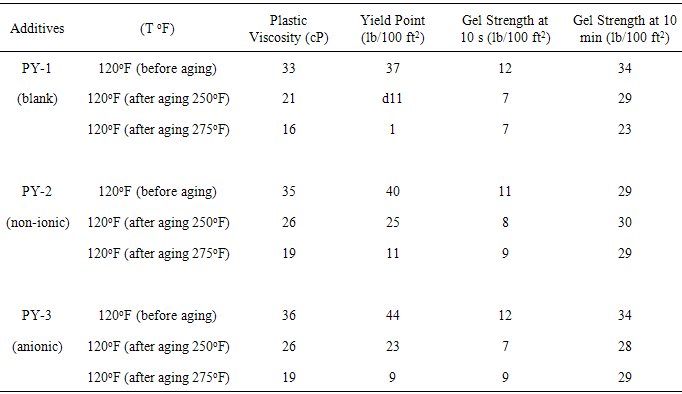
- The tested before and after dynamic aging for 16 hours at 250oF and 275oF. From data in Table 2, the plastic viscosity for the formulated water-based mud without surfactant (PY-1) is 33 cP, but the value of PV for formulated mud increased with the added the surfactants (PY-2 and PY-3) in 1% concentration. It can be seen from the result that the viscosity of the WBM increased with the surfactant additives to the mud.
|
3.1.2. Yield Point (YP)
- The yield point value at flowing conditions largely depends on the electro-chemical charges of the particles in the mud. The charged particles are believed to attract to each other giving way to a high yield point. On the other hand, the particles might repel one another which reduce the YP [15]. This phenomenon might show that the YP is controlled by th chemical additives used. According to Table 2, the yield point value of PY-1 is lower than PY-2 and PY-3, which are 37, 40 and 44 lb/100ft2 respectively. The result revealed that the YP of the mud had been improved with the addition of surfactants. As shown in fig 3, the addition of surfactants, both ionic and anionic (PY-2 and PY-3), increased the YP of the mud when compared to the formulation without surfactant (PY-1). Surfactant show an improvement in WBM compare to other surfactants [16].
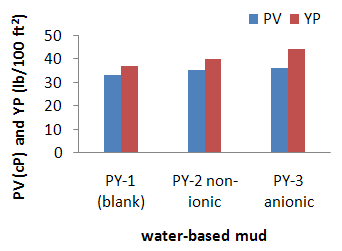 | Figure 3. Rheology of water-based mud formulated with 1% non-ionic surfactant (PY-2) and 1% anionic surfactant (PY-3) |
3.2. Determination of Gel Strength
- The value of gel strengths depend on the concentration of colloidal clays in the mud. In this study, it is analysed that the surfactant additive give little impacts to the value of gel strength. Although sufficient gel strength is needed to suspend and transport the rock cuttings, high gelation is also undesirable. Overly thick mud may delay the cuttings separation. From the Table 2 the gel strength (GS) 10 s of PY-1 (mud without surfactant) is 12 lb/100ft2 and PY-2 and PY-3 (mud with surfactant) the GS are 11 and 12 lb/100ft2 respectively and some with after aging 250oF GS for muds PY-1, PY-2 and PY-3 are 7, 8 and 7 lb/100ft2 . Comparison of gel strength with and without surfactant as shown in fig4. Gel strength of muds decrease when temperature increases [17].
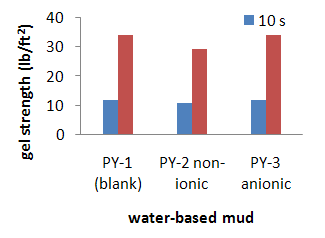 | Figure 4. Gel strength of water-based mud formulated with 1% non-ionic surfactant (PY-2) and 1% anionic surfactant (PY-3) |
3.3. Effect of Temperature on Rheology
- In Table 2 the plastic viscosity and the yield point of drilling mud ad 120oF before and after aging (250oF and 275oF) are compared to drilling fluid after additional 1% of non-ionic and anionic surfactant. As it can be seen, aging of mud with increasing temperature from 250oF to 275oF caused significant decrease in the PV and the YP of the mud. An increase in temperature aging on the dispersed suspensions of the mud might be caused by reducing the strength of particles bonds by thermal energy [15]. Water-based mud that used the addition of surfactant, reduction of plastic viscosity and yield point is not drastic than water-based mud that does not use surfactants. Its means the additives more efficient and had a higher temperature stability. The data indicate that the surfactant molecure protect the flowing behaviour of the mud by improving its thermal resistance.
3.4. Fluid Loss
- The surfactant’s surface active are suspected to affect the hydrophilicity and surface tension of the fluid and the filter cake formed. When the hydrophobic capacity of the phase boundary reduced, conceivably reducing the hydrophobic capacity of the phase boundary, the fluid loss is also expected reduced. The molecule of surfactant presumably block the pores of mud cake and alter the permeability into impermeable [8].
4. Conclusions
- It is concluded that the addition of surfactant when formulating WBM might considerably improve the temperature resistance of the mud against thermal degradation. The addition of the surfactant might also improve the fluid loss control, hence reduce the formation damage.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to thank Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS and Scomi oil tools Sdn Bhd for providing the lab facilities to run the experiment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML